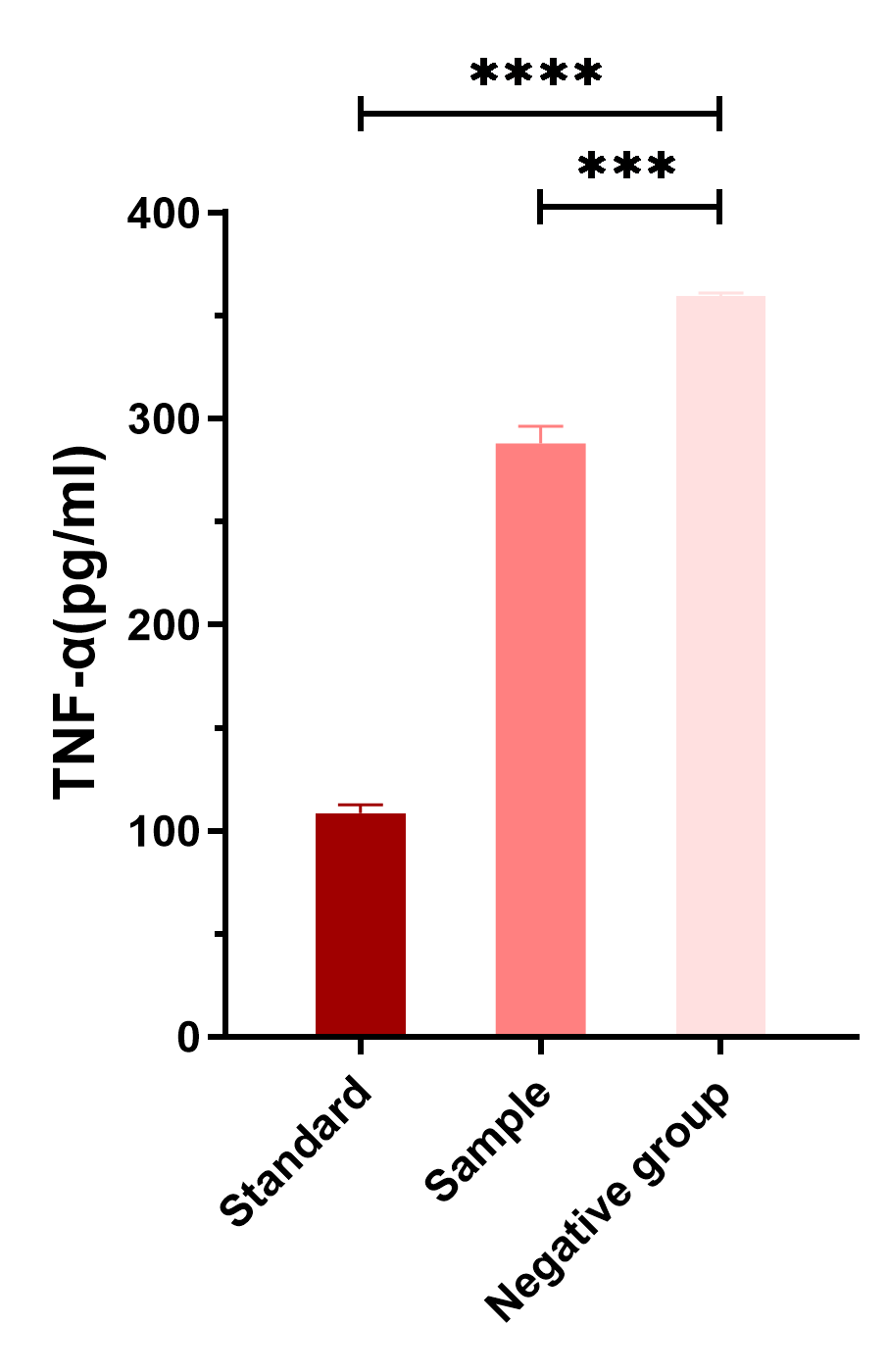Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3661002"
(→Characterization) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
===Characterization=== | ===Characterization=== | ||
| − | <p>We constructed a plasmid containing YebF-IL22. Meanwhile, | + | <p>We constructed a plasmid containing YebF-IL22. Meanwhile, we constructed a secretory expression vector for IL-22, using <i>E.coli</i> as chasis. IL-22 was detected using an ELISA kit.</p> |
[[File:T--CPU_CHINA--K3661002_p3.png|600px|thumb|center|'''Figure 3.'''Result of activity assay using human IL-22 ELISA kit.]] | [[File:T--CPU_CHINA--K3661002_p3.png|600px|thumb|center|'''Figure 3.'''Result of activity assay using human IL-22 ELISA kit.]] | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
<p>Both sample groups were significantly different compared to the negative control group.*P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 by t test.</p> | <p>Both sample groups were significantly different compared to the negative control group.*P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 by t test.</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:T--CPU_CHINA--K3661002_p9.png|600px|thumb|center|'''Figure 6.'''Comparison of the levels of TNF-α produced by different groups.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>We examined the TNF-α reducing efficacy of IL-22 standard samples and the culture supernatant of our engineered bacteria which contains secreted IL-22 protein for a concentration about 5ng/ml (analyzed by ELISA test). As can be seen, both groups of IL-22 significantly inhibited the production of TNF-α and were significantly different from the negative control group (without IL-22).*P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 by t test.</p> | ||
===Reference=== | ===Reference=== | ||
| − | <p>[1]ZHANG G,BROKX S,WEINER J H. Extracellular accumulation of recombinant proteins fused to the carrier protein YebF in <i>Escherichia coli</i> [J]. Nature Biotechnology.2006.24(1):100-104.</p> | + | <p>[1] ZHANG G, BROKX S, WEINER J H. Extracellular accumulation of recombinant proteins fused to the carrier protein YebF in <i>Escherichia coli</i> [J]. Nature Biotechnology.2006.24(1):100-104.</p> |
<p>[2] Shabgah A G , Navashenaq J G , Shabgah G , et al. Interleukin-22 in human inflammatory diseases and viral infections.[J]. Autoimmunity Reviews, 2017: S1568997217302549.</p> | <p>[2] Shabgah A G , Navashenaq J G , Shabgah G , et al. Interleukin-22 in human inflammatory diseases and viral infections.[J]. Autoimmunity Reviews, 2017: S1568997217302549.</p> | ||
<p>[3] Radaeva S, Sun R, Pan HN, Hong F, Gao B. Interleukin 22 (IL-22) plays a protective role in T cell-mediated murine hepatitis: IL-22 is a survival factor for hepatocytes via STAT3 activation [J]. Hepatology, 2004; 39: 1332-1342.</p> | <p>[3] Radaeva S, Sun R, Pan HN, Hong F, Gao B. Interleukin 22 (IL-22) plays a protective role in T cell-mediated murine hepatitis: IL-22 is a survival factor for hepatocytes via STAT3 activation [J]. Hepatology, 2004; 39: 1332-1342.</p> | ||
Latest revision as of 15:17, 27 October 2020
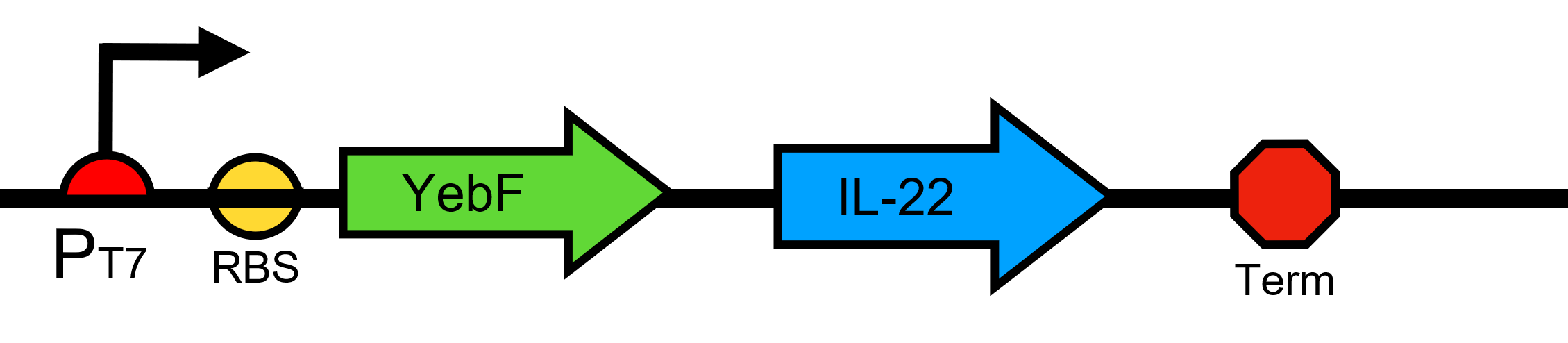
YebF-IL 22
This composite part is composed of the secretion part of YebF and the part of anti-inflammatory factor IL-22.The IL-22 is a natural immunosuppressive protein. We add a secretion tag to increase the extracellular concentration. YebF secretion system is widely used in E.coli.IL-22 can be secreted from our engineered bacteria through this system efficiently. Interleukin-22(IL-22) is a member of a group of the IL-10 family, a class of potent mediators of cellular inflammatory responses. IL-22 is produced by activated DC and T cells. IL-22 and IL-10 receptor chains play a role in cellular targeting and signal transduction. It can initiate and regulate innate immune responses against bacterial pathogens especially in epithelial cells such as respiratory and gut epithelial cells.
Usage
Interleukin-22(IL-22) is a cytokine that inhibits inflammation.
The secretory tag YebF increases extracellular concentrations of IL-22.
T7 promoter, the gene downstream of this promoter will be transcribed when there is T7 RNA polymerase. RBS, ribosome biding site. Terminator blocks gene sequence reads.
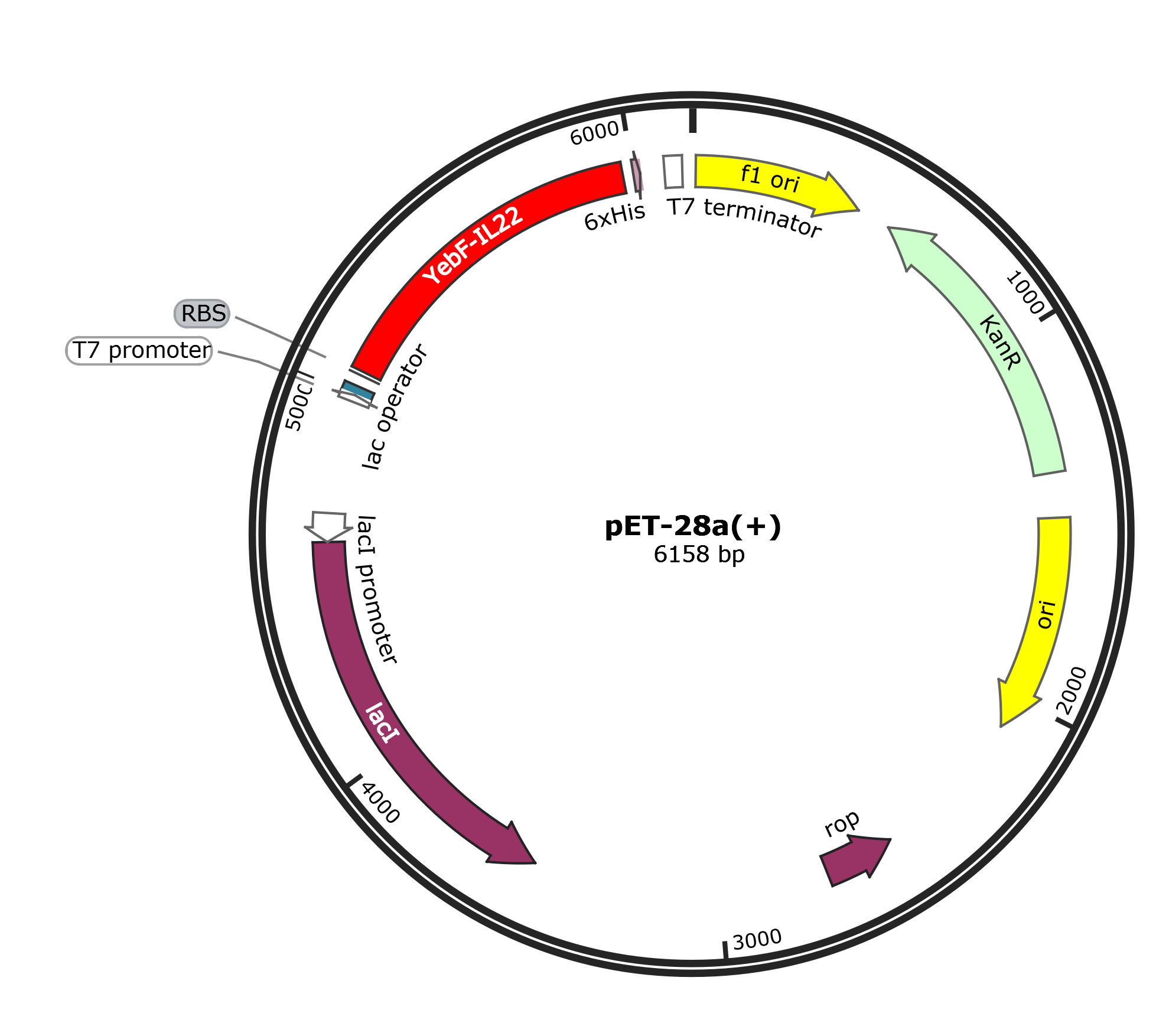
The plasmid carries the kanamycin resistance gene.
Biology
YebF proteins are widely found in Enterobacteriaceae bacteria, and are soluble endogenous short peptides that can be secreted into the extracellular medium. When other proteins are fused to the YebF sequence, YebF can help secrete these proteins out of the E.coli membrane.[1]
IL-22 is a member of the IL-10 family and is primarily a cytokine secreted by Th22 cells [2].
IL-22 reduces inflammation through the JAK-STAT pathway as well as the NF-κB pathway to inhibit TNF-α production, reducing hepatocyte apoptosis and protecting hepatocytes [3].
Characterization
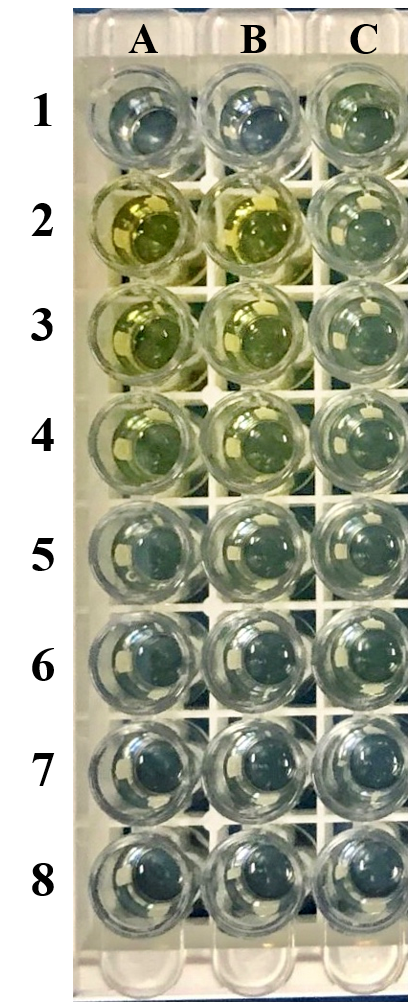
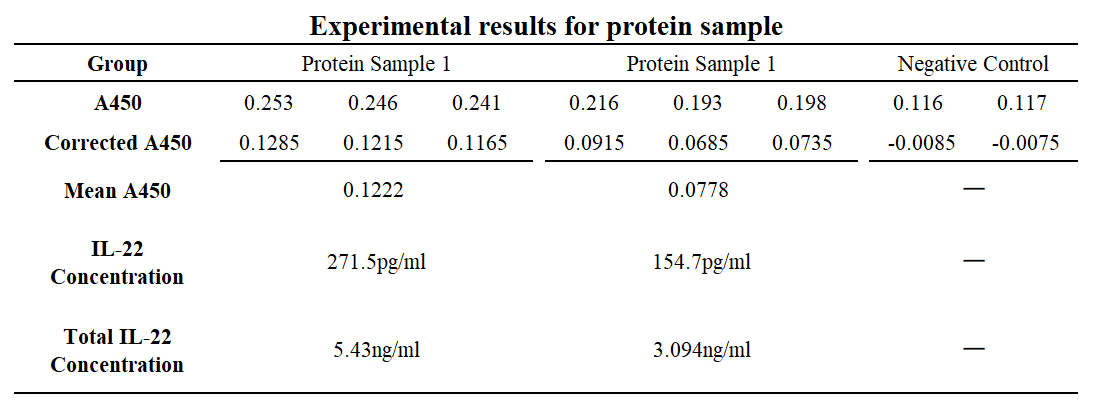
We constructed a plasmid containing YebF-IL22. Meanwhile, we constructed a secretory expression vector for IL-22, using E.coli as chasis. IL-22 was detected using an ELISA kit.
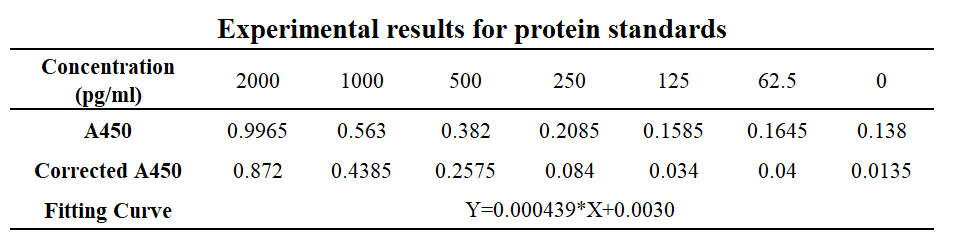
(A1/B1) are blank-corrected wells. Wells (A2/B2), (A3/B3), (A4/B4), (A5/B5), (A6/B6), (A7/B7), (A8/B8) are standard human IL-22 protein sample with concentration at 2000pg/ml, 1000pg/ml, 500pg/ml, 250pg/ml, 150pg/ml, 62.5pg/ml and 0pg/ml respectively. Wells C1-C3 are duplicate wells for protein sample 1 while C4-C6 are duplicate wells for protein sample 2. C7-C8 are negative control wells. Protein sample 1 was induced by adding 1M IPTG, and protein sample 2 was induced by adding 0.5M. No induction agent was added to the negative control group.
Table 1&2 Result of activity assay using human IL-22 ELISA kit.
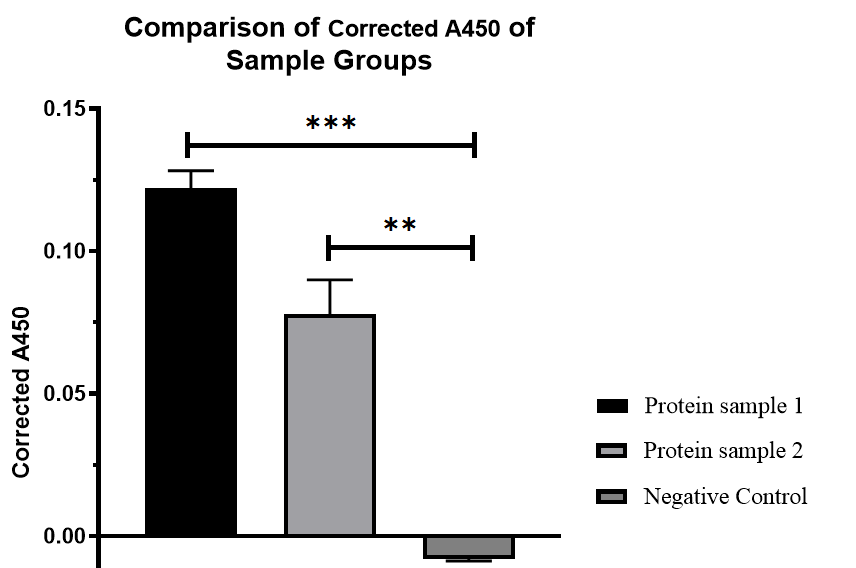
The protein expression of protein sample 1 is approximately 5.43ng/ml, while sample 2 is approximately 3.094ng/ml.
Both sample groups were significantly different compared to the negative control group.*P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 by t test.
We examined the TNF-α reducing efficacy of IL-22 standard samples and the culture supernatant of our engineered bacteria which contains secreted IL-22 protein for a concentration about 5ng/ml (analyzed by ELISA test). As can be seen, both groups of IL-22 significantly inhibited the production of TNF-α and were significantly different from the negative control group (without IL-22).*P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 by t test.
Reference
[1] ZHANG G, BROKX S, WEINER J H. Extracellular accumulation of recombinant proteins fused to the carrier protein YebF in Escherichia coli [J]. Nature Biotechnology.2006.24(1):100-104.
[2] Shabgah A G , Navashenaq J G , Shabgah G , et al. Interleukin-22 in human inflammatory diseases and viral infections.[J]. Autoimmunity Reviews, 2017: S1568997217302549.
[3] Radaeva S, Sun R, Pan HN, Hong F, Gao B. Interleukin 22 (IL-22) plays a protective role in T cell-mediated murine hepatitis: IL-22 is a survival factor for hepatocytes via STAT3 activation [J]. Hepatology, 2004; 39: 1332-1342.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 547
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 108
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]