Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3593001"
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Another aptamer of alpha amatoxin selected by SELEX which has a proved better ability of binding with its target. It is the optimized version by elimination of 10bp from BB3953000, with higher enrichment coefficient. Better result of ELONA and dot blot further reinforces its optimization. | Another aptamer of alpha amatoxin selected by SELEX which has a proved better ability of binding with its target. It is the optimized version by elimination of 10bp from BB3953000, with higher enrichment coefficient. Better result of ELONA and dot blot further reinforces its optimization. | ||
| + | =Background= | ||
| + | Amatoxins are chemicals present inside the genus Amanita and caused about 90% of mushroom poisoning. Being able to detect it before eating or in the field could possibly make a great decrease in people and animals who died because of poisonous mushrooms. Also being able to detect it in hospital can greatly help doctors in mushroom areas get correct information and do effective diagnosis to save the patient.<br> | ||
| + | Aptamers are oligonucleotides that form secondary structures, giving them the ability to bind targeted molecules, including ions or small molecules, and, in our case, amanitin. | ||
| + | =Sequence and features= | ||
| + | <partinfo>BBa_K3593001 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
| + | =Characterisation of this part= | ||
| + | ==Design== | ||
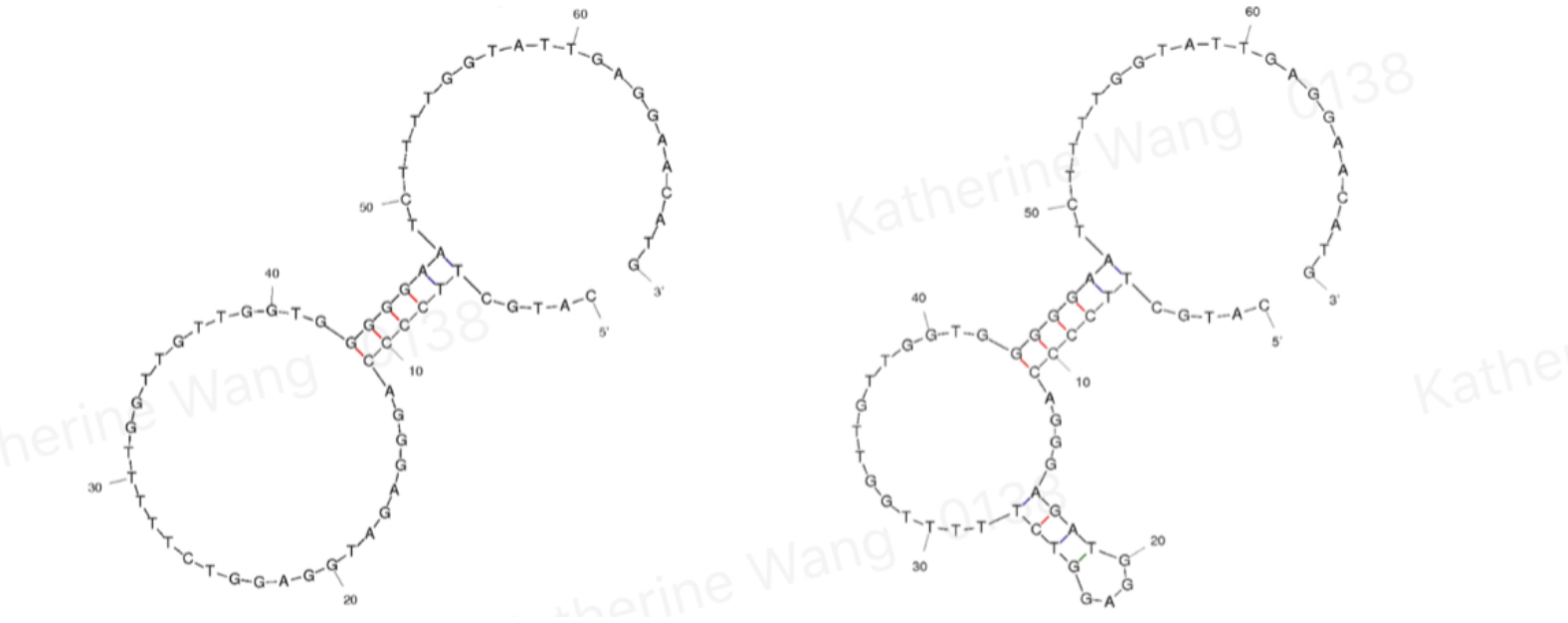
| + | BBa_K3593001 is an aptamer of α-amanitin named Best 2. It comes from the same literature[1] with Best 1, and is an improved version of Best 1- it is 10BP shorter than Best 1. Its binding is tested through qPCR. | ||
| + | [[File:T--GreatBay_SCIE--Fig.1 Structure of aptamer Best 1 and Best 2.png|600px|thumb|center]] | ||
| + | <p class="figure-description"><b><center>Fig.1 Structure of aptamer Best 1 and Best 2</center></b></p> | ||
| + | ==Experiment data== | ||
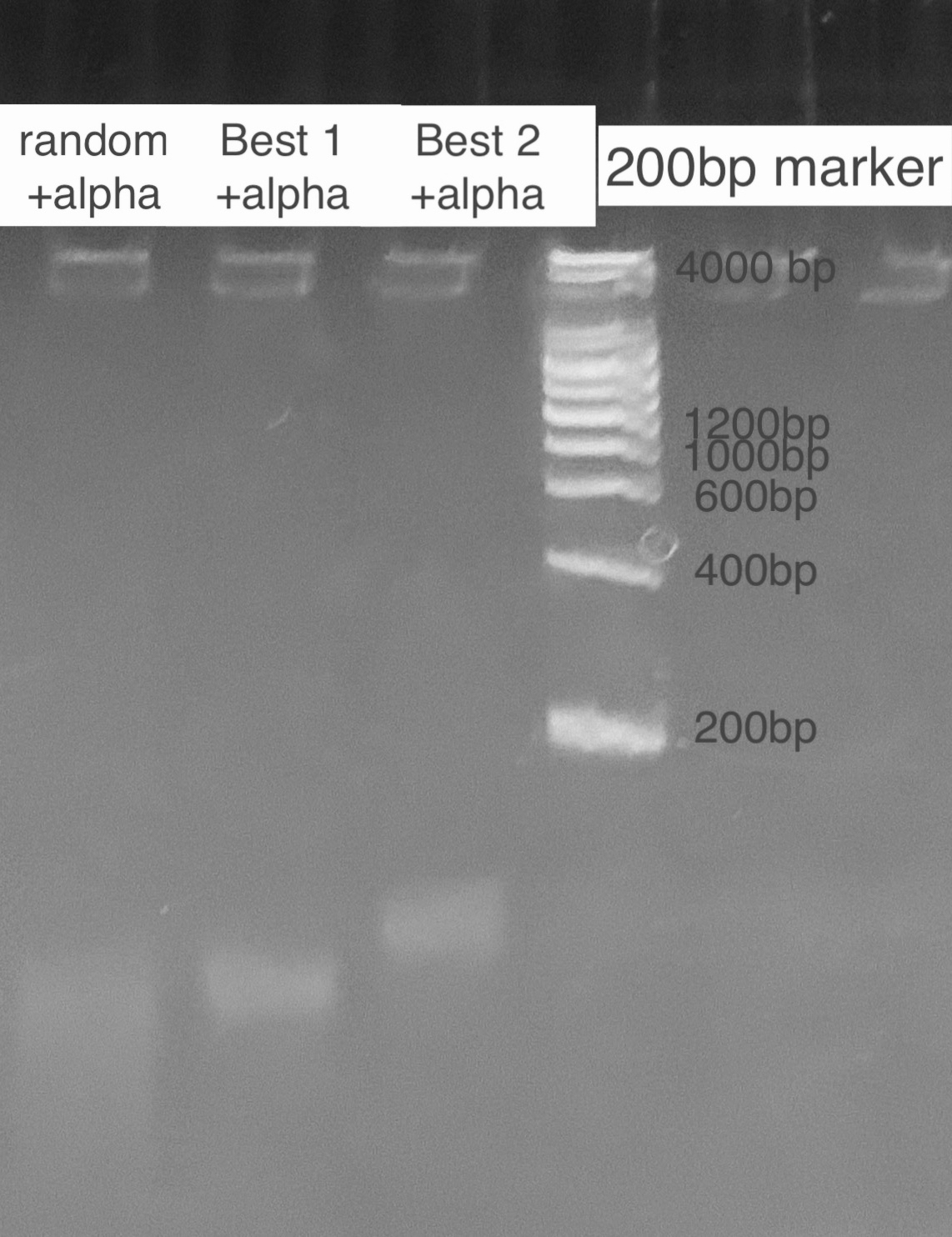
| + | According to the state of art in aptamer binding[3], we design an experiment based on the principle of Gel Shift(i.e lower rate of motion in electrophoresis when aptamer is bound to the toxin due to a conformational change). By mixing excess amatoxin determined by the calculation of dissociation constant and aptamer in certain reaction times, we expect to see 2 bands representing the bound and inbound aptamer respectively. For examination of specificity, we also mix a random ssDNA pool where we select aptamer from and compare the band with the correct aptamer. For a high resolution, we used the TBE PAGE gel for DNA, 12%.<br> | ||
| + | [[File:T--GreatBay_SCIE--Fig.2 Gel Shift of Best 1&Best 2.jpg|600px|thumb|center]] | ||
| + | <p class="figure-description"><b><center>Fig.2 Gel Shift of Best1&Best2</center></b></p> | ||
| + | We also verify its binding affinity via a method called Dot Blot, a method from another literature[2], with a similar principle to ELISA. The NC membrane turning blue indicates that Best 2 binds with alpha-amanitin.<br> | ||
| + | [[File:T--GreatBay_SCIE--Fig.3 Dot Blot of Best 2 aptamer on amanitin.jpg|600px|thumb|center]] | ||
| + | <p class="figure-description"><b><center>Fig.3 Dot Blot of Best 2 aptamer on amanitin.</center></b></p> | ||
| + | =References= | ||
| + | 1.Muszyńska K, Ostrowska D, Bartnicki F, et al. Selection and analysis of a DNA aptamer binding α-amanitin from Amanita phalloides. Acta Biochim Pol. 2017;64(3):401-406. <br> | ||
| + | 2.Han Q, Xia X, Jing L, et al. Selection and characterization of DNA aptamer specially targeting α-amanitin in wild mushrooms. SDRP J Food Sci Technol. 2018;3(6):497-508. <br> | ||
| + | 3.Muszyńska K, Ostrowska D, Bartnicki F, et al. Selection and analysis of a DNA aptamer binding α-amanitin from Amanita phalloides. Acta Biochim Pol. 2017;64(3):401-406. doi:10.18388/abp.2017_1615<br> | ||
| − | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | + | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here --> |
| − | + | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 04:17, 27 October 2020
ssDNA, aptamer for α-amanitin(Best 2)
Another aptamer of alpha amatoxin selected by SELEX which has a proved better ability of binding with its target. It is the optimized version by elimination of 10bp from BB3953000, with higher enrichment coefficient. Better result of ELONA and dot blot further reinforces its optimization.
Background
Amatoxins are chemicals present inside the genus Amanita and caused about 90% of mushroom poisoning. Being able to detect it before eating or in the field could possibly make a great decrease in people and animals who died because of poisonous mushrooms. Also being able to detect it in hospital can greatly help doctors in mushroom areas get correct information and do effective diagnosis to save the patient.
Aptamers are oligonucleotides that form secondary structures, giving them the ability to bind targeted molecules, including ions or small molecules, and, in our case, amanitin.
Sequence and features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Characterisation of this part
Design
BBa_K3593001 is an aptamer of α-amanitin named Best 2. It comes from the same literature[1] with Best 1, and is an improved version of Best 1- it is 10BP shorter than Best 1. Its binding is tested through qPCR.
Experiment data
According to the state of art in aptamer binding[3], we design an experiment based on the principle of Gel Shift(i.e lower rate of motion in electrophoresis when aptamer is bound to the toxin due to a conformational change). By mixing excess amatoxin determined by the calculation of dissociation constant and aptamer in certain reaction times, we expect to see 2 bands representing the bound and inbound aptamer respectively. For examination of specificity, we also mix a random ssDNA pool where we select aptamer from and compare the band with the correct aptamer. For a high resolution, we used the TBE PAGE gel for DNA, 12%.
We also verify its binding affinity via a method called Dot Blot, a method from another literature[2], with a similar principle to ELISA. The NC membrane turning blue indicates that Best 2 binds with alpha-amanitin.
References
1.Muszyńska K, Ostrowska D, Bartnicki F, et al. Selection and analysis of a DNA aptamer binding α-amanitin from Amanita phalloides. Acta Biochim Pol. 2017;64(3):401-406.
2.Han Q, Xia X, Jing L, et al. Selection and characterization of DNA aptamer specially targeting α-amanitin in wild mushrooms. SDRP J Food Sci Technol. 2018;3(6):497-508.
3.Muszyńska K, Ostrowska D, Bartnicki F, et al. Selection and analysis of a DNA aptamer binding α-amanitin from Amanita phalloides. Acta Biochim Pol. 2017;64(3):401-406. doi:10.18388/abp.2017_1615