Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3453012"
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K3453012 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K3453012 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | This part is a toehold switch sensor for sequence-based detection of rosewood. It targets a fragment of the MatK gene of ''Dalbergia maritima'' var. ''pubescens'' ([[Part:BBa_K3453020|BBa_K3453020]]) | + | This part is a toehold switch sensor for sequence-based detection of rosewood. It targets a fragment of the MatK gene of ''Dalbergia maritima'' var. ''pubescens'' ([[Part:BBa_K3453020|BBa_K3453020]]). |
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| − | + | ||
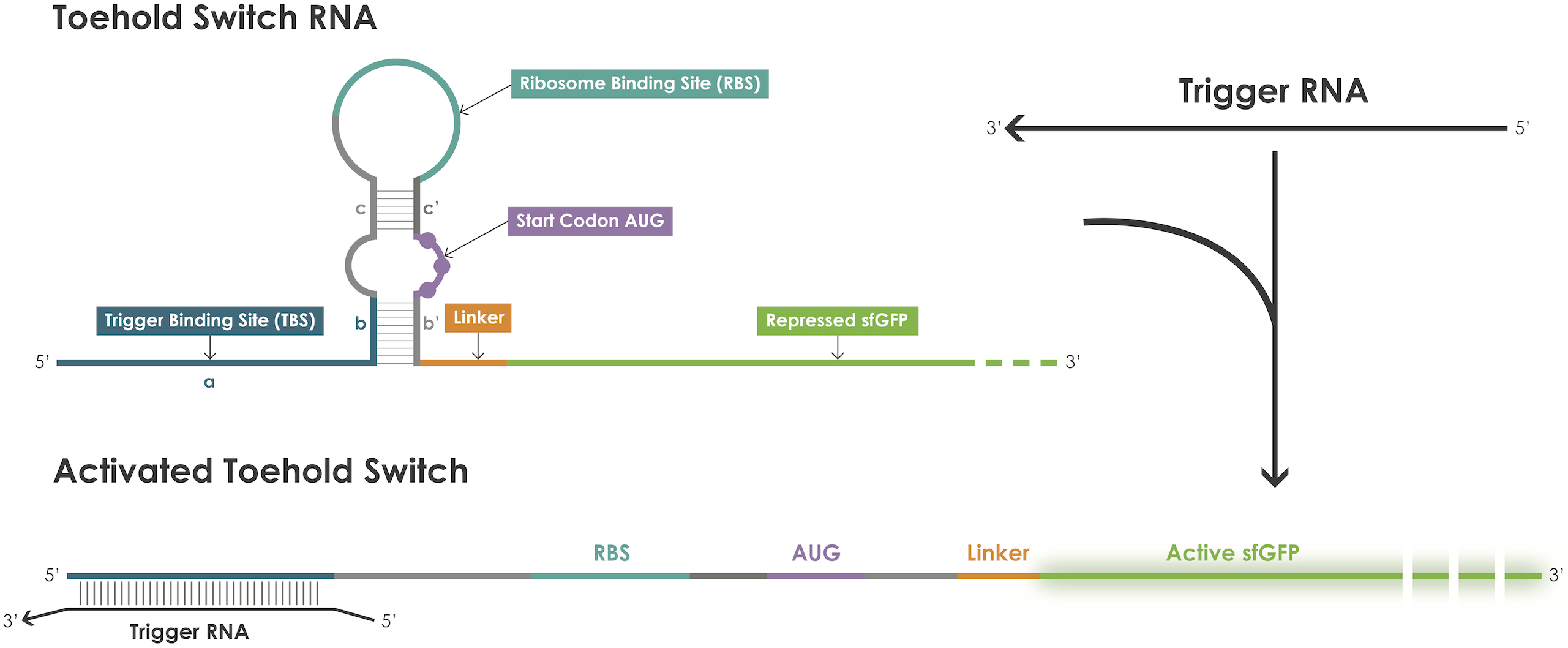
| + | A toehold switch is an RNA–based device containing a ribosome binding site (RBS) and an ATG start codon embedded in the middle of a hairpin structure that blocks translation initiation [1]. The hairpin can be unfolded upon binding of a trigger RNA thereby exposing the RBS and the ATG start codon and thus permitting translation of the reporter protein (Figure 1). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File: T--Evry_Paris-Saclay--toehold-switch.png|600px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Figure 1. Toehold switches principle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This part is a toehold switch sensor that targets a fragment of the MatK gene of ''Dalbergia maritima'' var. ''pubescens'' ([[Part:BBa_K3453020|BBa_K3453020]]). | ||
| + | It was designed using the web tool developed by To ''et al.'' [2] and follows the architecture of the Series B of toehold switch sensors for Zika virus detection [3] and of the BioBits™ toeholds [4]. Its secondary structure predicted by NUPACK web server [5] using default parameters is represented in Figure 2 and here-after in dot-bracket notation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ...............(((..(((((((((...((((((.(.(((((............))))).).))))))...)))))))))..))).(((....)))..... | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File: T--Evry_Paris-Saclay--RNAstructure_p36_DmMatK1-3.png|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Figure 2. Secondary-structure prediction of this part with the ATG of the reporter gene. The prediction was realised using the NUPACK web server [5] with default parameters and graphically represented using the ''forna'' RNA secondary structure visualization tool [6]. Nucleotides were coloured to match the different segments in Figure 1. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The corresponding trigger sequence of this toehold switch is [[Part:BBa_K3453022|BBa_K3453022]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The functionality of this part was tested using sfGFP-LVAtag ([[Part:BBa_K2675006|BBa_K2675006]]) as a reporter. The expression was controlled by the T7 promoter ([[Part:BBa_K2150031|BBa_K2150031]]) and the strong SBa_000587 synthetic terminator ([[Part:BBa_K3453000|BBa_K3453000]]) in the composite part [[Part:BBa_K3453112|BBa_K3453112]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This part proved to be functional: a readable output was generated only in the presence of rosewood RNA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Full results are available on the [[Part:BBa_K3453112|BBa_K3453112]] page in the registry. | ||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
| − | [1] | + | [1] Green AA, Silver PA, Collins JJ, Yin P. Toehold switches: de-novo-designed regulators of gene expression. Cell (2014) 159, 925-939. |
[2] To AC, Chu DH, Wang AR, Li FC, Chiu AW, Gao DY, Choi CHJ, Kong SK, Chan TF, Chan KM, Yip KY. A comprehensive web tool for toehold switch design. Bioinformatics (2018) 34, 2862-2864. | [2] To AC, Chu DH, Wang AR, Li FC, Chiu AW, Gao DY, Choi CHJ, Kong SK, Chan TF, Chan KM, Yip KY. A comprehensive web tool for toehold switch design. Bioinformatics (2018) 34, 2862-2864. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [3] Pardee K, Green AA, Takahashi MK, Braff D, Lambert G, Lee JW, Ferrante T, Ma D, Donghia N, Fan M, Daringer NM, Bosch I, Dudley DM, O'Connor DH, Gehrke L, Collins JJ. Rapid, low-cost detection of Zika virus using programmable biomolecular components. Cell (2016) 165, 1255-1266. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [4] Huang A, Nguyen PQ, Stark JC, Takahashi MK, Donghia N, Ferrante T, Dy AJ, Hsu KJ, Dubner RS, Pardee K, Jewett MC, Collins JJ. BioBits™ Explorer: A modular synthetic biology education kit. Sci Adv (2018) 4, eaat5105. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [5] Zadeh JN, Steenberg CD, Bois JS, Wolfe BR, Pierce MB, Khan AR, Dirks RM, Pierce NA. NUPACK: Analysis and design of nucleic acid systems. Journal of Computational Chemistry (2011) 32, 170–173. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [6] Kerpedjiev P, Hammer S, Hofacker IL. Forna (force-directed RNA): Simple and effective online RNA secondary structure diagrams. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) (2015) 31, 3377–3379. | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
Latest revision as of 21:23, 26 October 2020
Rosewood DmMatK Toehold Switch 1.3
This part is a toehold switch sensor for sequence-based detection of rosewood. It targets a fragment of the MatK gene of Dalbergia maritima var. pubescens (BBa_K3453020).
Usage and Biology
A toehold switch is an RNA–based device containing a ribosome binding site (RBS) and an ATG start codon embedded in the middle of a hairpin structure that blocks translation initiation [1]. The hairpin can be unfolded upon binding of a trigger RNA thereby exposing the RBS and the ATG start codon and thus permitting translation of the reporter protein (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Toehold switches principle.
This part is a toehold switch sensor that targets a fragment of the MatK gene of Dalbergia maritima var. pubescens (BBa_K3453020). It was designed using the web tool developed by To et al. [2] and follows the architecture of the Series B of toehold switch sensors for Zika virus detection [3] and of the BioBits™ toeholds [4]. Its secondary structure predicted by NUPACK web server [5] using default parameters is represented in Figure 2 and here-after in dot-bracket notation.
...............(((..(((((((((...((((((.(.(((((............))))).).))))))...)))))))))..))).(((....))).....
Figure 2. Secondary-structure prediction of this part with the ATG of the reporter gene. The prediction was realised using the NUPACK web server [5] with default parameters and graphically represented using the forna RNA secondary structure visualization tool [6]. Nucleotides were coloured to match the different segments in Figure 1.
The corresponding trigger sequence of this toehold switch is BBa_K3453022.
The functionality of this part was tested using sfGFP-LVAtag (BBa_K2675006) as a reporter. The expression was controlled by the T7 promoter (BBa_K2150031) and the strong SBa_000587 synthetic terminator (BBa_K3453000) in the composite part BBa_K3453112.
This part proved to be functional: a readable output was generated only in the presence of rosewood RNA.
Full results are available on the BBa_K3453112 page in the registry.
References
[1] Green AA, Silver PA, Collins JJ, Yin P. Toehold switches: de-novo-designed regulators of gene expression. Cell (2014) 159, 925-939.
[2] To AC, Chu DH, Wang AR, Li FC, Chiu AW, Gao DY, Choi CHJ, Kong SK, Chan TF, Chan KM, Yip KY. A comprehensive web tool for toehold switch design. Bioinformatics (2018) 34, 2862-2864.
[3] Pardee K, Green AA, Takahashi MK, Braff D, Lambert G, Lee JW, Ferrante T, Ma D, Donghia N, Fan M, Daringer NM, Bosch I, Dudley DM, O'Connor DH, Gehrke L, Collins JJ. Rapid, low-cost detection of Zika virus using programmable biomolecular components. Cell (2016) 165, 1255-1266.
[4] Huang A, Nguyen PQ, Stark JC, Takahashi MK, Donghia N, Ferrante T, Dy AJ, Hsu KJ, Dubner RS, Pardee K, Jewett MC, Collins JJ. BioBits™ Explorer: A modular synthetic biology education kit. Sci Adv (2018) 4, eaat5105.
[5] Zadeh JN, Steenberg CD, Bois JS, Wolfe BR, Pierce MB, Khan AR, Dirks RM, Pierce NA. NUPACK: Analysis and design of nucleic acid systems. Journal of Computational Chemistry (2011) 32, 170–173.
[6] Kerpedjiev P, Hammer S, Hofacker IL. Forna (force-directed RNA): Simple and effective online RNA secondary structure diagrams. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) (2015) 31, 3377–3379.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Unknown
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]