Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3332053"
AnnaTaylor (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
We anchored GOX protein onto membranes through Lpp-OmpA to catalyze the reaction of glyphosate to form glyoxalic acid and AMPA and add his-tag to purify the protein. We use K880005 to construct the expression system and anchor GOX on the surface of E.coli. | We anchored GOX protein onto membranes through Lpp-OmpA to catalyze the reaction of glyphosate to form glyoxalic acid and AMPA and add his-tag to purify the protein. We use K880005 to construct the expression system and anchor GOX on the surface of E.coli. | ||
| − | < | + | |
| − | ===Usage and | + | ===Biology === |
| + | |||
| + | Lpp-OmpA is an anchor protein from E. coli, which can anchor its passenger protein to the cell membrane. It has been widely used in cell-surface display. GOX, also known as EcAKR4-1, is found in ''Echinochloa colona''. It can decompose glyphosate into AMPA and glyoxylic acid. GOX is fused at N terminal with Lpp-OmpA so that GOX can be displayed on the surface of ''E. coli''. <ref>Pan L, Yu Q, Han H, et al. Aldo-keto Reductase Metabolizes Glyphosate and Confers Glyphosate Resistance in Echinochloa colona[J]. Plant Physiol, 2019, 181(4): 1519-1534.</ref><ref>http://2016.igem.org/Team:TJUSLS_China</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <figure> | ||
| + | <img src="https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/f/f1/T--XMU-China--XMU-China_2020-Mechanism_of_GOX_and_GRHPR.png" width="100%" style="float:center"> | ||
| + | <figcaption> | ||
| + | <p style="font-size:1rem"> | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | </figcaption> | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :'''Fig 1.''' Mechanism of GOX on the surface of ''E. Coli''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Usage=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here, we used <partinfo>BBa_K880005</partinfo> to construct the expression system and obtained the composite part <partinfo>BBa_K3332053</partinfo>, which may achieve surface display of GOX on our engineered bacteria. Due to the limited time, we did not get the gene in time. As a result, there is a lack of data about this part. The progress of this part remains in the stage of design. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <figure> | ||
| + | <img src="https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/f/f2/T--XMU-China--XMU-China_2020-J23100_B0034_lpp-ompA-gox_B0015.png" width="50%" style="float:center"> | ||
| + | <figcaption> | ||
| + | <p style="font-size:1rem"> | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | </figcaption> | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :'''Fig 2.''' Gene circuit of Lpp-OmpA-GOX. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | |||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
Revision as of 19:26, 26 October 2020
J23100-RBS-Lpp-OmpA-GOX-terminator
We anchored GOX protein onto membranes through Lpp-OmpA to catalyze the reaction of glyphosate to form glyoxalic acid and AMPA and add his-tag to purify the protein. We use K880005 to construct the expression system and anchor GOX on the surface of E.coli.
Biology
Lpp-OmpA is an anchor protein from E. coli, which can anchor its passenger protein to the cell membrane. It has been widely used in cell-surface display. GOX, also known as EcAKR4-1, is found in Echinochloa colona. It can decompose glyphosate into AMPA and glyoxylic acid. GOX is fused at N terminal with Lpp-OmpA so that GOX can be displayed on the surface of E. coli. [1][2]
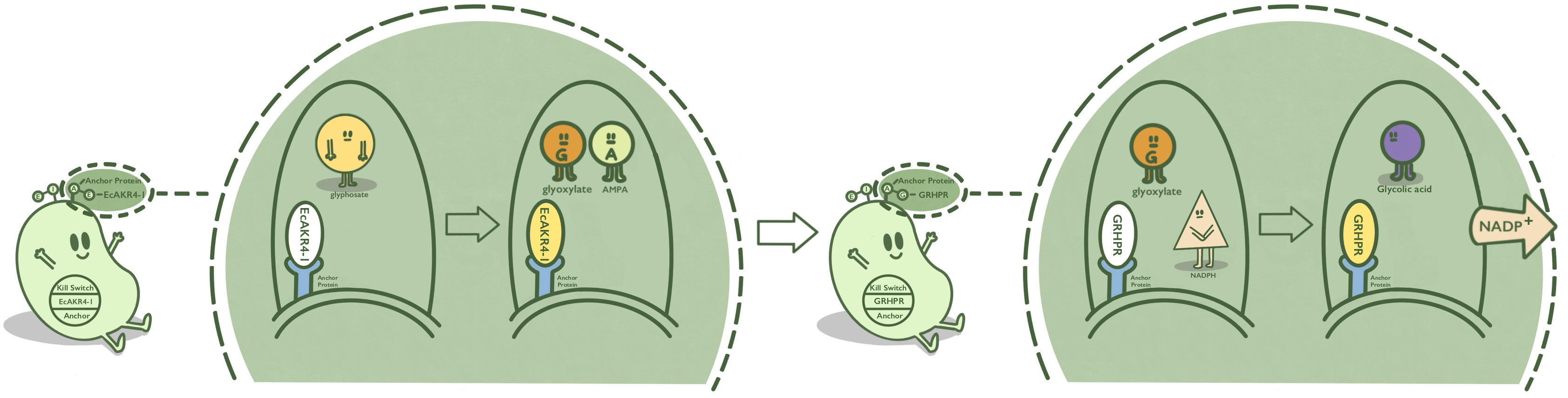
- Fig 1. Mechanism of GOX on the surface of E. Coli.
Usage
Here, we used BBa_K880005 to construct the expression system and obtained the composite part BBa_K3332053, which may achieve surface display of GOX on our engineered bacteria. Due to the limited time, we did not get the gene in time. As a result, there is a lack of data about this part. The progress of this part remains in the stage of design.

- Fig 2. Gene circuit of Lpp-OmpA-GOX.
References
- ↑ Pan L, Yu Q, Han H, et al. Aldo-keto Reductase Metabolizes Glyphosate and Confers Glyphosate Resistance in Echinochloa colona[J]. Plant Physiol, 2019, 181(4): 1519-1534.
- ↑ http://2016.igem.org/Team:TJUSLS_China
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 7
Illegal NheI site found at 30 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 820
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1039
Illegal AgeI site found at 1109
Illegal AgeI site found at 1186 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
