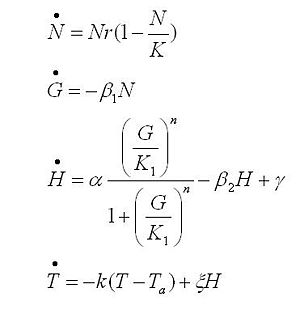Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K141003"
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
| + | [[Image:ownparameter82.jpg|800px]] | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | Galactose comsumption and heat effect. | ||
Latest revision as of 20:54, 29 October 2008
Ucp 76 deleted
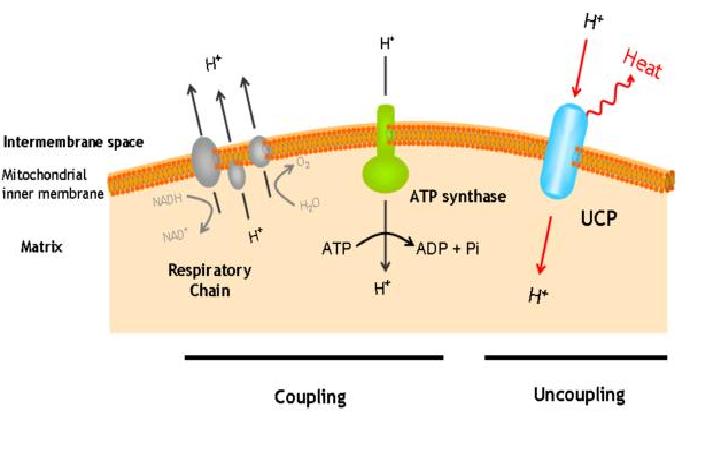
The uncoupling protein UCP 76 deleted is a proton carrier which is obtaines from the direct mugenesis of the Ucp1 gene.
Ucp 76 has a deletion in the triplet the encodes for the Glycine 76.
The mutant shows a generation time and an heat up capacity higher than UCP1.
UCP 76 deleted uncouples the respiratory chain of ATP production, converting the metabolic energy in heat.
The mutant shows a generation time and an heat up capacity higher than UCP1.
|
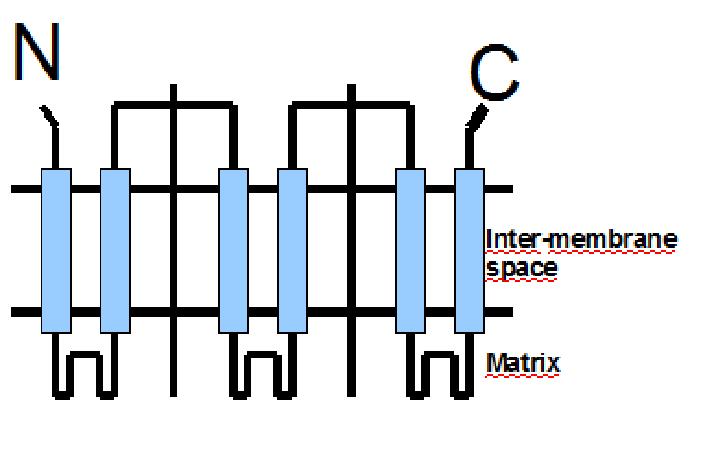
UCP 76 deleted is a 33kd protein.
The protein has a tripartite structure. The structure displays an around 100 residues region which is three times repeated. Each part encodes for two transmembrane segments and one long hydrophilic loop.The functional carrier unit is an homodimer.
|
The main difference between UCP 76 deleted and most of the proteins with a nuclear codification is the lack of the importation targeting to the mitochondria in UCP 76 deleted proteins.
The condition that determines the mitochondria as the protein target lays in the first loop which protudes in the mitochondrial matrix.
The second loop of the matrix is essential for the insertion of the protein in the inner mitochondrial matrix.
That protein is without direct regulation and its generation time depends on the inner activity the protein.
Strains growth
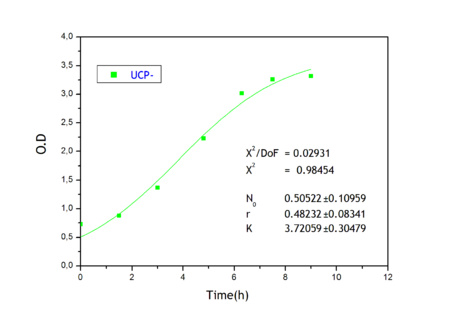
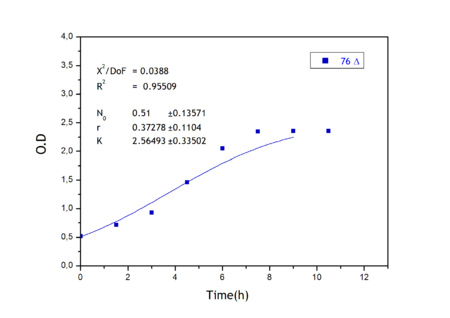
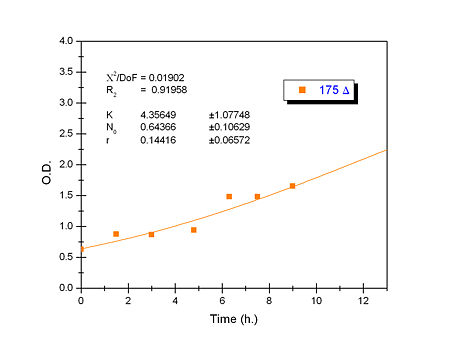
Apart from monitoring temperature evolution, we also characterized O.D. variations of each of our strains. We took O.D. measures every one a half hours for nine hours. We carried out this experiment both in Erlenmeyer flasks in the 30ºC shaking stove and in our LCCs. This measurements were useful in order to determine some parameters for our Black Box Model. Besides, we were able to prove that the UCP was indeed being produced even though we could not see the temperature increase. Since our mutant strains Gly175Δ and Gly76Δ do not have the same growing rate as UCP+ when they are expressing the protein, the difference between the results in the strains showed that the reason for our lack of temperature increase was that we had not found the optimum conditions yet. This results made us keep on working until we obtained successful results.
Strains growth equations:
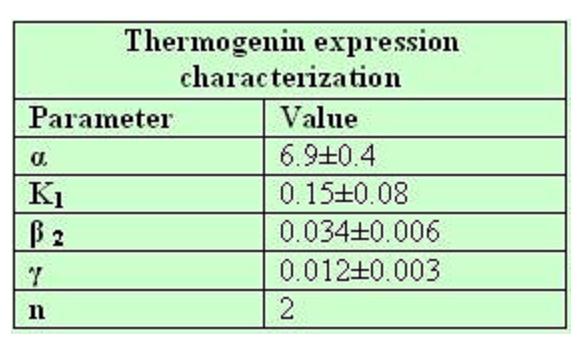
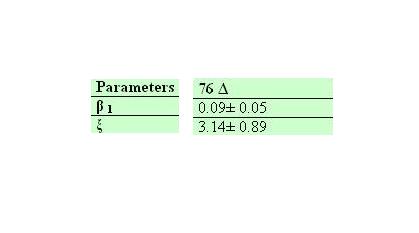
Model constants and parameters
The black box model simulates the temperature evolution of the system as a function of the growth rate, galactose concentration and thermogenin expresion. We assume that our system can be reproduced by the following system of equations:
where:
- first equation: Growth of the culture: logistic growth of the different mutants used in our experiments.
- second equation: Galactose evolution: Galactose is the metabolite which induces the thermogenin expresion.
- third equation: Thermogenin concentration level.
- Fourth equation: Temperature evolution. the first term of the equation represents the losses to the ambient of the calorimeter and the second one the temperature increase as a consequence of the thermogenin expresion.
From a sample of 10 experiments in which the evolution of the temperature of the four strain was measured we perform a fit using the software simulink.
Common parameters values
Own parameters of Ucp 76 deleted activity
Galactose comsumption and heat effect.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 47
Illegal BglII site found at 344
Illegal BamHI site found at 832 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 58
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]