Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3352004"
21tsuyoshim (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
The composite part utilizes a strong promoter (BBa_J23100), a ribosome binding site, SplintR ligase(BBa_K3352000), and a double terminator (BBa_K0015). | The composite part utilizes a strong promoter (BBa_J23100), a ribosome binding site, SplintR ligase(BBa_K3352000), and a double terminator (BBa_K0015). | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/thumb/2/2b/T--TAS_Taipei--Parts_BBa_K3352004.png/800px-T--TAS_Taipei--Parts_BBa_K3352004.png | ||
| + | |||
| + | <b>Figure 1: SplintR ligase with strong promoter, RBS, and double terminator</b> | ||
| + | |||
Latest revision as of 03:07, 26 October 2020
Strong Promoter and RBS SplintR Ligase Expressing Construct
The composite part utilizes a strong promoter (BBa_J23100), a ribosome binding site, SplintR ligase(BBa_K3352000), and a double terminator (BBa_K0015).
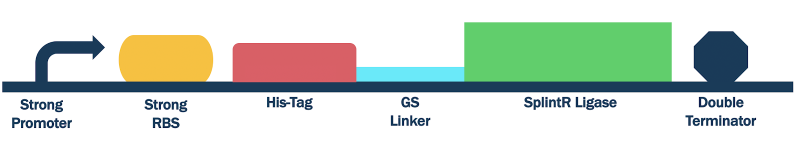
Figure 1: SplintR ligase with strong promoter, RBS, and double terminator
Construct Design
We optimized the DNA sequence for expression in E. coli and removed the PstI cutting site. We attached a 6x histidine tag (6x His-Tag) upstream of the SplintR ligase sequence for purification purposes followed by a glycine-serine linker (GS linker) to form our open reading frame (ORF) (BBa_K3352000). We flanked the open reading frame with an upstream strong promoter and strong ribosome binding site (RBS) combination (BBa_K880005) and downstream double terminator (BBa_B0015). This entire composite part was gene synthesized by IDT.
Results

Figure 2: Characterization of our Φ29 polymerase, parts BBa_K3352004 and BBa_K3352005, and SplintR ligase, BBa_K3352006 and BBa_K3352007.. All four constructs were ordered from Twist or IDT, conformed to a BioBrick assembly standard 10, and digested with EcoRI and PstI. Parts BBa_K3352004 and BBa_K3352005 were ordered from IDT and had a kanamycin backbone (pUCIDT KAN), which had a size of 2.7kB. BBa_K3352007 was also ordered from IDT, however, it contained an ampicillin backbone (pUCIDT AMP), which was also around 2.7kB. BBa_K3352006 was obtained from Twist Bioscience and was cloned into the ampicillin backbone (pSB1A3).
Characterization
Protein Expression and Purification
We transformed our designed plasmids (BBa_K3352004) into DH5⍺ E. coli cells. We grew overnight cultures, diluted those cultures, and then grew the cells to log phase. We lysed cells with xTractor Lysis Buffer (Takara Bio) and purified our His-tagged proteins using Ni sepharose affinity chromatography [2]. In order to check if our proteins were correct, we used SDS-PAGE.
Based on our results, our SplintR ligase construct that used a strong promoter and strong RBS combination (BBa_K3352004 and BBa_K3352005) did not express an appreciable amount of protein (Figure 3).

Figure 3: SDS-PAGE results show protein content at different steps of protein purification. A band around 35 kDa in the cell lysate (blue) and the eluate (red), matches our expected HIS-tagged Φ29. However, many other proteins were present in the eluate, and in the flowthrough lane (yellow). This prompted us to redesign our constructs.
References
1. Biolabs, N. E. (n.d.-c). SplintR® Ligase | NEB. Retrieved October 20, 2020, from https://international.neb.com/products/m0375-splintr-ligase
2. XTractorTM Buffer & xTractor Buffer Kit User Manual. (n.d.). 10.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 7
Illegal NheI site found at 30 - 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 851
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
