Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2150031"
(→Improvement: Jilin_China 2019) |
m |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Improvement: Jilin_China 2019== | ==Improvement: Jilin_China 2019== | ||
| − | + | <h3>'''Group:'''</h3> Jilin_China 2019 | |
| − | <h3>'''Authors:'''</h3 | + | <h3>'''Authors:'''</h3>Yu Ma |
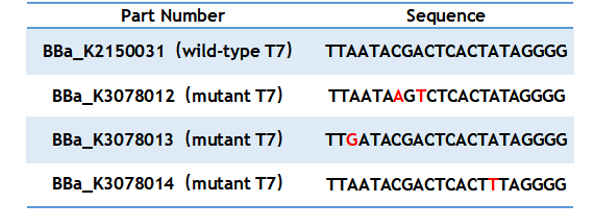
| − | <h3>'''Summary:'''</h3> | + | <h3>'''Summary:'''</h3> This year our team registered three mutated T7 promoters ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3078012 BBa_K3078012],[https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3078013 BBa_K3078013],[https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3078014 BBa_K3078014]) designed by Nie Z et al. Compared with the wild-type T7 promoter (BBa_K2150031), the expression intensity of BBa_K3078012 was 30% higher than that of wild-type T7 promoters. |
| + | |||
<h3>'''Documention:'''</h3> | <h3>'''Documention:'''</h3> | ||
<h4>'''1. Design'''</h4> | <h4>'''1. Design'''</h4> | ||
<h5> | <h5> | ||
<P style="text-indent:2em;"> | <P style="text-indent:2em;"> | ||
| − | T7 promoter is one of the most common promoters. But the intensity of the wild type T7 promoter often can’t meet our demand, so we mutated it and obtained an improved T7 promoter. According to previous studies, we selected the mutation site and constructed three mutated promoters ( | + | T7 promoter is one of the most common promoters. But the intensity of the wild type T7 promoter often can’t meet our demand, so we mutated it and obtained an improved T7 promoter. According to previous studies, we selected the mutation site and constructed three mutated promoters ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3078012 BBa_K3078012],[https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3078013 BBa_K3078013],[https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3078014 BBa_K3078014])based on the wild-type T7 promoter (BBa_K2150031) into the measurement vector ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3078100 BBa_K3078100]). |
</p> | </p> | ||
</h5> | </h5> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 40: | ||
[[File:T7突变-3.png|700px|center|T7突变-3]] | [[File:T7突变-3.png|700px|center|T7突变-3]] | ||
<center style="text-align:left;"> | <center style="text-align:left;"> | ||
| − | Figure 2. The plasmid was transferred to <i>E.coli</i> BL21, cultured overnight, and diluted OD<sub>600</sub> 0.02. IPTG was added at OD<sub>600</sub> 0.3 to make the final concentration of IPTG reach 1mM to measure at the indicated time | + | Figure 2. The plasmid was transferred to <i>E.coli</i> BL21, cultured overnight, and diluted OD<sub>600</sub> 0.02. IPTG was added at OD<sub>600</sub> 0.3 to make the final concentration of IPTG reach 1mM to measure at the indicated time. |
</center> | </center> | ||
| Line 49: | Line 50: | ||
</h5> | </h5> | ||
| + | <br /><br /> | ||
| + | ==<h3>Improvement: OUC-China 2020</h3>== | ||
| + | ===Design=== | ||
| + | We hope that the logic gates and some of the basics we designed will be widely used. Therefore, we add these structures after the promoter to assemble them into the entire circuit. | ||
| + | ====3WJ repressor==== | ||
| + | We added 3WJ repressor to the T7 promoter (BBa_K2150031) committed by the 2016 UCAS team. Our new part (BBa_K3328000) is an OFF-switch to regulate the expression of downstream gene. This design changes the original functionality of the T7 promoter and gives it new features. In addition, it is an integral part of NOT and IMPLY boolean calculation. | ||
| + | https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/thumb/a/af/T--OUC-China--design_fig4.png/800px-T--OUC-China--design_fig4.png.jpeg | ||
| + | 3WJ repressor switch RNA employs an unstable hairpin secondary structure. This unstable hairpin was previously demonstrated to be translationally active. When a complementary trigger RNA is expressed, the trigger will bind to the switch RNA, making the originally unstable 3WJ structure stable, and represses translation. | ||
| + | ==== NOT gate==== | ||
| + | We used 3WJ repressor to build NOT gate. Its unstable hairpin was previously demonstrated to be translationally active. | ||
| + | https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/thumb/1/1f/T--OUC-China--design_lunbo_not.jpg/799px-T--OUC-China--design_lunbo_not.jpg | ||
| + | When a complementary trigger RNA is expressed, the trigger will bind to the switch RNA, making the originally unstable 3WJ structure stable, and represses translation. | ||
| + | ==== IMPLY gate==== | ||
| + | We combined the 3WJ switch and toehold switch to realize the IMPLY Boolean calculation. | ||
| + | https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/thumb/8/88/T--OUC-China--design_fig6.jpg/799px-T--OUC-China--design_fig6.jpg | ||
| + | When no trigger expressed, this logic gate just likes a 3WJ switch. When trigger A expressed, the trigger will bind to the switch RNA. The binding allows for a branch migration process, exposing AUG and RBS for translation initiation. When trigger B expressed, the trigger will bind to 3WJ switch RNA. The resulting trigger–switch complex has a stable 3WJ structure that effectively sequesters the RBS and start codon within the loop and stem of the switch RNA, respectively, and strongly represses translation. When trigger A and B both expressed, the binding of trigger RNA to the toehold sequence allow the RNA polymerase binds to the former RBS and break open 3WJ stable hairpin. | ||
| + | ===Result=== | ||
| + | ====3WJ repressor==== | ||
| + | https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/thumb/c/c6/T--OUC-China--result_fig3.jpg/653px-T--OUC-China--result_fig3.jpg | ||
| + | In the validation of 3WJ, as with toehold, we also set blank control (IPTG=0 M, aTc=0 mg/ml). Compared with the group without trigger expression (IPTG=0.1 M, aTc=0 mg/ml), the group with trigger expression (IPTG=0.1 M, aTc=0.25 mg/ml) showed inhibitory effect. | ||
| + | https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/thumb/3/31/T--OUC-China--result_fig4.jpg/768px-T--OUC-China--result_fig4.jpg | ||
| + | Crosstalk was determined by dividing the arithmetic mean of the GFP fluorescence from a given trigger switch pair by the arithmetic mean of the GFP fluorescence for the cognate trigger switch interaction. GFP fluorescence was measured from n=9 biologically independent samples. | ||
| + | 3WJ repressor showed remarkable ON/OFF ratio and had good orthogonality, we choose it as OFF switch. And we used it in the construction of logic gates and the design of some more complex circuits. | ||
| + | ==== NOT gate==== | ||
| + | https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/thumb/4/4b/T--OUC-China--result_fig7.jpg/800px-T--OUC-China--result_fig7.jpg | ||
| + | The left figure shows that when INPUT=0, the fluorescence of GFP is high. And the fluorescence intensity of GFP was low when INPUT=1. This corresponds to the situation described in the truth table on the right. INPUT=1 means that aTc (0.25 mg/ml) is added. | ||
| + | ==== IMPLY gate==== | ||
| + | https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/thumb/5/52/T--OUC-China--part_IMPLY1.jpg/800px-T--OUC-China--part_IMPLY1.jpg | ||
| + | https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/thumb/6/66/T--OUC-China--part_IMPLY2.jpg/800px-T--OUC-China--part_IMPLY2.jpg | ||
| + | The left figure shows that when INPUT A=0, INPUT B=1, the fluorescence of GFP is low. And the fluorescence intensity of GFP was high in the other three groups. This corresponds to the situation described in the truth table on the right. INPUT A=1 means that aTc (0.25 mg/ml) is added, INPUT B=1 means that HSL (0.1 mg/ml) is added. | ||
| + | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| + | ===Contribution: New documentation from Evry_Paris-Saclay 2020=== | ||
| + | This part is the strong promoter from T7 bacteriophage (taatacgactcactata) with GGG at 3' end. | ||
| + | The T7 RNA polymerase initiates the transcription at the first guanidine of this stretch of three G and it was shown that +1 GGG is one of the best +1, +2 and +3 base combinations at the transcription initiation for enhanced promoter strength [1]. | ||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | [1] Imburgio D, Rong M, Ma K, McAllister WT. Studies of promoter recognition and start site selection by T7 RNA polymerase using a comprehensive collection of promoter variants. Biochemistry (2000) 39, 10419-10430. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
Latest revision as of 07:09, 25 October 2020
T7 promoter without RBS
This part is the T7 promoter without RBS. It has been reported that T7 promoter doesn't work with E.coli RNA polymerase, but only with T7 RNA polymerase(T7RNAP). However, we observed leakage of it in the absence of T7RNAP.
Improvement: Jilin_China 2019
Group:
Jilin_China 2019Authors:
Yu MaSummary:
This year our team registered three mutated T7 promoters (BBa_K3078012,BBa_K3078013,BBa_K3078014) designed by Nie Z et al. Compared with the wild-type T7 promoter (BBa_K2150031), the expression intensity of BBa_K3078012 was 30% higher than that of wild-type T7 promoters.Documention:
1. Design
T7 promoter is one of the most common promoters. But the intensity of the wild type T7 promoter often can’t meet our demand, so we mutated it and obtained an improved T7 promoter. According to previous studies, we selected the mutation site and constructed three mutated promoters (BBa_K3078012,BBa_K3078013,BBa_K3078014)based on the wild-type T7 promoter (BBa_K2150031) into the measurement vector (BBa_K3078100).
Table 1. Sequence of wild type and mutant T7 promoter.
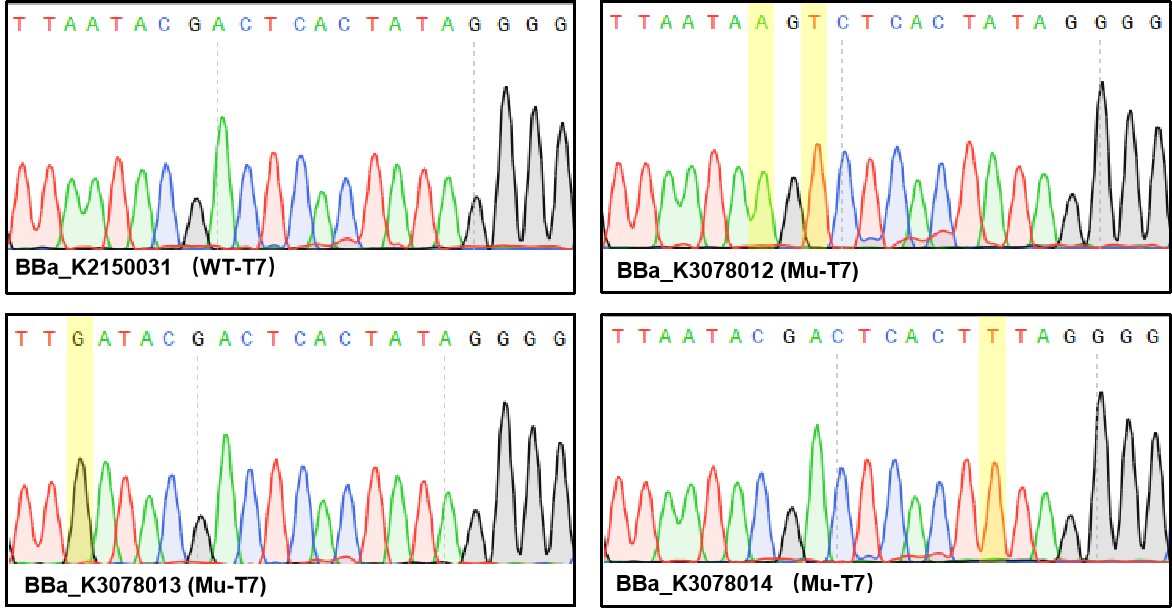
Figure 1. Sequencing the plasmids.
2. Measurement
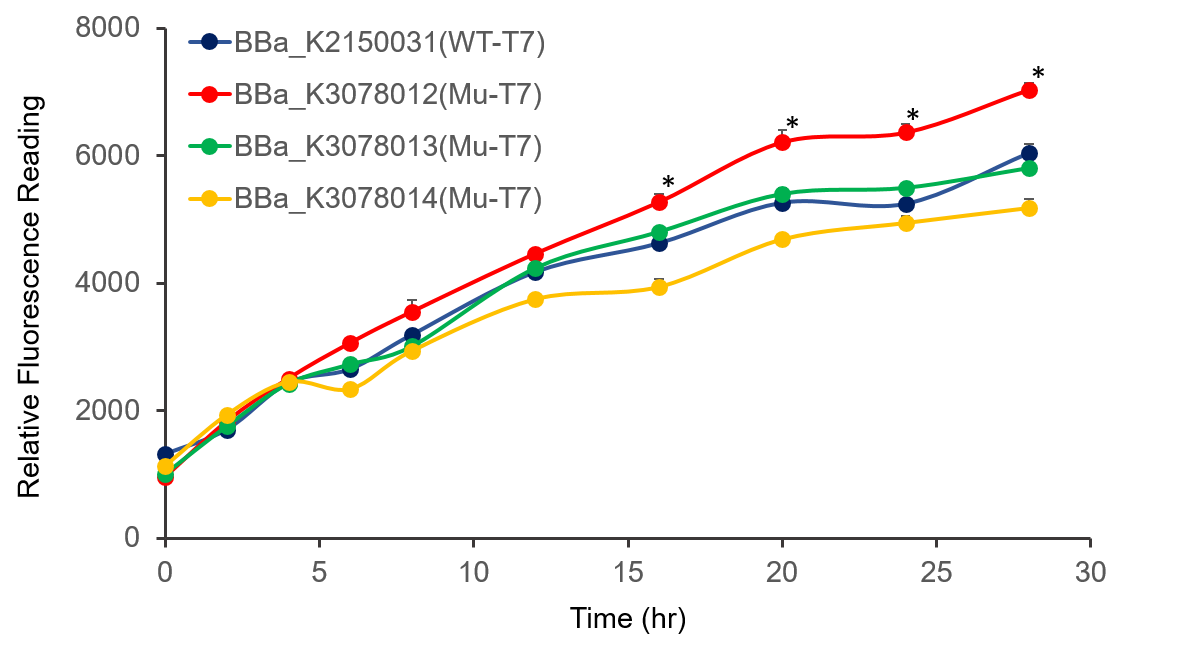
The promoter activity of wild-type and mutant T7 were measured through fluorescence intensity and normalized by OD600. BBa_K2150031 and the mutated T7 promoter lack of T7 RNA polymerase, so we added IPTG to induce the expression of T7 RNA polymerase downstream of promoter lacUV5 of on the BL21(DE3) genome, as shown in Figure 2.
It can be seen from the figure that the promoter strength of mutant is higher than wild type.
Figure 2. The plasmid was transferred to E.coli BL21, cultured overnight, and diluted OD600 0.02. IPTG was added at OD600 0.3 to make the final concentration of IPTG reach 1mM to measure at the indicated time.
3. Conclusion
In conclusion, we constructed wild-type and mutanted T7 promoters into the measurement vector (BBa_K3078100) by Golden Gate method, and confirmed by the fluorescence measurement of the expression intensity of BBa_K3078012 was 30% higher than that of wild-type T7 promoters.
Improvement: OUC-China 2020
Design
We hope that the logic gates and some of the basics we designed will be widely used. Therefore, we add these structures after the promoter to assemble them into the entire circuit.
3WJ repressor
We added 3WJ repressor to the T7 promoter (BBa_K2150031) committed by the 2016 UCAS team. Our new part (BBa_K3328000) is an OFF-switch to regulate the expression of downstream gene. This design changes the original functionality of the T7 promoter and gives it new features. In addition, it is an integral part of NOT and IMPLY boolean calculation.

3WJ repressor switch RNA employs an unstable hairpin secondary structure. This unstable hairpin was previously demonstrated to be translationally active. When a complementary trigger RNA is expressed, the trigger will bind to the switch RNA, making the originally unstable 3WJ structure stable, and represses translation.
NOT gate
We used 3WJ repressor to build NOT gate. Its unstable hairpin was previously demonstrated to be translationally active.

When a complementary trigger RNA is expressed, the trigger will bind to the switch RNA, making the originally unstable 3WJ structure stable, and represses translation.
IMPLY gate
We combined the 3WJ switch and toehold switch to realize the IMPLY Boolean calculation.

When no trigger expressed, this logic gate just likes a 3WJ switch. When trigger A expressed, the trigger will bind to the switch RNA. The binding allows for a branch migration process, exposing AUG and RBS for translation initiation. When trigger B expressed, the trigger will bind to 3WJ switch RNA. The resulting trigger–switch complex has a stable 3WJ structure that effectively sequesters the RBS and start codon within the loop and stem of the switch RNA, respectively, and strongly represses translation. When trigger A and B both expressed, the binding of trigger RNA to the toehold sequence allow the RNA polymerase binds to the former RBS and break open 3WJ stable hairpin.
Result
3WJ repressor

In the validation of 3WJ, as with toehold, we also set blank control (IPTG=0 M, aTc=0 mg/ml). Compared with the group without trigger expression (IPTG=0.1 M, aTc=0 mg/ml), the group with trigger expression (IPTG=0.1 M, aTc=0.25 mg/ml) showed inhibitory effect.

Crosstalk was determined by dividing the arithmetic mean of the GFP fluorescence from a given trigger switch pair by the arithmetic mean of the GFP fluorescence for the cognate trigger switch interaction. GFP fluorescence was measured from n=9 biologically independent samples.
3WJ repressor showed remarkable ON/OFF ratio and had good orthogonality, we choose it as OFF switch. And we used it in the construction of logic gates and the design of some more complex circuits.
NOT gate

The left figure shows that when INPUT=0, the fluorescence of GFP is high. And the fluorescence intensity of GFP was low when INPUT=1. This corresponds to the situation described in the truth table on the right. INPUT=1 means that aTc (0.25 mg/ml) is added.
IMPLY gate


The left figure shows that when INPUT A=0, INPUT B=1, the fluorescence of GFP is low. And the fluorescence intensity of GFP was high in the other three groups. This corresponds to the situation described in the truth table on the right. INPUT A=1 means that aTc (0.25 mg/ml) is added, INPUT B=1 means that HSL (0.1 mg/ml) is added.
Usage and Biology
Contribution: New documentation from Evry_Paris-Saclay 2020
This part is the strong promoter from T7 bacteriophage (taatacgactcactata) with GGG at 3' end.
The T7 RNA polymerase initiates the transcription at the first guanidine of this stretch of three G and it was shown that +1 GGG is one of the best +1, +2 and +3 base combinations at the transcription initiation for enhanced promoter strength [1].
References
[1] Imburgio D, Rong M, Ma K, McAllister WT. Studies of promoter recognition and start site selection by T7 RNA polymerase using a comprehensive collection of promoter variants. Biochemistry (2000) 39, 10419-10430.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]