Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3245001"
| (13 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | <h1> | + | <h1> luxpR-fus100</h1> |
| − | <p> | + | <p>This hybrid promoter has higher expression level when induced by luxR-AHL complex triggered by quorum sensing ( QS ) in some Gram-negative bacteria, meanwhile it’s leakage is also higher when not induced.</p> |
<h2>Usage and biology:</h2> | <h2>Usage and biology:</h2> | ||
| − | <p>This | + | <p>This fused promoter is designed for the situation that QS effect and high expression level are required at the same time in a circuit if leakage is acceptable to some extent. We applied this enhanced promoter to improve lacZ expression when bacteria reached a high density. </p> |
<h2>Design:</h2> | <h2>Design:</h2> | ||
| − | <p> | + | [[File:T--Fudan--Part50.png|700px]] |
| − | + | <p>As the figure shows, we substituted the -35 to -10 region of the original promoter luxpR with the one of J23100, a strong constitutive promoter. This region is rarely concerned as it’s rather conservative in promoters with the same function, but it has crucial structural effect on σ factor binding and other events in transcription regulation. Fortunately the change proved to be effective on adjusting the behavior of the regulatory promoter.</p> | |
| − | + | ||
<h2>Characterization:</h2> | <h2>Characterization:</h2> | ||
| − | <p> | + | <p>Measurement Protocol</p> |
| − | + | <p>1. Transform a control plasmid containing luxI and luxR ( BBa_K3245002) with pUC ori ( high copy number ) and an effect plasmid containing luxpR-fus100 and GFP behind the promoter with p15A ori (medium copy number ) into DH10B. </p> | |
| − | <p> | + | <p>2. Pick a single colony by a sterile tip from each of the LB plates for all the experimental and control groups. Add the colony into 3 ml LB with ampicillin at 100 μg/ml. Incubate overnight at 37℃ in a shaker.</p> |
| − | [[File:T--Fudan-- | + | <p>3. Measure and keep all groups OD600 reach 1. Inoculate each group with with 1/5000 concentration. Incubate 12 hours at 37℃ in a shaker.</p> |
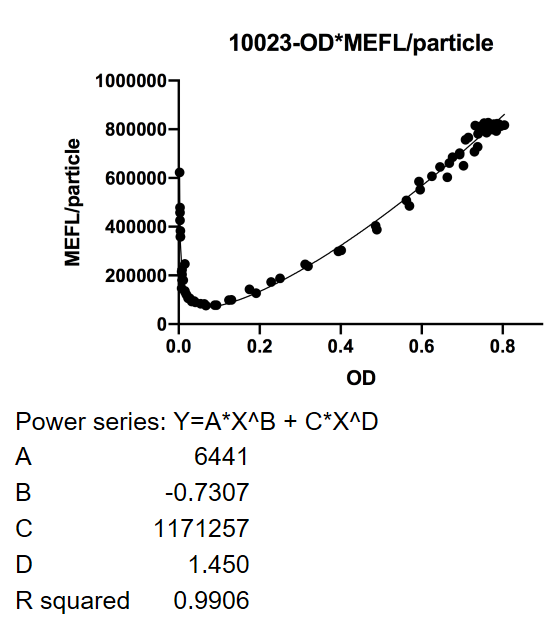
| − | <p>Fig. | + | <p>4. Add 100 µl bacteria culture medium into each well of a 96-well plate. One well of LB as blank, one group of wild type DH10B as control.</p> |
| + | <p>5. Measure OD600 and fluorescence continuously every 30 minutes with a microplate reader.</p> | ||
| + | [[File:T--Fudan--Part51.png|400px]] | ||
| + | <p><strong>Fig.1</strong> This figure used OD600 as X-axis unit. The MEFL/particle changes as the OD goes up after dilution. The downward curve before OD600 < 0.1 is due to the parental fluorescence and the dilution effect after proliferation. Data points are shown in the figure for fitting analysis. Here gives the parameters of the fitting equation. | ||
| + | <h2>Reference</h2> | ||
| + | Antunes, L. C., et al. "A mutational analysis defines Vibrio fischeri LuxR binding sites." Journal of Bacteriology 190.13(2008):4392-4397. | ||
| + | de Boer HA, Comstock LJ, Vasser M. The tac promoter: a functional hybrid derived from the trp and lac promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983;80(1):21–25. doi:10.1073/pnas.80.1.21 | ||
Latest revision as of 03:56, 22 October 2019
luxpR-fus100
This hybrid promoter has higher expression level when induced by luxR-AHL complex triggered by quorum sensing ( QS ) in some Gram-negative bacteria, meanwhile it’s leakage is also higher when not induced.
Usage and biology:
This fused promoter is designed for the situation that QS effect and high expression level are required at the same time in a circuit if leakage is acceptable to some extent. We applied this enhanced promoter to improve lacZ expression when bacteria reached a high density.
Design:
As the figure shows, we substituted the -35 to -10 region of the original promoter luxpR with the one of J23100, a strong constitutive promoter. This region is rarely concerned as it’s rather conservative in promoters with the same function, but it has crucial structural effect on σ factor binding and other events in transcription regulation. Fortunately the change proved to be effective on adjusting the behavior of the regulatory promoter.
Characterization:
Measurement Protocol
1. Transform a control plasmid containing luxI and luxR ( BBa_K3245002) with pUC ori ( high copy number ) and an effect plasmid containing luxpR-fus100 and GFP behind the promoter with p15A ori (medium copy number ) into DH10B.
2. Pick a single colony by a sterile tip from each of the LB plates for all the experimental and control groups. Add the colony into 3 ml LB with ampicillin at 100 μg/ml. Incubate overnight at 37℃ in a shaker.
3. Measure and keep all groups OD600 reach 1. Inoculate each group with with 1/5000 concentration. Incubate 12 hours at 37℃ in a shaker.
4. Add 100 µl bacteria culture medium into each well of a 96-well plate. One well of LB as blank, one group of wild type DH10B as control.
5. Measure OD600 and fluorescence continuously every 30 minutes with a microplate reader.
Fig.1 This figure used OD600 as X-axis unit. The MEFL/particle changes as the OD goes up after dilution. The downward curve before OD600 < 0.1 is due to the parental fluorescence and the dilution effect after proliferation. Data points are shown in the figure for fitting analysis. Here gives the parameters of the fitting equation.
Reference
Antunes, L. C., et al. "A mutational analysis defines Vibrio fischeri LuxR binding sites." Journal of Bacteriology 190.13(2008):4392-4397.
de Boer HA, Comstock LJ, Vasser M. The tac promoter: a functional hybrid derived from the trp and lac promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983;80(1):21–25. doi:10.1073/pnas.80.1.21