Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3078002"
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
<h5> | <h5> | ||
<P style="text-indent:2em;"> | <P style="text-indent:2em;"> | ||
| − | It is reported that the proportion of chitin is three times higher than that of yeast cell wall in the hypha cell wall of C. albicans. Due to chitinase activity of Msp1, we inferred that Msp1 can cause the inhibition and degradation of hypha cell wall. | + | It is reported that the proportion of chitin is three times higher than that of yeast cell wall in the hypha cell wall of <i>C. albicans</i>. Due to chitinase activity of Msp1, we inferred that Msp1 can cause the inhibition and degradation of hypha cell wall. |
</p> | </p> | ||
<P style="text-indent:2em;"> | <P style="text-indent:2em;"> | ||
| − | To detect the inhibition ability of Msp1, C. albicans was co-cultured with Msp1 to observe the change of hyphae. Compared to the control, the hyphae were inhibited, which indicated that Msp1 exhibited the capacity of destabilizing hyphae (Figure 2). | + | To detect the inhibition ability of Msp1, <i>C. albicans</i> was co-cultured with Msp1 to observe the change of hyphae. Compared to the control, the hyphae were inhibited, which indicated that Msp1 exhibited the capacity of destabilizing hyphae (Figure 2). |
</p> | </p> | ||
</h5> | </h5> | ||
[[File:Msp1-3.png|600px|center|Msp1-3]] | [[File:Msp1-3.png|600px|center|Msp1-3]] | ||
<center style="text-align:left;"> | <center style="text-align:left;"> | ||
| − | Figure 2. Inhibition ability of Msp1. C. albicans and the supernatant of control or Msp1 were co-cultured in YPD medium supplementary with 10% serum in 96-well plate at 37℃ for 4 hours. After incubation, the plate was observed with inverted microscope. A, mock control; B, Msp1. | + | Figure 2. Inhibition ability of Msp1. <i>C. albicans</i> and the supernatant of control or Msp1 were co-cultured in YPD medium supplementary with 10% serum in 96-well plate at 37℃ for 4 hours. After incubation, the plate was observed with inverted microscope. A, mock control; B, Msp1. |
</center> | </center> | ||
<h5> | <h5> | ||
<P style="text-indent:2em;"> | <P style="text-indent:2em;"> | ||
| − | To further test the degradation ability of Msp1, C. albicans was firstly only cultured by medium with serum to produce hyphae and then we added the concentrated bacteria supernatant into the cultured C. albicans. Compared to the control, the hyphae became shorter, indicating that Msp1 exhibited the capacity of destabilizing hyphae (Figure 3). | + | To further test the degradation ability of Msp1, <i>C. albicans</i> was firstly only cultured by medium with serum to produce hyphae and then we added the concentrated bacteria supernatant into the cultured <i>C. albicans</i>. Compared to the control, the hyphae became shorter, indicating that Msp1 exhibited the capacity of destabilizing hyphae (Figure 3). |
</p> | </p> | ||
</h5> | </h5> | ||
[[File:Msp1-4.png|600px|center|Msp1-4]] | [[File:Msp1-4.png|600px|center|Msp1-4]] | ||
<center style="text-align:left;"> | <center style="text-align:left;"> | ||
| − | Figure 3. Degradation ability of Msp1. C. albicans was cultured in YPD medium supplementary with 10% serum in 96-well plate at 37℃. 4 hours later, the supernatant of control or Msp1 was added into the plate respectively. After another 3-hour incubation, the plate was observed with inverted microscope. A, mock control; B, Msp1. | + | Figure 3. Degradation ability of Msp1. <i>C. albicans</i> was cultured in YPD medium supplementary with 10% serum in 96-well plate at 37℃. 4 hours later, the supernatant of control or Msp1 was added into the plate respectively. After another 3-hour incubation, the plate was observed with inverted microscope. A, mock control; B, Msp1. |
</center> | </center> | ||
<h5> | <h5> | ||
<P style="text-indent:2em;"> | <P style="text-indent:2em;"> | ||
| − | Msp1 can combine with lactic acid and some proteins secreted by Lactobacillus and synergistically abolish hyphal morphogenesis. We reasonably predict that Msp1 will have better effect when Lactobacillus jensenii is used as the chassis for our project in the future. | + | Msp1 can combine with lactic acid and some proteins secreted by <i>Lactobacillus</i> and synergistically abolish hyphal morphogenesis. We reasonably predict that Msp1 will have better effect when Lactobacillus jensenii is used as the chassis for our project in the future. |
</p> | </p> | ||
</h5> | </h5> | ||
Revision as of 23:26, 21 October 2019
Msp1
Msp1 protein coding region. Msp1 is a protein with chitinase activity.
1. Usage and Biology
C. albicans in hypha phase can invade human epithelial cells and cause infection. In order to eliminate the hyphae of C. albicans, we choose the protein Msp1 with the function of destabilizing hyphae.
Msp1 is a protein secreted by rhamnose GG and has chitinase activity. There is a large amount of chitin in the hypha cell wall of C. albicans, so Msp1 can hydrolyze chitin to achieve the effect of destabilising hyphae.
2. Characterization
2.1 Validation of Msp1 construction
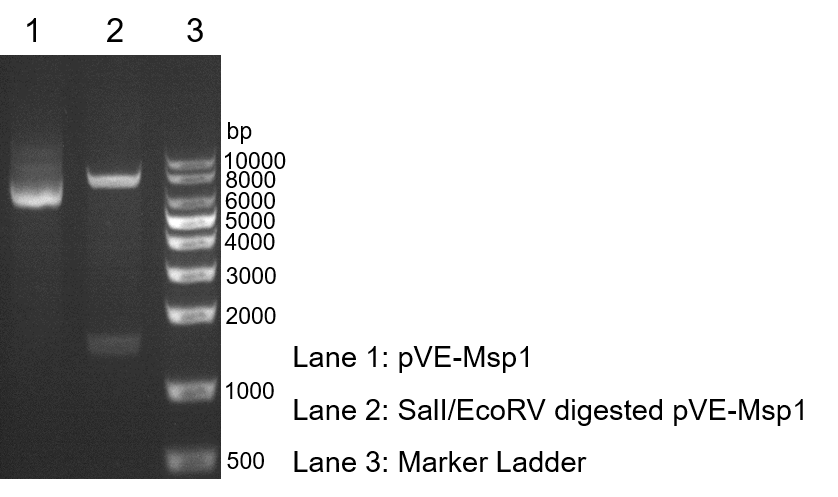
To verify the construction of pVE-Msp1 which we generated, the digestion by SalI/EcoRV was performed by a standard protocol followed by agarose gel electrophoresis (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Digestion and electrophoresis of pVE-Msp1.
2.2 Chitinase activity of Msp1
Msp1 has the chitinase activity which can destabilize hyphae. Chitinase activity kit was used to detect the chitinase activity of Msp1.
Table 1. Chitinase activity of Msp1. The chitinase activity was performed by the standard protocol. In brief, after incubation, the absorbance was measured at 540 nm. The concentrated bacteria supernatant pVE5523 was used as control. Then the chitinase activity was calculated according to the standard curve, y=0.3331x-0.2557(R2=0.991). Production of 1 μmol N-acetylglucosamine in 1 mL culture medium decomposes chitin in 1 hour at 37℃ is defined as an active unit.
2.3 Destabilization of C. albicans hyphae by Msp1
It is reported that the proportion of chitin is three times higher than that of yeast cell wall in the hypha cell wall of C. albicans. Due to chitinase activity of Msp1, we inferred that Msp1 can cause the inhibition and degradation of hypha cell wall.
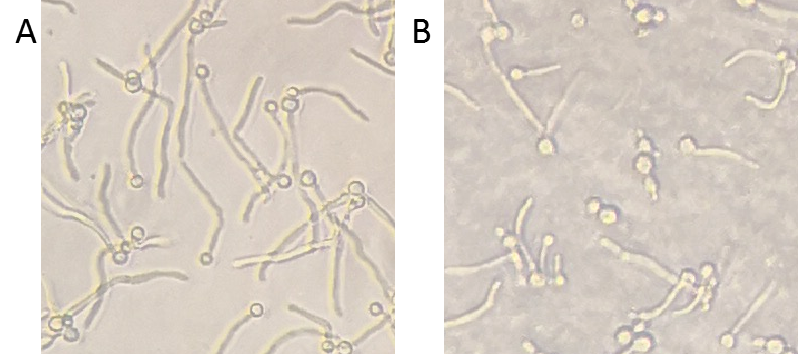
To detect the inhibition ability of Msp1, C. albicans was co-cultured with Msp1 to observe the change of hyphae. Compared to the control, the hyphae were inhibited, which indicated that Msp1 exhibited the capacity of destabilizing hyphae (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Inhibition ability of Msp1. C. albicans and the supernatant of control or Msp1 were co-cultured in YPD medium supplementary with 10% serum in 96-well plate at 37℃ for 4 hours. After incubation, the plate was observed with inverted microscope. A, mock control; B, Msp1.
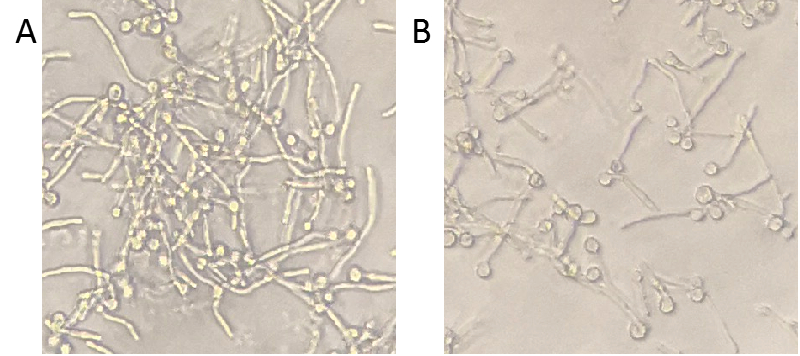
To further test the degradation ability of Msp1, C. albicans was firstly only cultured by medium with serum to produce hyphae and then we added the concentrated bacteria supernatant into the cultured C. albicans. Compared to the control, the hyphae became shorter, indicating that Msp1 exhibited the capacity of destabilizing hyphae (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Degradation ability of Msp1. C. albicans was cultured in YPD medium supplementary with 10% serum in 96-well plate at 37℃. 4 hours later, the supernatant of control or Msp1 was added into the plate respectively. After another 3-hour incubation, the plate was observed with inverted microscope. A, mock control; B, Msp1.
Msp1 can combine with lactic acid and some proteins secreted by Lactobacillus and synergistically abolish hyphal morphogenesis. We reasonably predict that Msp1 will have better effect when Lactobacillus jensenii is used as the chassis for our project in the future.
3. Conclusion
After verification of experiments,the results showed that MSP1 had chitinase activity and the ability of destabilizing C. albicans hyphae.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1011
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]