Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3190601"
Hitesh Gelli (Talk | contribs) (→Usage and Biology) |
Hitesh Gelli (Talk | contribs) (→Usage and Biology) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
<b><font size="3">Improvement of kill switch system</font></b> | <b><font size="3">Improvement of kill switch system</font></b> | ||
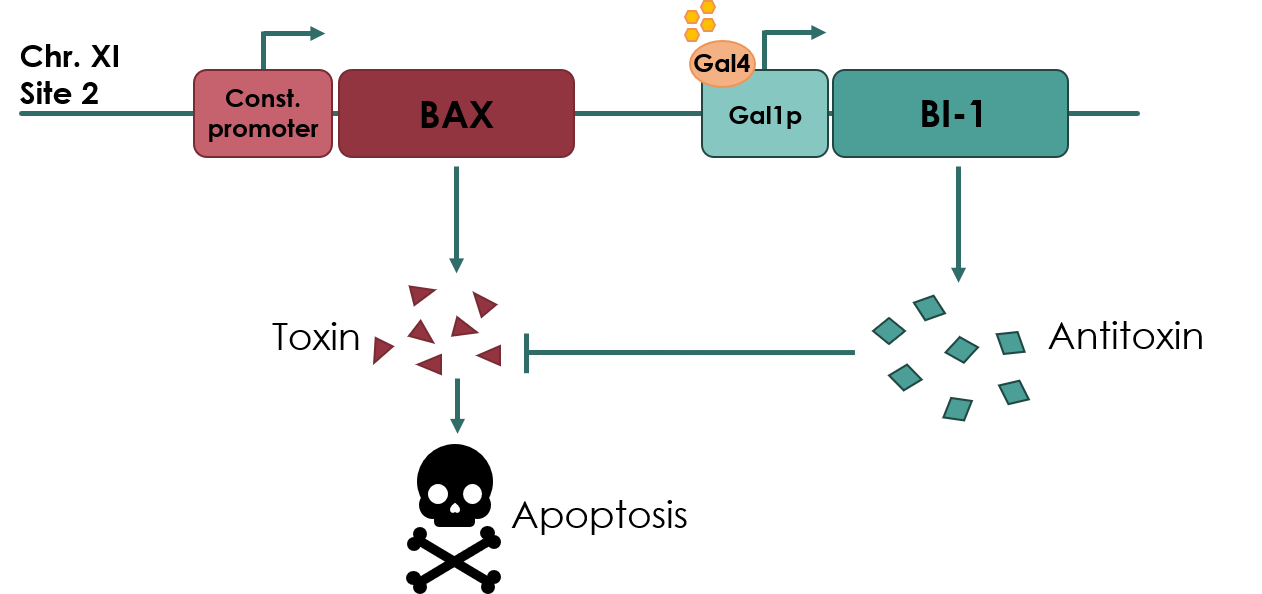
| − | We | + | We wanted to improve the BI-1 coding sequence (BBa_K2365518), which was submitted by the iGEM team NAU_CHINA 2017. They used it as part of their kill switch system and also submitted a composite part consisting of the TEF1 constitutive promoter, BI-1, and the yeast CYC1 terminator. |
| − | The kill switch proposed by team NAU China works by co-expressing the BAX gene ( | + | The kill switch proposed by team NAU China works by co-expressing the BAX gene (BBa_K2365048), which encodes the pro-apoptotic Bax protein, under a constitutive promoter, together with BI-1 under the galactose inducible GAL1 promoter. In theory, as long as galactose is present in the media BI-1 will be expressed, inhibiting the Bax protein. Should the yeast cell escape the media or matrix, BAX will be expressed, causing apoptosis of the cell. |
[[File:UCopenhagen Killswitch.jpeg|600px]] | [[File:UCopenhagen Killswitch.jpeg|600px]] | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
Our improvement lays in the addition of the pGAL1 promoter in front of the BI-1 sequence. This improvement will allow us to control the expression of BI-1, as the GAL1 promoter allows transcription of BI-1 only in the presence of galactose. | Our improvement lays in the addition of the pGAL1 promoter in front of the BI-1 sequence. This improvement will allow us to control the expression of BI-1, as the GAL1 promoter allows transcription of BI-1 only in the presence of galactose. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<b><font size="3">BAX rescue assay</font></b> | <b><font size="3">BAX rescue assay</font></b> | ||
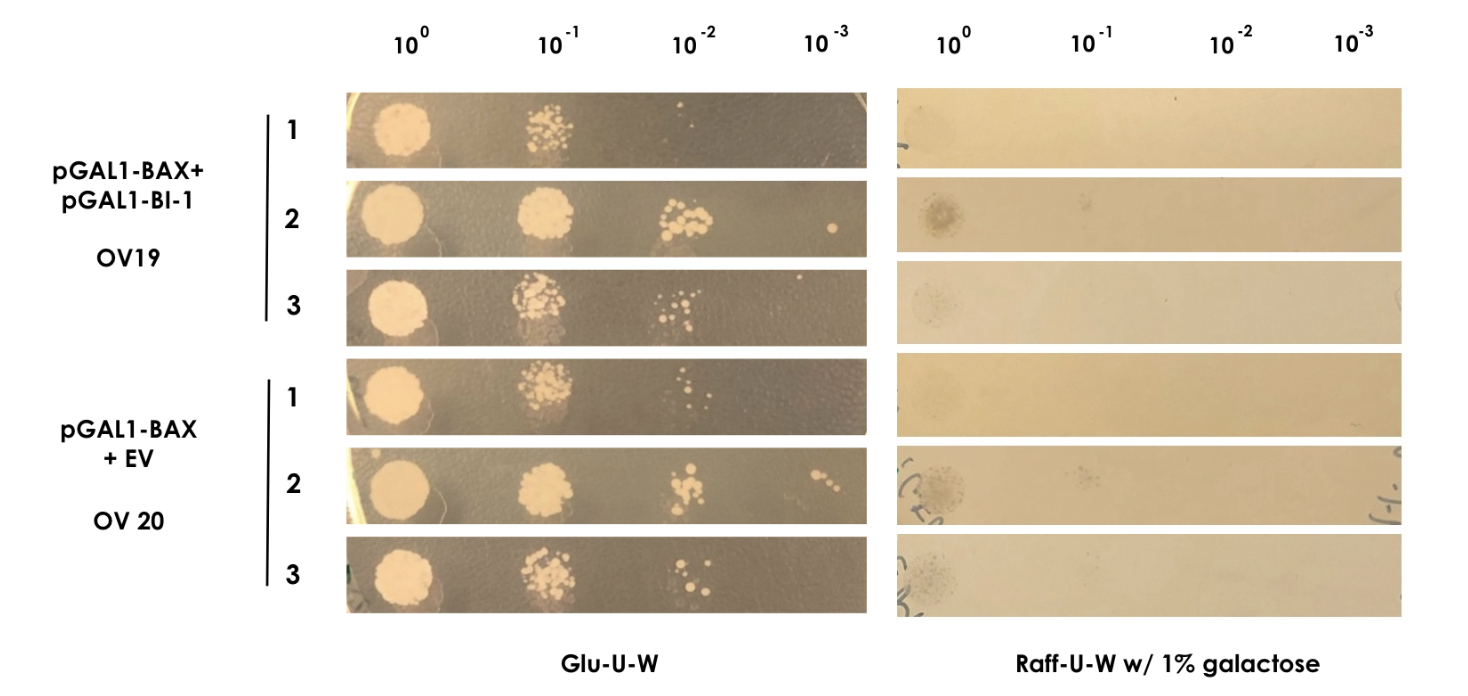
| − | + | In order to show that BI-1 is able to neutralize the lethal impact of BAX, we performed a rescue assay in which both BAX and BI-1 were placed under the control of the GAL1 promoter. For this, we constructed two strains; OV19, which had pGAL1-BAX integrated into the genome and pGAL1-BI-1 on a high-copy number episomal plasmid, and OV20, which had pGAL1-BAX integrated into the genome and carried an empty vector. | |
| − | For | + | For the assay colonies were picked and diluted in sterile water. Using the comparative galactose induction assay as a template, the ODs at 600 nm were equalized to 0.035 and different dilutions of the colonies (10^-0 to 10^-3) were spotted on plates with glu-U-W agar and raff-U-W agar with 1% galactose in volumes of 10 µl. A yeast strain containing only pGAL1-BAX and the empty pWUS plasmid served as control (OV20) and was spotted along with the sample (Figure 2). |
| − | + | ||
[[File:ovulaid35.png|500px]] | [[File:ovulaid35.png|500px]] | ||
| Line 32: | Line 30: | ||
<small><b>Figure 2: BAX rescue assay</b> | In this assay, the strains OV19 and OV20 were grown on both glu-U-W agar (left) and raff-U-W (1% galactose) agar in different dilutions of OD600nm (10-0 to 10-3). </small> | <small><b>Figure 2: BAX rescue assay</b> | In this assay, the strains OV19 and OV20 were grown on both glu-U-W agar (left) and raff-U-W (1% galactose) agar in different dilutions of OD600nm (10-0 to 10-3). </small> | ||
| − | As BAX was expressed under the inducible promoter pGAL1 in both strains, we expected normal growth on the glu-U-W plates. On the raff-U-W plates with 1% galactose, we expected the control strain OV20 to show decreased colony size and number compared the | + | As BAX was expressed under the inducible promoter pGAL1 in both strains, we expected normal growth on the glu-U-W plates. On the raff-U-W plates with 1% galactose, we expected the control strain OV20 to show decreased colony size and number compared to the OV19 strain that should be rescued by the BI-1 plasmid. However, as seen on figure 2, no significant growth was seen for either strain in the presence of galactose. As such, we saw no indication that BI-1 was able to prevent BAX induced apoptosis. While it is possible that the lack of function of BI-1 could be the result of a loss of function during transformation, our data suggests BI-1 is not able to prevent BAX induced apoptosis in our system, and is therefore not suitable for our kill switch. |
Revision as of 22:55, 21 October 2019
pGAL1-BI-I: BI-I CDS under inducible promoter
The coding sequence of BAX Inhibitor-I (BI-1) anti-toxin under the control of inducible promoter GAL1 (Basic part BBa_K3190050) for the design of a kill switch system for a yeast wherein a BAX toxin is expressed under a constitutive promoter. This system ensures that the yeast will not survive if it escapes the medium containing the inducer.
Usage and Biology
Improvement of kill switch system
We wanted to improve the BI-1 coding sequence (BBa_K2365518), which was submitted by the iGEM team NAU_CHINA 2017. They used it as part of their kill switch system and also submitted a composite part consisting of the TEF1 constitutive promoter, BI-1, and the yeast CYC1 terminator.
The kill switch proposed by team NAU China works by co-expressing the BAX gene (BBa_K2365048), which encodes the pro-apoptotic Bax protein, under a constitutive promoter, together with BI-1 under the galactose inducible GAL1 promoter. In theory, as long as galactose is present in the media BI-1 will be expressed, inhibiting the Bax protein. Should the yeast cell escape the media or matrix, BAX will be expressed, causing apoptosis of the cell.
Figure 1: Overview of the kill switch
Our improvement lays in the addition of the pGAL1 promoter in front of the BI-1 sequence. This improvement will allow us to control the expression of BI-1, as the GAL1 promoter allows transcription of BI-1 only in the presence of galactose.
BAX rescue assay
In order to show that BI-1 is able to neutralize the lethal impact of BAX, we performed a rescue assay in which both BAX and BI-1 were placed under the control of the GAL1 promoter. For this, we constructed two strains; OV19, which had pGAL1-BAX integrated into the genome and pGAL1-BI-1 on a high-copy number episomal plasmid, and OV20, which had pGAL1-BAX integrated into the genome and carried an empty vector. For the assay colonies were picked and diluted in sterile water. Using the comparative galactose induction assay as a template, the ODs at 600 nm were equalized to 0.035 and different dilutions of the colonies (10^-0 to 10^-3) were spotted on plates with glu-U-W agar and raff-U-W agar with 1% galactose in volumes of 10 µl. A yeast strain containing only pGAL1-BAX and the empty pWUS plasmid served as control (OV20) and was spotted along with the sample (Figure 2).
Figure 2: BAX rescue assay | In this assay, the strains OV19 and OV20 were grown on both glu-U-W agar (left) and raff-U-W (1% galactose) agar in different dilutions of OD600nm (10-0 to 10-3).
As BAX was expressed under the inducible promoter pGAL1 in both strains, we expected normal growth on the glu-U-W plates. On the raff-U-W plates with 1% galactose, we expected the control strain OV20 to show decreased colony size and number compared to the OV19 strain that should be rescued by the BI-1 plasmid. However, as seen on figure 2, no significant growth was seen for either strain in the presence of galactose. As such, we saw no indication that BI-1 was able to prevent BAX induced apoptosis. While it is possible that the lack of function of BI-1 could be the result of a loss of function during transformation, our data suggests BI-1 is not able to prevent BAX induced apoptosis in our system, and is therefore not suitable for our kill switch.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 954
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 377
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]