Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3147003"
(→I : parts BBa_K3147003 (mRFP1-TEVcs-SSRA) function) |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| − | <partinfo>BBa_K3147003 short</partinfo> | + | <div align="center"><partinfo>BBa_K3147003 short</partinfo></div> |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===I : parts BBa_K3147003 function=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | This construction produces an mRFP1 [[Part:BBa_E1010]][1] fused in C-ter with a ssrA fast degradation tag [2] [[Part:BBa_M0050]]. The TEV cutting site ([[Part:BBa_J18918]]) was added between the mRFP1 and the ssrA tag. This construction was used to test the specificity of KARMA using a VHH targeting GFP. In the presence of TEV the ssrA is cleaved and mRFP1 is not degraded anymore. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<div align="center">[[File:designK3147003.png|650px]]</div> | <div align="center">[[File:designK3147003.png|650px]]</div> | ||
| − | <div align="center"><b>Figure 1</b>: Construct Design: mRFP1 fused to an | + | <div align="center"><b>Figure 1</b>: Construct Design: mRFP1 fused to an ssrA proteolysis tag with a TEV cutting site between the two.</div> |
===II. Proof of function=== | ===II. Proof of function=== | ||
| − | + | This construction was cloned by Gibson Assembly in a pBbB8k-GFP (https://www.addgene.org/35363/ ) backbone under the control of a pBAD promoter. | |
| − | + | ||
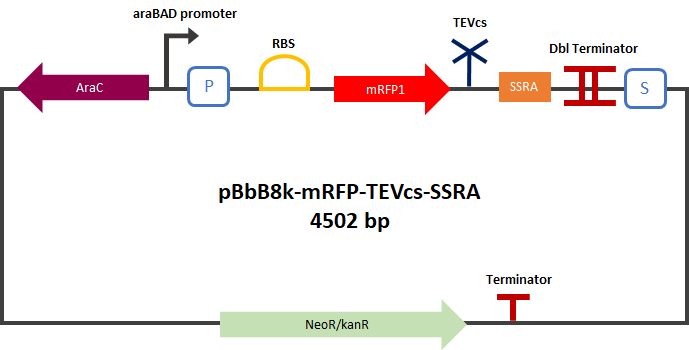
<div align="center">[[File:PlasmideK3147003.png|400px]]</div> | <div align="center">[[File:PlasmideK3147003.png|400px]]</div> | ||
<div align="center"><b>Figure 2</b>: mRFP1-TEVcs-ssrA reporter gene in its pBbB8k-GFP backbone.</div> | <div align="center"><b>Figure 2</b>: mRFP1-TEVcs-ssrA reporter gene in its pBbB8k-GFP backbone.</div> | ||
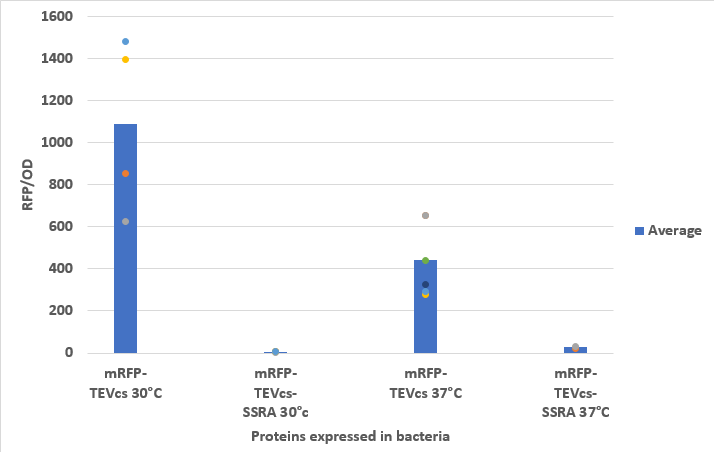
| − | We compared the basal fluorescence of strain E. coli NEB10β transformed with the mRFP1-TEVcs construction to an E. coli NEB10β strain transformed with the mRFP1-TEVcs-ssrA construction. Fluorescence was quantified after induction with | + | We compared the basal fluorescence of strain <i>E. coli</i> NEB10β transformed with the mRFP1-TEVcs construction to an <i>E. coli</i> NEB10β strain transformed with the mRFP1-TEVcs-ssrA construction. Fluorescence was quantified after overnight induction with 1% arabinose on a plate reader. |
| + | |||
| + | Below are the fluorescence measurements of the mRFP1-TEVcs-ssrA and of the mRFP1-TEVcss at 30 and 37°C. | ||
<div align="center">[[File:resultK3147003.png|500px]]</div> | <div align="center">[[File:resultK3147003.png|500px]]</div> | ||
| − | <div align="center"><b>Figure 3</b>: Measurement of the fluorescence at 30°C and 37°C of bacteria expressing mRFP-TEVcs or mRFP-TEVcs-ssrA | + | <div align="center"><b>Figure 3</b>: Measurement of the fluorescence at 30°C and 37°C of bacteria expressing mRFP-TEVcs or mRFP-TEVcs-ssrA</div> |
| + | |||
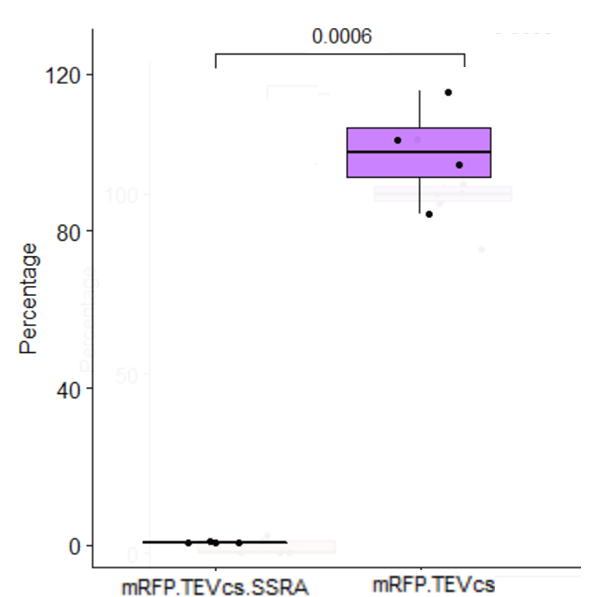
| + | We also did statistical analysis of the fluorescence from both construct with a Welch two sample test by normalizing the data,taking the version without proteolysis tag as 100%. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div align="center">[[File:Stats30CK3147003.png|500px]]</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div align="center"><b>Figure 4</b>: Statistical analysis of the effect of ssrA tag on the mRFP-TEVcs at 30°C</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | At 30°C, the ssrA tag reduce by 99% the fluorescence obtained by mRFP-TEVcs. The p-value obtained is 0.0006. | ||
| + | |||
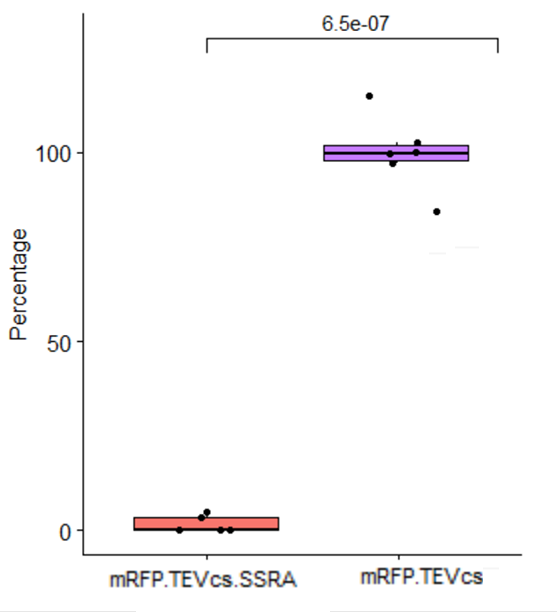
| + | <div align="center">[[File:Stats37CK3147003.png|500px]]</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div align="center"><b>Figure 5</b>: Statistical analysis of the effect of ssrA tag on the mRFP-TEVcs at 37°C</div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | At 37°C, the ssrA tag reduce by 96% the fluorescence obtained by mRFP-TEVcs. The p-value calculated is 6.5e-07. | ||
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
Latest revision as of 07:32, 21 October 2019
I : parts BBa_K3147003 function
This construction produces an mRFP1 Part:BBa_E1010[1] fused in C-ter with a ssrA fast degradation tag [2] Part:BBa_M0050. The TEV cutting site (Part:BBa_J18918) was added between the mRFP1 and the ssrA tag. This construction was used to test the specificity of KARMA using a VHH targeting GFP. In the presence of TEV the ssrA is cleaved and mRFP1 is not degraded anymore.
II. Proof of function
This construction was cloned by Gibson Assembly in a pBbB8k-GFP (https://www.addgene.org/35363/ ) backbone under the control of a pBAD promoter.
We compared the basal fluorescence of strain E. coli NEB10β transformed with the mRFP1-TEVcs construction to an E. coli NEB10β strain transformed with the mRFP1-TEVcs-ssrA construction. Fluorescence was quantified after overnight induction with 1% arabinose on a plate reader.
Below are the fluorescence measurements of the mRFP1-TEVcs-ssrA and of the mRFP1-TEVcss at 30 and 37°C.
We also did statistical analysis of the fluorescence from both construct with a Welch two sample test by normalizing the data,taking the version without proteolysis tag as 100%.
At 30°C, the ssrA tag reduce by 99% the fluorescence obtained by mRFP-TEVcs. The p-value obtained is 0.0006.
At 37°C, the ssrA tag reduce by 96% the fluorescence obtained by mRFP-TEVcs. The p-value calculated is 6.5e-07.
Reference
[1] Levraud, Jean-Pierre et al. 2007. « Identification of the Zebrafish IFN Receptor: Implications for the Origin of the Vertebrate IFN System ». The Journal of Immunology 178(7): 4385‑94. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.178.7.4385
[2] Sunohara, T., Abo, T., Inada, T., & Aiba, H. (2002). The C-terminal amino acid sequence of nascent peptide is a major determinant of SsrA tagging at all three stop codons. RNA (New York, N.Y.), 8(11), 1416–1427. doi:10.1017/s1355838202020198
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 691
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]