Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1921021"
(→Characterization) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
By expressing the fusion protein , PETase ,which can degrade macromolecular polymers into monomerswas, expressed on the surface of Pichia pastoris,. And the whole cell catalyst for the degradation of PET was obtained. Have the PETase fixed on the cell wall, on the one hand can improve the stability of PETase, on the other hand, it is easy to control the degradation reaction of PET and PETase recycling. <br> | By expressing the fusion protein , PETase ,which can degrade macromolecular polymers into monomerswas, expressed on the surface of Pichia pastoris,. And the whole cell catalyst for the degradation of PET was obtained. Have the PETase fixed on the cell wall, on the one hand can improve the stability of PETase, on the other hand, it is easy to control the degradation reaction of PET and PETase recycling. <br> | ||
We co-displayed PETase-linker.b-GCW51 along with inJanus-linker.b-GCW61, in attempt to make our whole cell biocatalyst more efficient and tolerant. Previous studies on co-displaying hydrophobin with lipases have already shown positive results on the promotion of efficiency. It is confirmed that most lipases are more active when entering a more hydrophobic environment. Since PETase is also classified as lipase, we decided to build this construction and make this attempt.<br> | We co-displayed PETase-linker.b-GCW51 along with inJanus-linker.b-GCW61, in attempt to make our whole cell biocatalyst more efficient and tolerant. Previous studies on co-displaying hydrophobin with lipases have already shown positive results on the promotion of efficiency. It is confirmed that most lipases are more active when entering a more hydrophobic environment. Since PETase is also classified as lipase, we decided to build this construction and make this attempt.<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Characterization=== | ||
| + | '''Group:''' TJUSLS_China 2019<br> | ||
| + | '''Author:''' Dongxu Li<br> | ||
| + | '''Summary:''' In 2019, our team TJUSLS_China conducted further experiments in Purified PETase or induced display cells. | ||
| + | Purified PETase or induced display cells were incubated with 0.9mM BHET in buffer containing 50 mM glycine-NaOH (pH 9.0) for 18 h at 30 ℃ and the product was analyzed by HPLC. According to the results, we found that, compared with purified protein, the hydrolysis efficiency of surface display cells to substrate BHET was greatly improved, indicating the effectiveness and feasibility of displaying cell functions.<br> | ||
| + | <p style="text-align: center;"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:File.jpeg|500px|]]<br> | ||
| + | '''Figure 1.''' HPLC analysis after BHET hydrolysis by purified PETase or induced display cells. The peak appeared around 42.8 min and 44.6min are the product MHET and BHET respectively.<br> | ||
| + | </p> | ||
===Biology=== | ===Biology=== | ||
| Line 70: | Line 83: | ||
https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/igem.org/e/ea/ProofTJU21.jpg<br> | https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/igem.org/e/ea/ProofTJU21.jpg<br> | ||
'''Figure 6.''' The activity of ppic9-PETase-GCW51 & ppiczaA-inJanus-GCW61 co-display transformant and ppic9-PETase-GCW51 & ppiczaA-sJanus-GCW61 co-display transformant in best condition.<br> | '''Figure 6.''' The activity of ppic9-PETase-GCW51 & ppiczaA-inJanus-GCW61 co-display transformant and ppic9-PETase-GCW51 & ppiczaA-sJanus-GCW61 co-display transformant in best condition.<br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</p> | </p> | ||
Latest revision as of 15:26, 16 October 2019
PETase+linker.b+GCW51
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 1068
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Usage
As a cell wall protein, GCW51 is often used as an anchor protein in Pichia pastoris to display some protein on the surface. By fusing GCW51 with the PETase, it can be displayed on the outer of the yeast cell wall.
By expressing the fusion protein , PETase ,which can degrade macromolecular polymers into monomerswas, expressed on the surface of Pichia pastoris,. And the whole cell catalyst for the degradation of PET was obtained. Have the PETase fixed on the cell wall, on the one hand can improve the stability of PETase, on the other hand, it is easy to control the degradation reaction of PET and PETase recycling.
We co-displayed PETase-linker.b-GCW51 along with inJanus-linker.b-GCW61, in attempt to make our whole cell biocatalyst more efficient and tolerant. Previous studies on co-displaying hydrophobin with lipases have already shown positive results on the promotion of efficiency. It is confirmed that most lipases are more active when entering a more hydrophobic environment. Since PETase is also classified as lipase, we decided to build this construction and make this attempt.
Characterization
Group: TJUSLS_China 2019
Author: Dongxu Li
Summary: In 2019, our team TJUSLS_China conducted further experiments in Purified PETase or induced display cells.
Purified PETase or induced display cells were incubated with 0.9mM BHET in buffer containing 50 mM glycine-NaOH (pH 9.0) for 18 h at 30 ℃ and the product was analyzed by HPLC. According to the results, we found that, compared with purified protein, the hydrolysis efficiency of surface display cells to substrate BHET was greatly improved, indicating the effectiveness and feasibility of displaying cell functions.
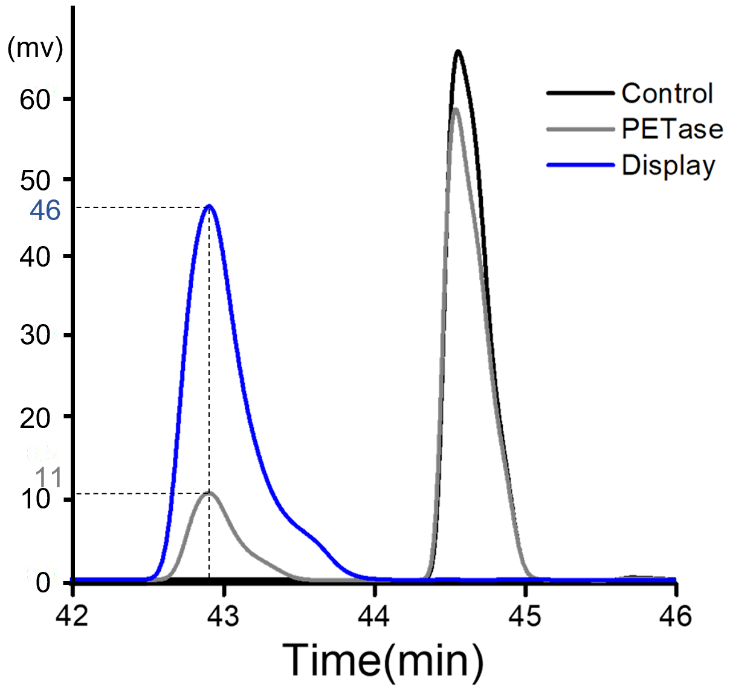
Figure 1. HPLC analysis after BHET hydrolysis by purified PETase or induced display cells. The peak appeared around 42.8 min and 44.6min are the product MHET and BHET respectively.
Biology
GCW51 was gained from Pichia pastoris GS115.As one of the Glycosylphosphatidylinositoled cell wall proteins (GPI-CWPs), GCW51 is located in the outer layer of yeast cell wall, its C terminal is oligo mannose glycosylated. Subsequently, the mannose chain of GCW21 connect with the β-1,6 dextranomer of inner cell wall layer by forming covalent connection, thus, the GCW21 is fixed in the outer layer of the cell wall protein.
PETase was found from a kind of microorganism living on PET as the main carbon source. It can degrade macromolecular polymers into monomers. Surface display can reveal the protein whose gene code is coalescing the gene code of target protein or polypeptide with the counterpart of ankyrin on the surface of the host cell wall to harvest the whole cell catalyst.
Reference
[1] Kinoshita T, Fujiata M. Overview of GPI biosynthesis [J]. The enzymes. 2009;26:1-30.
[2] Orlean P, Mennon AK. Thematic review series: lipid posttranslational modifications. GPI anchoring of protein in yeast and mammalian cells, or: how we learned to stop worrying and love glycophospholipids [J]. Journal of lipid research.2007;48(5):993-1011.
[3] Mouyna I, Fontaine T, Vai M, et al. Glycosylphosphatidy linositol-anchored glucanosyltransferases play an active role in the biosynthesis of the fungal cell wall[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry.2000;275(20):14882-14889.
[4]Shosuke Yoshida, Kazumi Hiraga, Toshihiko Takehana, Ikuo Taniguchi,Hironao Yamaji, Yasuhito Maeda, Kiyotsuna Toyohara,Kenji Miyamoto, Yoshiharu Kimura, Kohei Oda. A bacterium that degrades and assimilates poly(ethylene terephthalate) [J].science,2016(351):1196-1199.
[5] DongHeng Guo, YanShan Xu, YaJun Kang et al (2016). Synthesis of octyl-β- d -glucopyranoside catalyzed by Thai rosewood β-glucosidase - displaying Pichia pastoris, in an aqueous/organic two-phase system[J]. Enzyme & Microbial Technology, 2016, 85:90–97.
Surface display in Pichia Pastoris:


Figure 1. The activity of P. pastoris PETase-GCW51. a&b used the first group of yeast; c&d used the third of yeast; a&c:the activity in different yeasts'concentration under the best hour; b&d: the activity in different hours under the best concentration.
Co-display in Pichia Pastoris:

Figure 2. The activity of the first group of ppic9-PETase-GCW51 & ppiczaA-sJanus-GCW61 co-display transformants in different hours and amount of yeast.

Figure 3. The activity of the second group of ppic9-PETase-GCW51 & ppiczaA-sJanus-GCW61 co-display transformants in different hours and amount of yeast.

Figure 4. The activity of the first group of ppic9-PETase-GCW51 & ppiczaA-inJanus-GCW61 co-display transformants in different hours and amount of yeast.

Figure 5. The activity of the second group of ppic9-PETase-GCW51 & ppiczaA-inJanus-GCW61 co-display transformants in different hours and amount of yeast.

Figure 6. The activity of ppic9-PETase-GCW51 & ppiczaA-inJanus-GCW61 co-display transformant and ppic9-PETase-GCW51 & ppiczaA-sJanus-GCW61 co-display transformant in best condition.
