Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3168004"
CMichielsen (Talk | contribs) |
CMichielsen (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
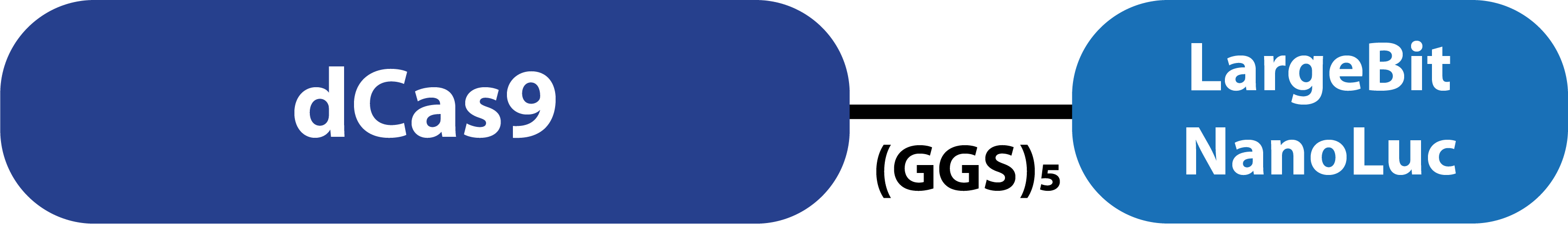
This composite part is made up of two basic parts. The first basic part (CODE) codes for a catalytically dead CRISPR associated protein 9 (dCas9). This protein binds to a specific target on double stranded DNA. This specific target is determined by the guide RNA, which makes this protein very modular. The second basic part, which is fused to dCas9, consist of a (GGS)5 linker and the large bit of NanoLuc. When the large bit of Split-NanoLuc forms a complex with the small bit in the presence of the substrate (Furimazine), blue light is emitted. dCas9-LargeBit itself is slightly bioluminescent when the substrate is added. However, the intensity is more bright when a complex is formed with the small bit. Thus this composite part is part of a Split-NanoLuc detection system, which targets a specific sequence on dsDNA and sends out a bioluminescent signal (figure 1). | This composite part is made up of two basic parts. The first basic part (CODE) codes for a catalytically dead CRISPR associated protein 9 (dCas9). This protein binds to a specific target on double stranded DNA. This specific target is determined by the guide RNA, which makes this protein very modular. The second basic part, which is fused to dCas9, consist of a (GGS)5 linker and the large bit of NanoLuc. When the large bit of Split-NanoLuc forms a complex with the small bit in the presence of the substrate (Furimazine), blue light is emitted. dCas9-LargeBit itself is slightly bioluminescent when the substrate is added. However, the intensity is more bright when a complex is formed with the small bit. Thus this composite part is part of a Split-NanoLuc detection system, which targets a specific sequence on dsDNA and sends out a bioluminescent signal (figure 1). | ||
| − | [[File:T--TU_Eindhoven--dCas9-LargeBit.png| | + | [[File:T--TU_Eindhoven--dCas9-LargeBit.png|400px|]] |
| − | ''Figure 1. Schematic representation of dCas9- | + | ''Figure 1. Schematic representation of dCas9-LargeBitNanoLuc.'' |
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
[[File:T--TU_Eindhoven--dCas9-SplitNL.png|800px|]] | [[File:T--TU_Eindhoven--dCas9-SplitNL.png|800px|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Figure 2. Schematic represenation of dCas9-Split-NanoLuc system.'' | ||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
Revision as of 13:43, 12 September 2019
dCas9-LargeBitNanoLuc
This composite part is made up of two basic parts. The first basic part (CODE) codes for a catalytically dead CRISPR associated protein 9 (dCas9). This protein binds to a specific target on double stranded DNA. This specific target is determined by the guide RNA, which makes this protein very modular. The second basic part, which is fused to dCas9, consist of a (GGS)5 linker and the large bit of NanoLuc. When the large bit of Split-NanoLuc forms a complex with the small bit in the presence of the substrate (Furimazine), blue light is emitted. dCas9-LargeBit itself is slightly bioluminescent when the substrate is added. However, the intensity is more bright when a complex is formed with the small bit. Thus this composite part is part of a Split-NanoLuc detection system, which targets a specific sequence on dsDNA and sends out a bioluminescent signal (figure 1).
Figure 1. Schematic representation of dCas9-LargeBitNanoLuc.
Usage and Biology
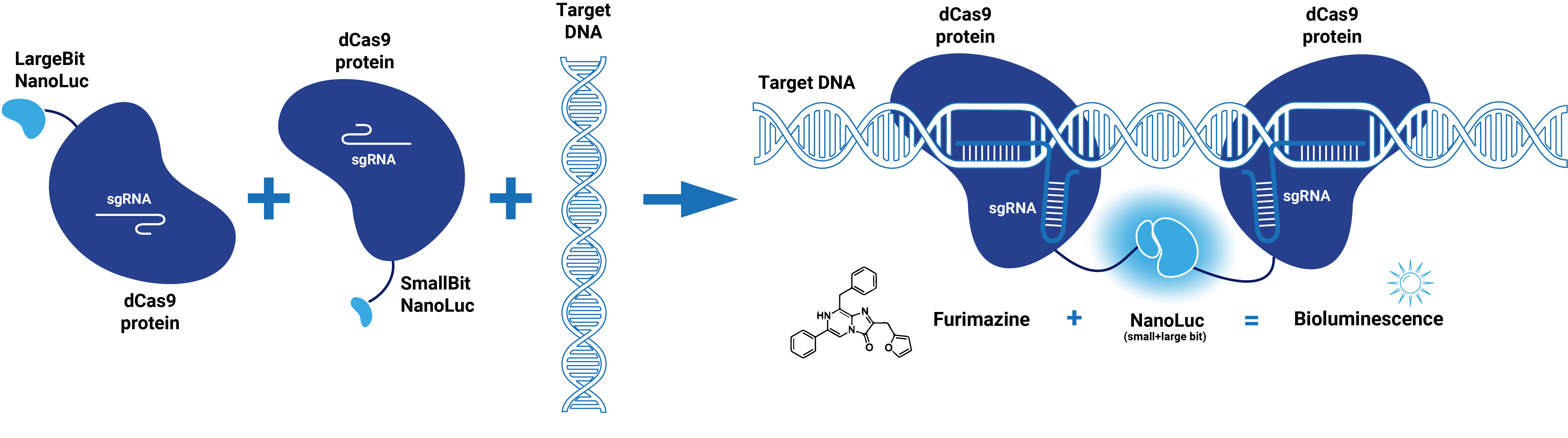
dCas9 in combination with guide RNA forms a dsDNA recognition complex. A stronger bioluminescent signal is created when dCas9-LargBitNanoLuc and dCas9-SmallBitNanoLuc bind in close proximity.
Figure 2. Schematic represenation of dCas9-Split-NanoLuc system.
References
Dixon, A. S., Schwinn, M. K., Hall, M. P., Zimmerman, K., Otto, P., Lubben, T. H., ... & Wood, M. G. (2015). NanoLuc complementation reporter optimized for accurate measurement of protein interactions in cells. ACS chemical biology, 11(2), 400-408.
Zhang, Y., Qian, L., Wei, W., Wang, Y., Wang, B., Lin, P., ... & Cheng, S. (2016). Paired design of dCas9 as a systematic platform for the detection of featured nucleic acid sequences in pathogenic strains. ACS synthetic biology, 6(2), 211-216.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 1099
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 3378
Illegal BamHI site found at 4630 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]