Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2314831"
A357034555 (Talk | contribs) |
A357034555 (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
"Most of native yeast promoters can stretch hundreds of base pairs. Specifically, a single-gene circuit carrying a 1.5kb gene requires an additional 1kb of regulatory DNA (between the promoter and terminator) for appropriate expression, thus increasing the DNA cargo load by over 60%. However, this problem hasn’t been focused widely. With the development of synthetic biology, creating short but strong promoter is more important. | "Most of native yeast promoters can stretch hundreds of base pairs. Specifically, a single-gene circuit carrying a 1.5kb gene requires an additional 1kb of regulatory DNA (between the promoter and terminator) for appropriate expression, thus increasing the DNA cargo load by over 60%. However, this problem hasn’t been focused widely. With the development of synthetic biology, creating short but strong promoter is more important. | ||
| − | Pmini is a short but strong constitutive promoter in yeast. It consists three main elements. Core element determines the shortest length required for transcription and serves as a platform for hybrid promoter technology. This core element scaffold was built on distinct, essential sequences for promoter function—a TATA box with consensus sequence of | + | Pmini is a short but strong constitutive promoter in yeast. It consists three main elements. Core element determines the shortest length required for transcription and serves as a platform for hybrid promoter technology. This core element scaffold was built on distinct, essential sequences for promoter function—a TATA box with consensus sequence of TATAWAWR followed by a transcription start site (TSS) with consensus sequence of A(A<sub>rich</sub>)<sub>5</sub>NYAWNN(A<sub>rich</sub>)<sub>6</sub>. UAS element contains transcription factor-binding sites (TFBS) and can aid in RNAP stabilization to enhanced transcription rates. The AT-rich spacer containing 30 nucleotides has a better performance.[1] |
We used Pmini promoter with synthetic terminator Tmini(BBa_K2314608) to construct a minimal genetic regulatory element “MINI-GRE“ combination. We also selected a commonly used promoter CYC1 and terminator CYC1, and contrusted four circuits to measure the performance of MINI-GRE combination. The fluorescent protein yECitrine (BBa_K2314024)was selected as the reporter protein. | We used Pmini promoter with synthetic terminator Tmini(BBa_K2314608) to construct a minimal genetic regulatory element “MINI-GRE“ combination. We also selected a commonly used promoter CYC1 and terminator CYC1, and contrusted four circuits to measure the performance of MINI-GRE combination. The fluorescent protein yECitrine (BBa_K2314024)was selected as the reporter protein. | ||
More details can be viewed in our project page. | More details can be viewed in our project page. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| − | + | The structure of MINI promoter: | |
https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/parts/1/18/T--OUC-China--MINIP.jpg | https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/parts/1/18/T--OUC-China--MINIP.jpg | ||
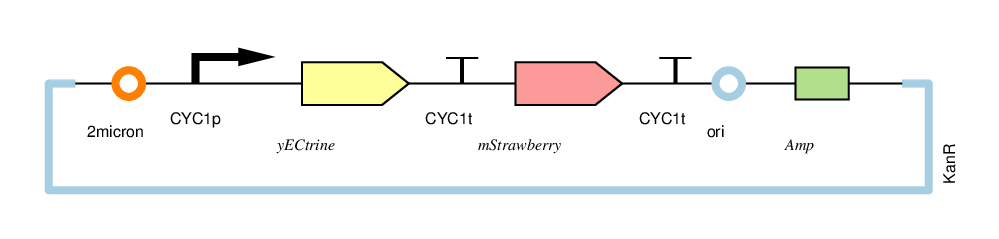
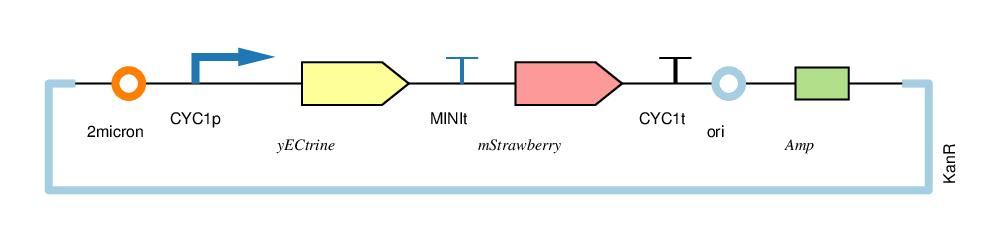
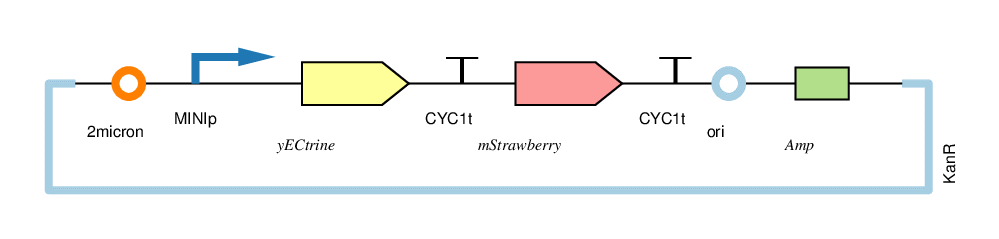
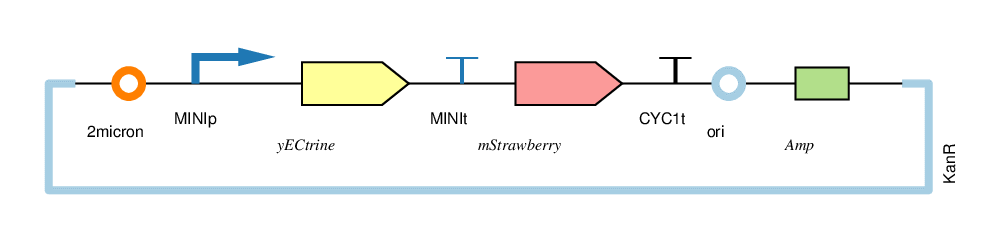
| − | + | The four circuits used in our project: | |
| − | + | [[Image:T--OUC-China--MINI-GRE_CC_PLASMID.png|800px|thumb|center]] | |
| − | + | [[Image:T--OUC-China--MINI-GRE_CM_PLASMID.png|800px|thumb|center]] | |
| − | + | [[Image:T--OUC-China--MINI-GRE_MC_PLASMID.png|800px|thumb|center]] | |
| − | + | [[Image:T--OUC-China--MINI-GRE_MM_PLASMID.png|800px|thumb|center]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| Line 35: | Line 32: | ||
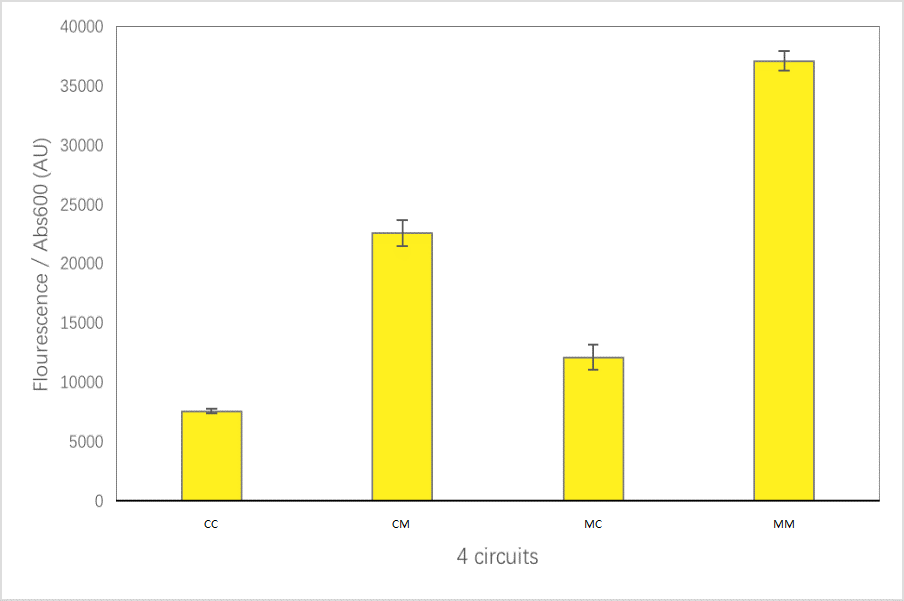
| − | The expression level of | + | The expression level of MINI-GRE: |
| − | + | ||
| + | [[Image:Abs600_of_strains_with_different_promoter-terminator_pairs.png|800px|thumb|center]] | ||
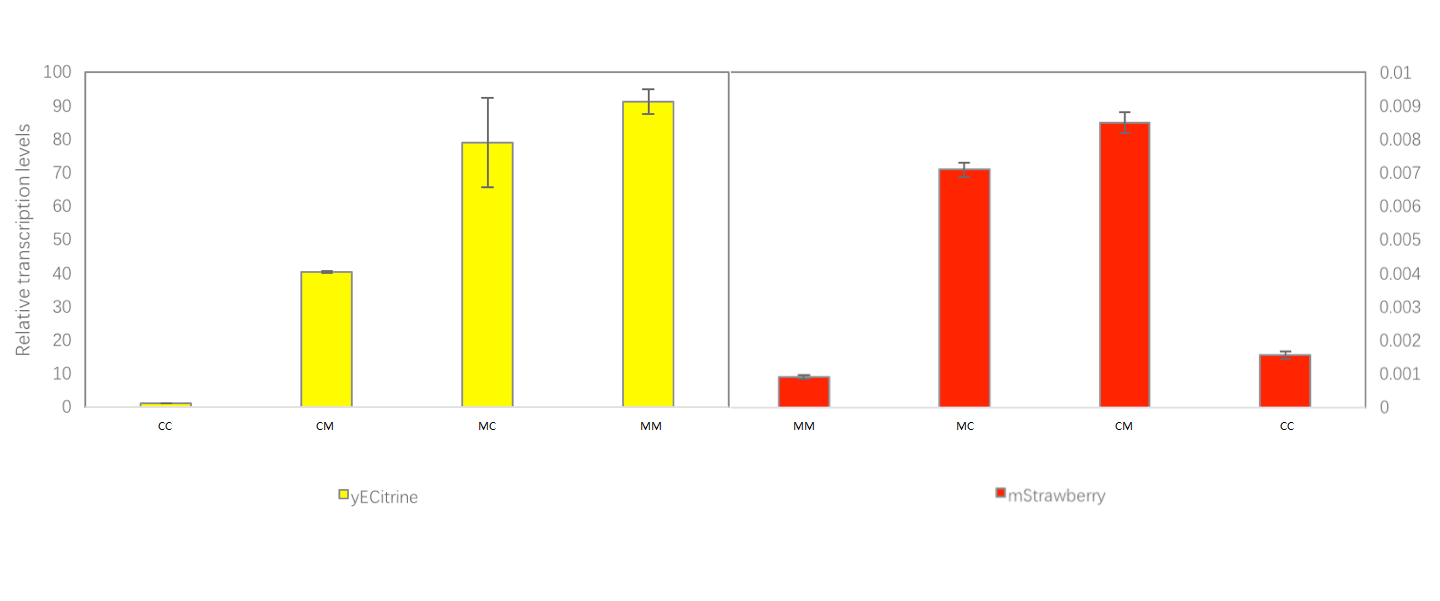
The RT-PCR result of mini system: | The RT-PCR result of mini system: | ||
| − | + | [[Image:T--OUC-China--MINI-GRE_qPCR_.png|800px|thumb|center]] | |
| + | Here, the transcript level of mStrawberry is very low, which means the transcription read through of MINI terminator can be overlooked. You can learn more from our project. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 19:22, 1 November 2017
Pmini is a very short constitutive promoter in yeast, which is only 116bp, but with a good strength.
"Most of native yeast promoters can stretch hundreds of base pairs. Specifically, a single-gene circuit carrying a 1.5kb gene requires an additional 1kb of regulatory DNA (between the promoter and terminator) for appropriate expression, thus increasing the DNA cargo load by over 60%. However, this problem hasn’t been focused widely. With the development of synthetic biology, creating short but strong promoter is more important. Pmini is a short but strong constitutive promoter in yeast. It consists three main elements. Core element determines the shortest length required for transcription and serves as a platform for hybrid promoter technology. This core element scaffold was built on distinct, essential sequences for promoter function—a TATA box with consensus sequence of TATAWAWR followed by a transcription start site (TSS) with consensus sequence of A(Arich)5NYAWNN(Arich)6. UAS element contains transcription factor-binding sites (TFBS) and can aid in RNAP stabilization to enhanced transcription rates. The AT-rich spacer containing 30 nucleotides has a better performance.[1] We used Pmini promoter with synthetic terminator Tmini(BBa_K2314608) to construct a minimal genetic regulatory element “MINI-GRE“ combination. We also selected a commonly used promoter CYC1 and terminator CYC1, and contrusted four circuits to measure the performance of MINI-GRE combination. The fluorescent protein yECitrine (BBa_K2314024)was selected as the reporter protein. More details can be viewed in our project page.
[1]Redden H,Alper HS,The development and characterization of synthetic minimal yeast promoters[J],Nature Communication,2015,6 : 7810 "
In short,Pmini is a very short constitutive promoter in yeast, which is only 116bp in length, but with strong expression.
The structure of MINI promoter:

The four circuits used in our project:
For convenience, we named the“CYC1p-yECitrine-CYC1t-mStrawberry-CYC1t”as“CC”,“CYC1p-yECitrine-MINIt-mStrawberry-CYC1t”as“CM”,“MINIp-yECitrine-CYC1t-mStrawberry-CYC1t”as“MC”, and“MINIp-yECitrine-MINIt-mStrawberry-CYC1t” as “MM”,hereafter.
The expression level of MINI-GRE:
The RT-PCR result of mini system:
Here, the transcript level of mStrawberry is very low, which means the transcription read through of MINI terminator can be overlooked. You can learn more from our project.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]