Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1033932"
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18648549] Alieva, Naila O., et al. "Diversity and evolution of coral fluorescent proteins." PLoS One 3.7 (2008): e2680. | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18648549] Alieva, Naila O., et al. "Diversity and evolution of coral fluorescent proteins." PLoS One 3.7 (2008): e2680. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | =====Contribution===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Group: Team Tsinghua 2017 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Author: Boyang Gao | ||
| + | |||
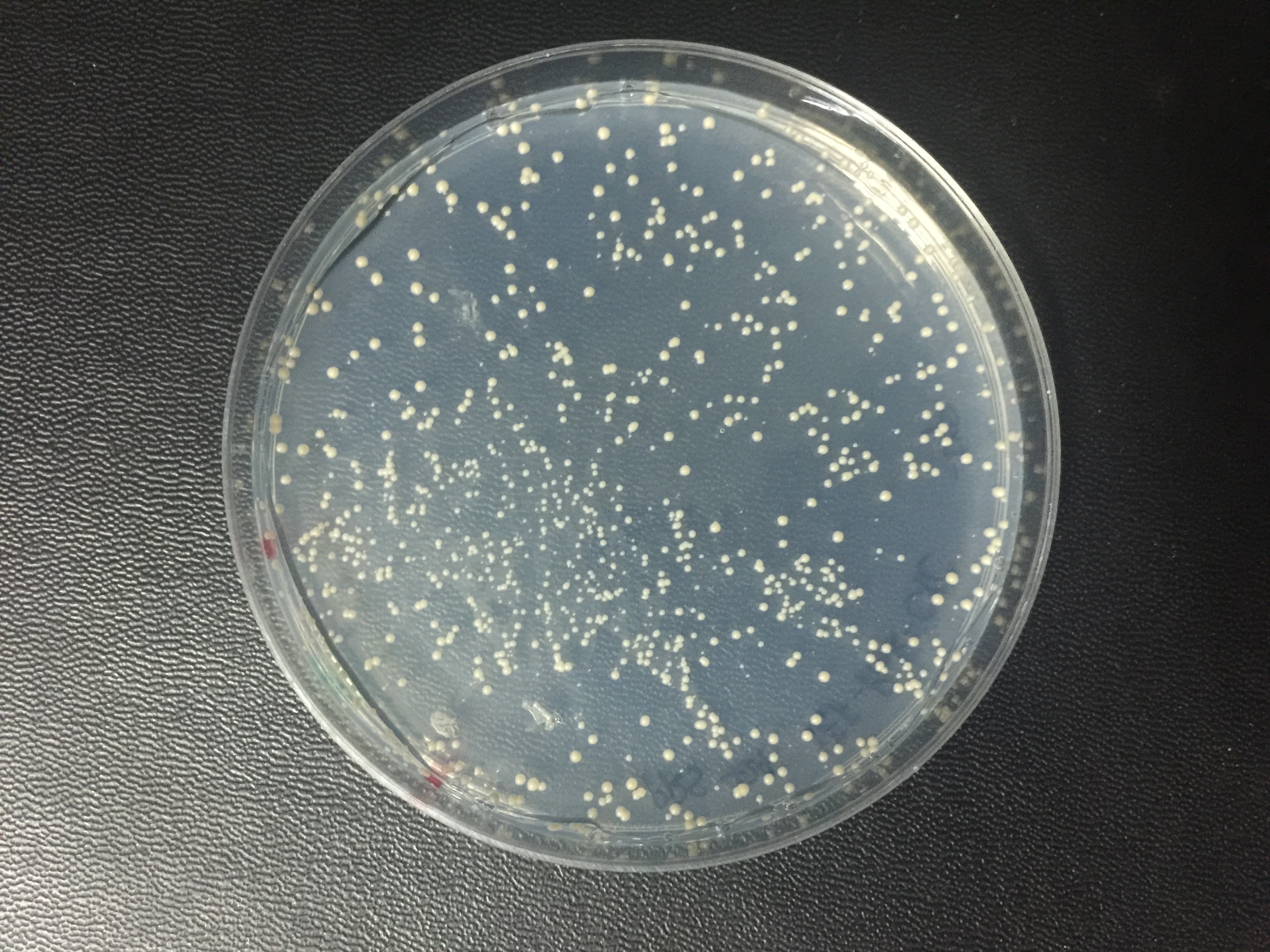
| + | Summary: We have improved the characterization of this part by constructing it into a yeast expression vector and expressing it in a new chassis organism, S. cerevisiae. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:SpisPink expression in yeast cells.jpeg|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | =====The expression of spisPink protein in yeast cells===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Yeast cells were transformed with plasmids (backbone: pRS424; Promoter: TEF2; Terminator: CYC1) constitutively expressing spisPink protein. auxotrophic medium was used to ensure the successful transformation of plasmids, and this picture was taken 72 h after transformation. As shown in the picture, the yeast colonies did not turn pink apparently. Thus spisPink might not work as well in yeast cells as in bacteria. | ||
Revision as of 18:07, 1 November 2017
spisPink, pink chromoprotein
This chromoprotein from the coral Stylophora pistillata, spisPink (also known as spisCP), naturally exhibits strong color when expressed. The protein has an absorption maximum at 560 nm giving it a pink color visible to the naked eye. The strong color is readily observed in both LB or on agar plates after less than 24 hours of incubation. The protein spisPink has significant sequence homologies with proteins in the GFP family.
Important: This part is not available in the registry yet, however, the same part is available from the registry with the standard RBS B0034: BBa_K1033925.
Usage and Biology
This part is useful as a reporter.
spisPink does not exist as CDS only but only as RBS-spisPink (BBa_K1033925), J23110-RBS-spisPink (BBa_K1033923) and J23106-RBS-spisPink (BBa_K1033924)
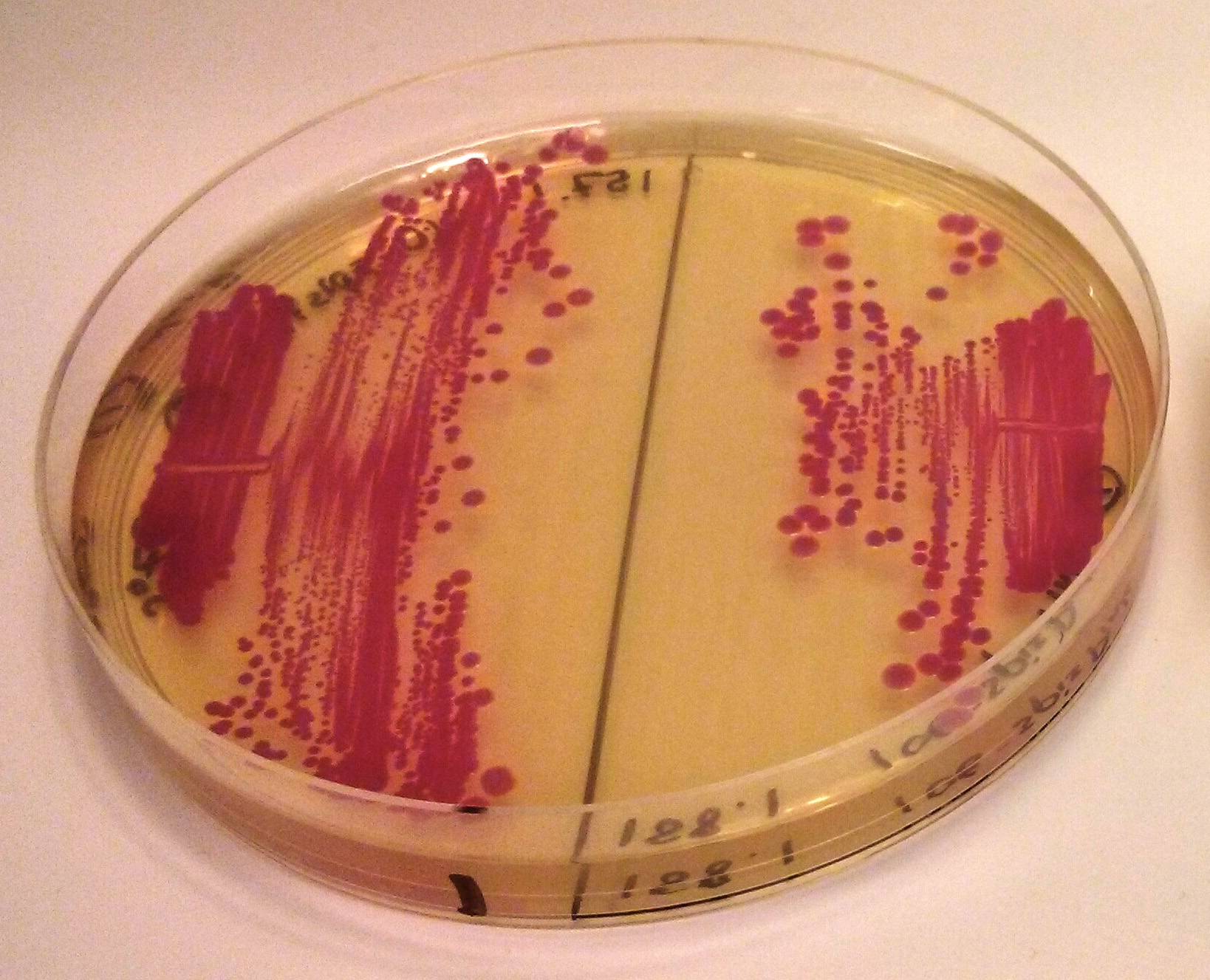
iGEM2013 Uppsala: The images above show E coli constitutively expressing spisPink BBa_K1033925 from the high copy plasmid pSB1C3 from the promoters J23110 (left) and J23106 (right).
Source
Stylophora pistillata. The protein was first extracted and characterized by Alieva et. al. under the name spisCP (GenBank: ABB17971.1). This version is codon optimized for E coli by Genscript.
References
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18648549] Alieva, Naila O., et al. "Diversity and evolution of coral fluorescent proteins." PLoS One 3.7 (2008): e2680.
Contribution
Group: Team Tsinghua 2017
Author: Boyang Gao
Summary: We have improved the characterization of this part by constructing it into a yeast expression vector and expressing it in a new chassis organism, S. cerevisiae.
The expression of spisPink protein in yeast cells
Yeast cells were transformed with plasmids (backbone: pRS424; Promoter: TEF2; Terminator: CYC1) constitutively expressing spisPink protein. auxotrophic medium was used to ensure the successful transformation of plasmids, and this picture was taken 72 h after transformation. As shown in the picture, the yeast colonies did not turn pink apparently. Thus spisPink might not work as well in yeast cells as in bacteria.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]