Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2448024"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
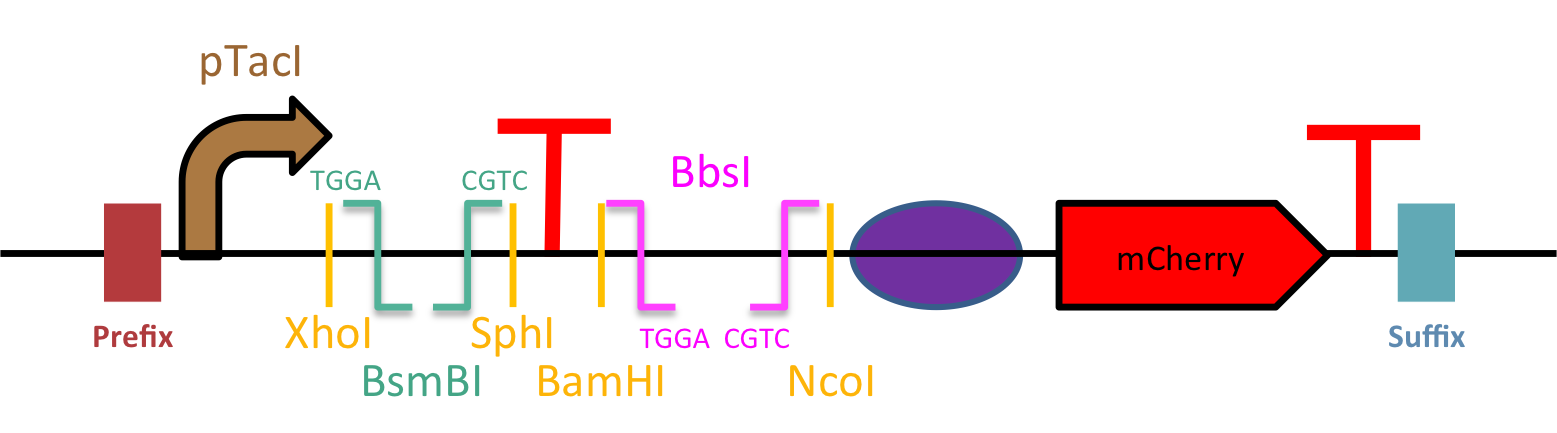
| − | The this short version of UBC have the most important features of the full version ( [[Part:BBa_K2448023|BBa_K2448023]]) that allow rapid engineering of your biosensor (Figure 1): | + | The this short version of UBC have the most important features of the full version ([[Part:BBa_K2448023|BBa_K2448023]]) that allow rapid engineering of your biosensor (Figure 1): |
*Standardized Fusion sites for Golden Gate Assembly: The UBC has been design to facilitate the DNA insertion hence improving speed and ease of construction. You will only need transcription factors and promoters flanked by BsmBI or BbsI, respectively, with appropriate cutting sites for these type IIS restriction enzymes (5’-TGGA and GCAG-3’). | *Standardized Fusion sites for Golden Gate Assembly: The UBC has been design to facilitate the DNA insertion hence improving speed and ease of construction. You will only need transcription factors and promoters flanked by BsmBI or BbsI, respectively, with appropriate cutting sites for these type IIS restriction enzymes (5’-TGGA and GCAG-3’). | ||
Latest revision as of 09:49, 1 November 2017
Universal Biosensing Chassis (UBC) short version
This part is the short version of Universal Biosensing Chassis (UBC, BBa_K2448023), a highly modular plateforme for rapid biosensor engineering.
Usage and Biology
The this short version of UBC have the most important features of the full version (BBa_K2448023) that allow rapid engineering of your biosensor (Figure 1):
- Standardized Fusion sites for Golden Gate Assembly: The UBC has been design to facilitate the DNA insertion hence improving speed and ease of construction. You will only need transcription factors and promoters flanked by BsmBI or BbsI, respectively, with appropriate cutting sites for these type IIS restriction enzymes (5’-TGGA and GCAG-3’).
- Many restriction sites: If Golden Gate assembly isn’t convenient for you, we have included various restriction sites to allow the insertion of promoters and transcription factors (with the RBS) using traditional digestion-ligation protocol.
- An inducible promoter to control the transcription factor expression: pTacI (BBa_K864400). This well-known promoter is IPTG inducible and remains very strong. To better regulate its expression, and consequently the production of the transcription factor, it could be worthwhile to use our pSB1C3 LacIq (BBa_K2448038) as vector.
- An efficient reporter: mCherry (BBa_K2448004). This fluorescent monomeric protein widely used in biotechnology is derived from the RFP. Its rapid maturation, low brightness as well as its improved photostability and resistance to bleaching makes it the perfect reporter for biosensors for precise measurements. Moreover, unlike GFP like proteins, there is no cell auto-fluorescence effect at its excitation wavelength.
- Strong RBSs (BBa_BBa_B0034) and efficient synthetic terminators (BBa_B0015, BBa_K2448018).
Figure 1 : Schematic design of the short version of UBC.
Sequence and Features
Assembly Compatibility:
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 248
Illegal XhoI site found at 62 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 884
Illegal AgeI site found at 996 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]