Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1933001"
(→Characterization) |
(→Western blotting) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
===Western blotting=== | ===Western blotting=== | ||
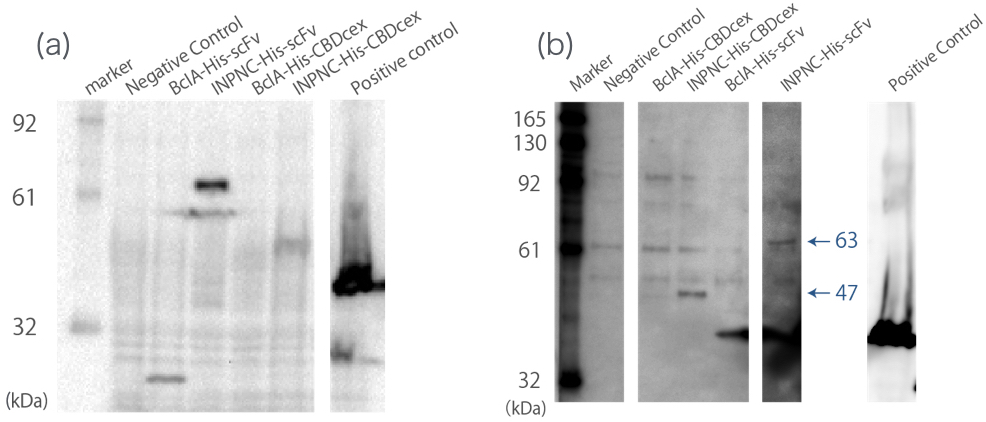
We added His-tag to <big>[https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K811005 BBa_K811005]</big>. This addition introduces two new functions to the fusion protein: | We added His-tag to <big>[https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K811005 BBa_K811005]</big>. This addition introduces two new functions to the fusion protein: | ||
| − | <br>First, we can use anti-His tag antibody to detect their surface expression regardless of passenger protein placed downstream. We confirmed this with detections of the INPNC-His-(passenger protein) by Western blotting using anti-His tag antibody. (Fig.1(a)) | + | <br><br>First, we can use anti-His tag antibody to detect their surface expression regardless of passenger protein placed downstream. We confirmed this with detections of the INPNC-His-(passenger protein) by Western blotting using anti-His tag antibody. (Fig.1(a)) |
| − | <br>Second, INPNC-His-(passenger protein) can be purified using His tag’s affinity to nickel columns even in denaturing conditions to recollect it from membrane fractions of E.coli. This would allow fusion protein detection even if the protein’s expression levels are low, further strengthening the first function. We tested this function with Western | + | <br><br>Second, INPNC-His-(passenger protein) can be purified using His tag’s affinity to nickel columns even in denaturing conditions to recollect it from membrane fractions of E.coli. This would allow fusion protein detection even if the protein’s expression levels are low, further strengthening the first function. We tested this function with Western |
blotting. Sample was prepared by obtaining the membrane fraction from the E. coli lysate by ultracentrifugation, and solubilized them using 7M guanidine-HCl, then purification of the target protein using Nickel Sepharose. (Fig.1(b)) | blotting. Sample was prepared by obtaining the membrane fraction from the E. coli lysate by ultracentrifugation, and solubilized them using 7M guanidine-HCl, then purification of the target protein using Nickel Sepharose. (Fig.1(b)) | ||
Revision as of 06:31, 16 October 2016
INPNC fused to 6xHis tag
INPNC codes for N- and C- terminal domain of Ice-Nucleation Protein (INP) from Pseudomonas syringae , connected by a 6xHis tag to be easily identified by Western blotting[1]. This is used as an anchoring motif for the cell surface display of passengers. This domain does not have signal peptide for anchoring on the cell surface[2]. Surface displayed passengers retain enzyme activity even when it is linked to INPNC with 6xHis tag.
For more information, please visit [http://2016.igem.org/Team:Kyoto our wiki]
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 952
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 72
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 405
Illegal AgeI site found at 823 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Usage and Biology
We used this part for construction of BBa_K1933100, BBa_K1933101, BBa_K1933200
Characterization
We improved BBa_K811005 from Penn 2012!!
Western blotting
We added His-tag to BBa_K811005. This addition introduces two new functions to the fusion protein:
First, we can use anti-His tag antibody to detect their surface expression regardless of passenger protein placed downstream. We confirmed this with detections of the INPNC-His-(passenger protein) by Western blotting using anti-His tag antibody. (Fig.1(a))
Second, INPNC-His-(passenger protein) can be purified using His tag’s affinity to nickel columns even in denaturing conditions to recollect it from membrane fractions of E.coli. This would allow fusion protein detection even if the protein’s expression levels are low, further strengthening the first function. We tested this function with Western
blotting. Sample was prepared by obtaining the membrane fraction from the E. coli lysate by ultracentrifugation, and solubilized them using 7M guanidine-HCl, then purification of the target protein using Nickel Sepharose. (Fig.1(b))
These two results confirms the enhanced functions of INPNC parts (BBa_K811005) existing in the iGEM Regisrtry.
Please see BBa_K1933100, BBa_K1933101, and BBa_K1933200 for full characterization .
Contribution
Reference
[1]Yim, Sung-Kun, et al. "Surface display of heme-and diflavin-containing cytochrome P450 BM3 in Escherichia coli: a whole cell biocatalyst for oxidation." Journal of microbiology and biotechnology, 20.4, (2010): 712-717.
[2]Park, Tae Jung, et al. "Surface display of recombinant proteins on Escherichia coli by BclA exosporium of Bacillus anthracis." Microbial cell factories, 12.1, (2013): 1.