Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1856000"
Jinchentian (Talk | contribs) |
Jinchentian (Talk | contribs) (Page update) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1856000 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1856000 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | bacA promoter | + | bacA promoter assembled to citrine and T7 terminator |
| − | |||
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| + | bacA is an inducible promoter native to rhizobium species (notably R. tropici and S. meliloti) that is induced by flavonoids such as apigenin. The Yale iGEM team has assembled this promoter to citrine (an improved version of YFP, with excitation peak at 514nm and emission peak at 527nm) and a T7-terminator to quantify the level of expression in E. coli and in non-model organism hosts. | ||
| − | + | This construct has been successfully cloned into E. coli using the broad-host range vector pKT230, a RSF1010 derived plasmid, as well as using the pPZP200 plasmid which can be transformed into agrobacterium and rhizobium. Leaky expression of citrine was observed. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | RSF1010 plasmids belong to the IncQ group and can be transformed into a wide range of gram-negative bacteria as well as some gram-positive bacteria. These include cyanobacteria genera such as Synechocystis, Synechococcus and Anabaena, rhizobium genera such as Rhizobium and Sinorhizobium, and other genera such as Pseudomonas, Streptomyces and Mycobacterium. The plasmid is mobilizable by conjugation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We have used a derivative of pKT230 that is compatible with ligation-independent cloning using BsaI. pKT230 has a kanamycin-resistance marker. | ||
| + | |||
| + | pPZP200 is a agrobacterium binary plasmid that can also be transformed into rhizobium genera. We also used a derivative that is LIC compatible for high-efficiency cloning of our constructs. pPZP200 has a spectinomycin-resistance marker. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Beyond the E. coli work, the construct has also been successfully cloned into S. meliloti and PCR-verified. | ||
<!-- Uncomment this to enable Functional Parameter display | <!-- Uncomment this to enable Functional Parameter display | ||
| Line 17: | Line 22: | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Characterization== |
| − | + | [[Image:Expression Level for bacA-citrine (pKT230-Lic).jpg|300px|right]] | |
| + | ===Measured strength=== | ||
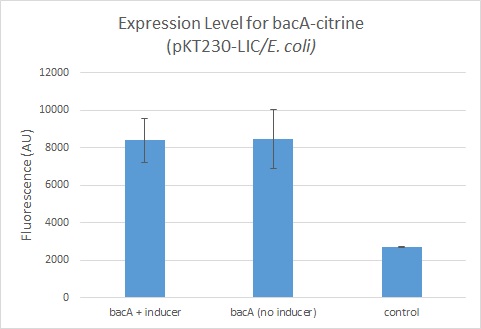
| + | Leaky expression of BacA was observed, with 3 times more fluorescence than background readings. | ||
| − | + | These fluorescence readings are part of a series of readings taken using different inducible and constitutive promoters to drive citrine expression. See parts [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1856001 K1856001], [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1856002 K1856002], [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1856003 K1856003], [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1856004 K1856004], [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1856005 K1856005], [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1856006 K1856006] for details of the full characterization set. | |
| − | == | + | ==Obtaining the BacA promoter-citrine construct== |
| − | + | The sequences of construct can be found via the table below. The physical DNA can be obtained from: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | '''Via request''': The Yale iGEM team has the construct cloned into the broad-host range plasmid, pKT230, a RSF1010 derivative. This plasmid is known to work in cyanobacteria genera such as Synechocystis, Synechococcus and Anabaena, in rhizobium genera such as Rhizobium and Sinorhizobium. The team has also cloned the construct into pPZP200. Both are extremely versatile expression vectors. Please contact the Yale team if you would like to request for an aliquot of the constructs in these plasmids. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | '''Via | + | |
| − | '''Via the Registry distribution''': The | + | '''Via the Registry distribution''': The constructs are included in the Registry distribution, cloned in [https://parts.igem.org/Part:pSB1C3 pSB1C3] backbone. |
<br style="clear:both" /> | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- --> | ||
| + | <span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | ||
| + | <partinfo>BBa_K1856000 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
Latest revision as of 22:59, 20 September 2015
bacA-citrine-T7 terminator
bacA promoter assembled to citrine and T7 terminator
Usage and Biology
bacA is an inducible promoter native to rhizobium species (notably R. tropici and S. meliloti) that is induced by flavonoids such as apigenin. The Yale iGEM team has assembled this promoter to citrine (an improved version of YFP, with excitation peak at 514nm and emission peak at 527nm) and a T7-terminator to quantify the level of expression in E. coli and in non-model organism hosts.
This construct has been successfully cloned into E. coli using the broad-host range vector pKT230, a RSF1010 derived plasmid, as well as using the pPZP200 plasmid which can be transformed into agrobacterium and rhizobium. Leaky expression of citrine was observed.
RSF1010 plasmids belong to the IncQ group and can be transformed into a wide range of gram-negative bacteria as well as some gram-positive bacteria. These include cyanobacteria genera such as Synechocystis, Synechococcus and Anabaena, rhizobium genera such as Rhizobium and Sinorhizobium, and other genera such as Pseudomonas, Streptomyces and Mycobacterium. The plasmid is mobilizable by conjugation.
We have used a derivative of pKT230 that is compatible with ligation-independent cloning using BsaI. pKT230 has a kanamycin-resistance marker.
pPZP200 is a agrobacterium binary plasmid that can also be transformed into rhizobium genera. We also used a derivative that is LIC compatible for high-efficiency cloning of our constructs. pPZP200 has a spectinomycin-resistance marker.
Beyond the E. coli work, the construct has also been successfully cloned into S. meliloti and PCR-verified.
Characterization
Measured strength
Leaky expression of BacA was observed, with 3 times more fluorescence than background readings.
These fluorescence readings are part of a series of readings taken using different inducible and constitutive promoters to drive citrine expression. See parts K1856001, K1856002, K1856003, K1856004, K1856005, K1856006 for details of the full characterization set.
Obtaining the BacA promoter-citrine construct
The sequences of construct can be found via the table below. The physical DNA can be obtained from:
Via request: The Yale iGEM team has the construct cloned into the broad-host range plasmid, pKT230, a RSF1010 derivative. This plasmid is known to work in cyanobacteria genera such as Synechocystis, Synechococcus and Anabaena, in rhizobium genera such as Rhizobium and Sinorhizobium. The team has also cloned the construct into pPZP200. Both are extremely versatile expression vectors. Please contact the Yale team if you would like to request for an aliquot of the constructs in these plasmids.
Via the Registry distribution: The constructs are included in the Registry distribution, cloned in pSB1C3 backbone.
Sequence and Features
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal EcoRI site found at 920
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal EcoRI site found at 920
Illegal NotI site found at 945 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal EcoRI site found at 920
Illegal BamHI site found at 914
Illegal XhoI site found at 954 - 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal EcoRI site found at 920
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal EcoRI site found at 920
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]