Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1688006"
(→Usage and Biology) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
This particular Biobrick also has an export tag (HlyA) attatched to the C-terminus. The enzymatic activities was measured on the enzyme without the HlyA-tag, so the results regarding the enzyme kinetics assay is necessarirly not transferable to this specific Biobrick. The modified CueO laccase that we synthesized had a double mutation (D439A/M510L) that has been proven to increase the enzymatic activity (Kataoka K et al. 2012). A polyhistidine-tag was also added at the N-terminus so that it could be purified easily. | This particular Biobrick also has an export tag (HlyA) attatched to the C-terminus. The enzymatic activities was measured on the enzyme without the HlyA-tag, so the results regarding the enzyme kinetics assay is necessarirly not transferable to this specific Biobrick. The modified CueO laccase that we synthesized had a double mutation (D439A/M510L) that has been proven to increase the enzymatic activity (Kataoka K et al. 2012). A polyhistidine-tag was also added at the N-terminus so that it could be purified easily. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Characterizing == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:uppsala_modlacvsecol.png]] | ||
| + | |||
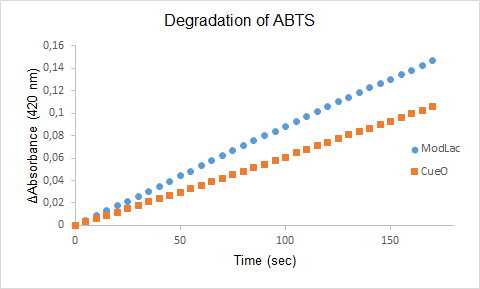
| + | Figure 1. The degradation of ABTS by the lysate of ModLac whitout export tag and the lysate of CueO over time. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Note:''' The Characterizing was made of the same modified laccase but with the exeption that the export tag was removed (See figure 1). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The enzymatic activities of the laccases was measured using ABTS. ABTS is a commonly used substrate when evaluating reaction kinetics of specific enzymes. Due to its reduction potential, it acts as an effective electron donor. Since we are working with laccases, that have the capability to oxidize ring structure, ABTS is a suitable substrate. ABTS will donate an electron to reduce molecular oxygen. The oxidized ABTS has a different absorption spectrum and the reaction can thus be observed in a spectrophotometer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The enzyme assays of the lysates with ABTS showed a significant difference in enzyme activity between CueO and the mutant CueO, also known as ModLac. The modifications of the laccase that was made increased the enzymatic degradation of ABTS. This is confirmed by our results (See Figure 1). | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Kataoka, K, Kogi H, Tsujimura S, Sakurai T. 2012. Modifications of laccase activities of copper efflux oxidase, CueO by synergistic mutations in the first and second coordination spheres of the type I copper center. Faculty of pure and applied science , University of Tsukuba, | ||
Latest revision as of 01:58, 19 September 2015
ModLac laccase with His-tag and HlyA export tag (inc RBS)
A modified laccase (D439A/M510L CueO) with N-His6 tag attached to it via a linker sequence and an export tag (HlyA, BBa_K554002) attached to its C-terminus.
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 267
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Usage and Biology
Laccases (originally from Chinese lacquer tree sap) are multicopper oxidases, that are employed in various industries, where they take part in beer maturation, textile dyeing, and enzymatic biofuel cells. Due to their broad specificity and ability to oxidize aromatic compounds, their application in bioremediation is a topic under investigation. The laccase we chose is a modified laccase, CueO, a laccase from E. coli.
The enzymatic activities of the laccases was measured using ABTS. ABTS is a commonly used substrate when evaluating reaction kinetics of specific enzymes. Due to its reduction potential, it acts as an effective electron donor. Since we are working with laccases, which are multi copper oxidases, which oxidize substrates, ABTS is a suitable substrate. ABTS will donate electron to reduce molecular oxygen. The oxidized ABTS has a different absorption spectrum and the reaction can thus be observed in a spectrophotometer.
Design Notes
This particular Biobrick also has an export tag (HlyA) attatched to the C-terminus. The enzymatic activities was measured on the enzyme without the HlyA-tag, so the results regarding the enzyme kinetics assay is necessarirly not transferable to this specific Biobrick. The modified CueO laccase that we synthesized had a double mutation (D439A/M510L) that has been proven to increase the enzymatic activity (Kataoka K et al. 2012). A polyhistidine-tag was also added at the N-terminus so that it could be purified easily.
Characterizing
Figure 1. The degradation of ABTS by the lysate of ModLac whitout export tag and the lysate of CueO over time.
Note: The Characterizing was made of the same modified laccase but with the exeption that the export tag was removed (See figure 1).
The enzymatic activities of the laccases was measured using ABTS. ABTS is a commonly used substrate when evaluating reaction kinetics of specific enzymes. Due to its reduction potential, it acts as an effective electron donor. Since we are working with laccases, that have the capability to oxidize ring structure, ABTS is a suitable substrate. ABTS will donate an electron to reduce molecular oxygen. The oxidized ABTS has a different absorption spectrum and the reaction can thus be observed in a spectrophotometer.
The enzyme assays of the lysates with ABTS showed a significant difference in enzyme activity between CueO and the mutant CueO, also known as ModLac. The modifications of the laccase that was made increased the enzymatic degradation of ABTS. This is confirmed by our results (See Figure 1).
References
Kataoka, K, Kogi H, Tsujimura S, Sakurai T. 2012. Modifications of laccase activities of copper efflux oxidase, CueO by synergistic mutations in the first and second coordination spheres of the type I copper center. Faculty of pure and applied science , University of Tsukuba,