Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1321101"
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1321101 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1321101 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | + | A T7-promoter expression construct of Synthetic phytochelatin EC20 (metal binding peptide) fused N-terminally to CBDclos (a cellulose-binding domain). | |
| + | |||
| + | This construct is part of a library of fusions with cellulose binding domains which we designed to bind to cellulose and enable capture of heavy metals ([http://2014.igem.org/Team:Imperial/Functionalisation project page]). Other fusion parts with this metal binding protein can be seen in the table below: [[File:IC14-PC-part-table.PNG]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note that the stop codon plus 6 bp at the end of the sequence are included the RFC25 suffix which is not shown. The prefix to this part is RFC10 format. | ||
| − | |||
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| + | For reference, the cellulose binding domain binding capability of CBDclos (C-terminally fused) to bacterial cellulose was measured relative to other cellulose binding domains when fused to sfGFP, the data for which can be seen ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1321341 here]) - K1321341. | ||
| + | |||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
Latest revision as of 06:10, 2 November 2014
Phytochelatin (PC) EC20 fused to CBDclos with T7 promoter
A T7-promoter expression construct of Synthetic phytochelatin EC20 (metal binding peptide) fused N-terminally to CBDclos (a cellulose-binding domain).
This construct is part of a library of fusions with cellulose binding domains which we designed to bind to cellulose and enable capture of heavy metals ([http://2014.igem.org/Team:Imperial/Functionalisation project page]). Other fusion parts with this metal binding protein can be seen in the table below: 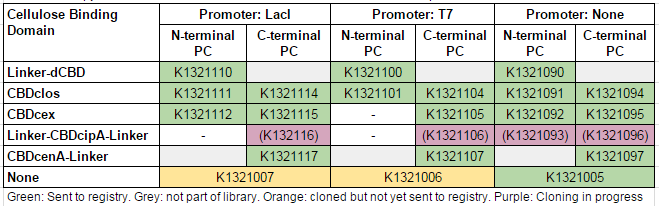
Note that the stop codon plus 6 bp at the end of the sequence are included the RFC25 suffix which is not shown. The prefix to this part is RFC10 format.
Usage and Biology
For reference, the cellulose binding domain binding capability of CBDclos (C-terminally fused) to bacterial cellulose was measured relative to other cellulose binding domains when fused to sfGFP, the data for which can be seen (here) - K1321341.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 53
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
