Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1529301:Experience"
(→Materials and Methods) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
All the samples were JM2.300 strain with antibiotic resistance to ampicillin and kanamycin.<br> | All the samples were JM2.300 strain with antibiotic resistance to ampicillin and kanamycin.<br> | ||
| − | A. Ptet_RhlR (6A1) | + | A. Ptet_RhlR (6A1) Prhl-GFP (3K3) <br> |
| − | B. Ptet_RhlR (6A1) Prhl( | + | B. Ptet_RhlR (6A1) Prhl(RR)-GFP (3K3) <br> |
| − | C. Ptet_RhlR (6A1) Prhl( | + | C. Ptet_RhlR (6A1) Prhl(LR)-GFP (3K3) <br> |
| − | D. Ptet_RhlR (6A1) | + | D. Ptet_RhlR (6A1) Prhl(RL)-GFP (3K3) <br> |
| − | E. Ptet_RhlR (6A1) | + | E. Ptet_RhlR (6A1) Placuv5-GFP (3K3) …positive control<br> |
| − | F. Ptet_RhlR (6A1) | + | F. Ptet_RhlR (6A1) promoter less-GFP(3K3) …negative control<br> |
| − | [[Image:Improved_Prhl_Promoter_Assay_Construction.png|thumb|center|600px|<b>Fig. .</b> ]]<br> | + | [[Image:Improved_Prhl_Promoter_Assay_Construction.png|thumb|center|600px|<b>Fig. 1. </b>Plasmids]]<br> |
<b>2. Assay protocol</b><br> | <b>2. Assay protocol</b><br> | ||
| − | 1.Prepare overnight cultures | + | 1.Prepare 2 overnight cultures for each sample A~F in 3 mL LB medium, containing ampicillin (50 microg / mL) and kanamycin (30 microg / mL) at 37°C for 12 h.<br> |
| − | 2.Dilute the overnight | + | 2.Dilute the overnight cultures to 1 / 100 in fresh LB medium (3 mL) containing ampicillin (50 microg / mL) and kanamycin (30 microg / mL) (→fresh culture).<br> |
| − | 3.Incubate the fresh cultures in 37°C until the | + | 3.Incubate the fresh cultures in 37°C until the OD590 reaches 0.3.<br> |
4.Add 30 microL of 500 microM C4HSL or DMSO as listed below:<br> | 4.Add 30 microL of 500 microM C4HSL or DMSO as listed below:<br> | ||
| − | + | A-5 microM: A + C4HSL<br> | |
| − | + | A-0 microM: A + DMSO<br> | |
| − | + | B-5 microM: B + C4HSL<br> | |
| − | + | B-0 microM: B + DMSO<br> | |
| − | + | C-5 microM: C + C4HSL<br> | |
| − | + | C-0 microM: C + DMSO<br> | |
| − | + | D-5 microM: D + C4HSL<br> | |
| − | + | D-0 microM: D + DMSO<br> | |
| − | + | E-5 microM: E + C4HSL<br> | |
| − | + | E-0 microM: E + DMSO<br> | |
| − | + | F-5 microM: F + C4HSL<br> | |
| − | + | F-0 microM: F + DMSO<br> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
5.Incubate the samples at 37°C for 4 h.<br> | 5.Incubate the samples at 37°C for 4 h.<br> | ||
6.Start preparing the flow cytometer 1 h before the end of incubation.<br> | 6.Start preparing the flow cytometer 1 h before the end of incubation.<br> | ||
| − | 7.Take 200 microL of the sample, and centrifuge at | + | 7.Take 200 microL of the sample, and centrifuge at 9000x g, 1 min., 4°C.<br> |
8.Remove the supernatant by using P1000 pipette.<br> | 8.Remove the supernatant by using P1000 pipette.<br> | ||
9.Add 1 mL of filtered PBS (phosphate-buffered saline) and suspend.<br> | 9.Add 1 mL of filtered PBS (phosphate-buffered saline) and suspend.<br> | ||
| − | 10.Dispense all of each suspension into a disposable tube through a cell strainer.<br> | + | 10.Dispense all of each suspension into a disposable tube through a cell strainer. <br> |
| − | 11.Measure fluorescence intensity with a flow cytometer (We used BD FACSCaliburTM Flow Cytometer of Becton, Dickenson and Company). | + | 11.Measure fluorescence intensity with a flow cytometer (We used BD FACSCaliburTM Flow Cytometer of Becton, Dickenson and Company). |
===Results=== | ===Results=== | ||
| − | [[Image:Improved_Prhl_Promoter_Assay_Result.png|thumb|center|600px|<b>Fig. | + | [[Image:Improved_Prhl_Promoter_Assay_Result.png|thumb|center|600px|<b>Fig. 2. </b> The fluorescence intensity of the cells (with positive and negative controls)]] |
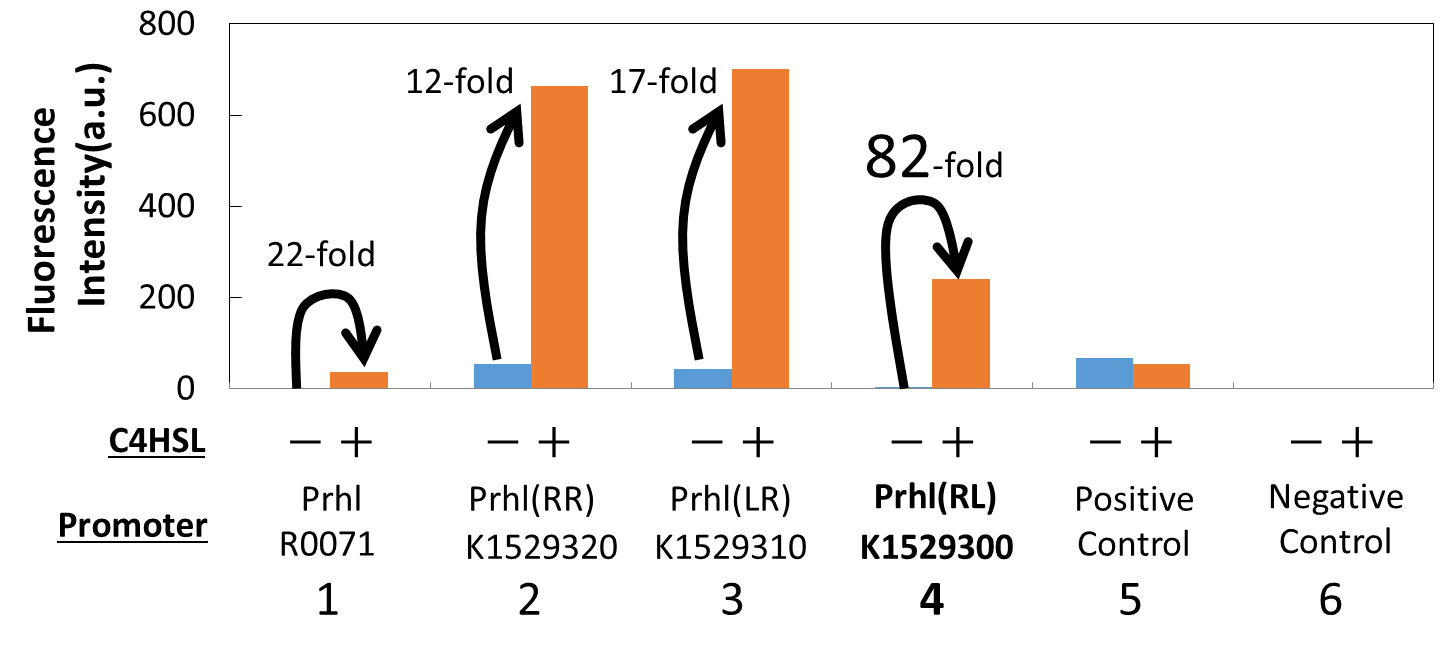
| − | [[Image:Improved_Prhl_Promoter_Assay_Extracted_Result.png|thumb|center| | + | [[Image:Improved_Prhl_Promoter_Assay_Extracted_Result.png|thumb|center|500px|<b>Fig. 3. </b> The fluorescence intensity of the cells with the original Prhl, Prhl(RR), and Prhl(RL)]] |
<br> | <br> | ||
===Discussion=== | ===Discussion=== | ||
| − | We measured the GFP expression with the four different promoters (Prhl, Prhl(RR), Prhl(LR), and Prhl(RL)) by flow cytometer. Each promoter was tested in the presence and also in the absence of C4HSL (See Materials and Methods for detailed procedures).<br> | + | We measured the GFP expression with the four different promoters (Prhl : <partinfo>BBa_R0071</partinfo>, Prhl(RR) : <partinfo>BBa_K1529320</partinfo>, Prhl(LR) : <partinfo>BBa_K1529310</partinfo>, and Prhl(RL) : <partinfo>BBa_K1529300</partinfo>) by flow cytometer. Each promoter was tested in the presence and also in the absence of C4HSL (See Materials and Methods for detailed procedures).<br> |
| − | Fig. shows the fluorescence intensity detected by flow cytometer. <br> | + | Fig. 2. shows the fluorescence intensity detected by flow cytometer. <br> |
| − | Fig. is the extracted data which shows the comparison of the promoters: Prhl, Prhl(RR), and Prhl(RL).<br> | + | Fig. 3. is the extracted data which shows the comparison of the promoters: Prhl, Prhl(RR), and Prhl(RL).<br> |
| − | As Fig. shows, when induced by C4HSL, Prhl(RR) promoter showed higher maximum expression level and higher leak than the original Prhl promoter.<br> | + | As Fig. 3 shows, when induced by C4HSL, Prhl(RR) promoter showed higher maximum expression level and higher leak than the original Prhl promoter.<br> |
Although Prhl(RL) promoter had lower maximum expression level compared to Prhl(RR) promoter, it had the highest induced/not-induced ratio. <br> | Although Prhl(RL) promoter had lower maximum expression level compared to Prhl(RR) promoter, it had the highest induced/not-induced ratio. <br> | ||
This means Prhl(RL) promoter has little leak.<br> | This means Prhl(RL) promoter has little leak.<br> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:50, 20 October 2014
Prhl(RL)-GFP
Contents
Materials and Methods
1. Construction
All the samples were JM2.300 strain with antibiotic resistance to ampicillin and kanamycin.
A. Ptet_RhlR (6A1) Prhl-GFP (3K3)
B. Ptet_RhlR (6A1) Prhl(RR)-GFP (3K3)
C. Ptet_RhlR (6A1) Prhl(LR)-GFP (3K3)
D. Ptet_RhlR (6A1) Prhl(RL)-GFP (3K3)
E. Ptet_RhlR (6A1) Placuv5-GFP (3K3) …positive control
F. Ptet_RhlR (6A1) promoter less-GFP(3K3) …negative control
2. Assay protocol
1.Prepare 2 overnight cultures for each sample A~F in 3 mL LB medium, containing ampicillin (50 microg / mL) and kanamycin (30 microg / mL) at 37°C for 12 h.
2.Dilute the overnight cultures to 1 / 100 in fresh LB medium (3 mL) containing ampicillin (50 microg / mL) and kanamycin (30 microg / mL) (→fresh culture).
3.Incubate the fresh cultures in 37°C until the OD590 reaches 0.3.
4.Add 30 microL of 500 microM C4HSL or DMSO as listed below:
A-5 microM: A + C4HSL
A-0 microM: A + DMSO
B-5 microM: B + C4HSL
B-0 microM: B + DMSO
C-5 microM: C + C4HSL
C-0 microM: C + DMSO
D-5 microM: D + C4HSL
D-0 microM: D + DMSO
E-5 microM: E + C4HSL
E-0 microM: E + DMSO
F-5 microM: F + C4HSL
F-0 microM: F + DMSO
5.Incubate the samples at 37°C for 4 h.
6.Start preparing the flow cytometer 1 h before the end of incubation.
7.Take 200 microL of the sample, and centrifuge at 9000x g, 1 min., 4°C.
8.Remove the supernatant by using P1000 pipette.
9.Add 1 mL of filtered PBS (phosphate-buffered saline) and suspend.
10.Dispense all of each suspension into a disposable tube through a cell strainer.
11.Measure fluorescence intensity with a flow cytometer (We used BD FACSCaliburTM Flow Cytometer of Becton, Dickenson and Company).
Results
Discussion
We measured the GFP expression with the four different promoters (Prhl : BBa_R0071, Prhl(RR) : BBa_K1529320, Prhl(LR) : BBa_K1529310, and Prhl(RL) : BBa_K1529300) by flow cytometer. Each promoter was tested in the presence and also in the absence of C4HSL (See Materials and Methods for detailed procedures).
Fig. 2. shows the fluorescence intensity detected by flow cytometer.
Fig. 3. is the extracted data which shows the comparison of the promoters: Prhl, Prhl(RR), and Prhl(RL).
As Fig. 3 shows, when induced by C4HSL, Prhl(RR) promoter showed higher maximum expression level and higher leak than the original Prhl promoter.
Although Prhl(RL) promoter had lower maximum expression level compared to Prhl(RR) promoter, it had the highest induced/not-induced ratio.
This means Prhl(RL) promoter has little leak.
Therefore, we can say that Prhl(RL) promoter is the best improved Prhl promoter due to the advantages of less leak and higher expression level.
For more information, see [http://2014.igem.org/Team:Tokyo_Tech/Experiment/Prhl_reporter_assay our work in Tokyo_Tech 2014 wiki].
Applications of BBa_K1529301
User Reviews
UNIQ04a092e815c9249c-partinfo-00000005-QINU UNIQ04a092e815c9249c-partinfo-00000006-QINU