Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa J58105"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_J58105 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_J58105 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | This part corresponds to the coding sequence of a computationally engineered protein designed by Pablo Tortosa and Alfonso Jaramillo at the [http://www. | + | This part corresponds to the coding sequence of a computationally engineered protein designed by Pablo Tortosa and Alfonso Jaramillo at the [http://www.enseignement.polytechnique.fr/profs/biochimie/Alfonso.Jaramillo/ Synthetic Biology group at the Ecole Polytechnique (France)]. This protein is based on a ribose-binding protein template and has been designed to stabilize its closed conformation after binding a vanillin molecule. The closed conformation is able to bind a Trg protein. This part can be used to engineer a sensor genetic device if used with the part <partinfo>J58104</partinfo> (which implements a synthetic two-component signal transduction pathway based on a Trg-EnvZ fusion protein). This device would use phosphorylated OmpR as output. |
| + | |||
| + | This receptor protein has been designed computationally using a ribose binding protein as a scaffold and finding the necessary mutations to change its ligand affinity towards a vanillin molecule making E. Coli tasting flavors. | ||
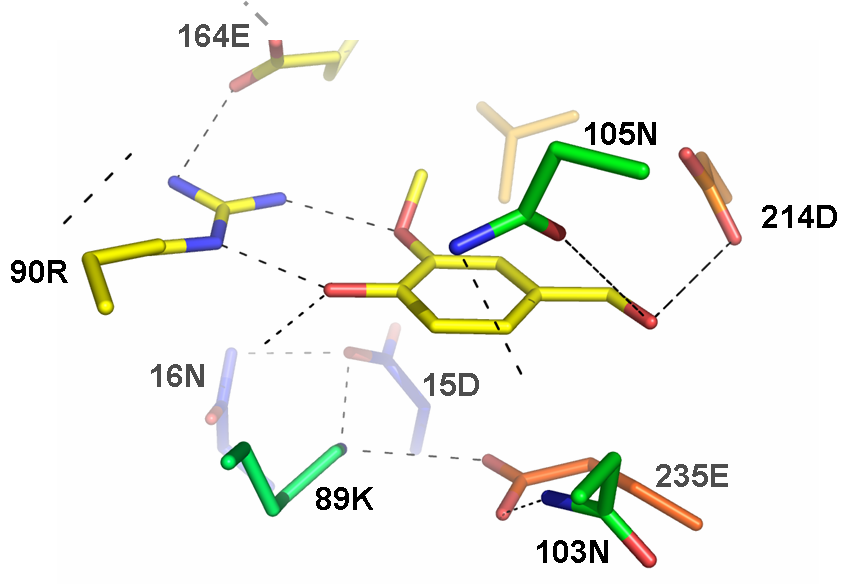
| + | [[Image:vanbp.png|thumb|300px|Part of the active site of the computationally designed vanillin-binding protein. Dashed lines denote h-bonds. Only the residues making h-bonds with the vanillin molecule are shown on top.]] | ||
'''By Valencia iGEM 2006''' | '''By Valencia iGEM 2006''' | ||
| Line 14: | Line 17: | ||
''3 Ecole Polytechnique, France'' | ''3 Ecole Polytechnique, France'' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| − | |||
<span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | <span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | ||
<partinfo>BBa_J58105 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_J58105 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
Revision as of 10:37, 29 October 2006
Synthetic periplasmic binding protein that docks a vanillin molecule
This part corresponds to the coding sequence of a computationally engineered protein designed by Pablo Tortosa and Alfonso Jaramillo at the [http://www.enseignement.polytechnique.fr/profs/biochimie/Alfonso.Jaramillo/ Synthetic Biology group at the Ecole Polytechnique (France)]. This protein is based on a ribose-binding protein template and has been designed to stabilize its closed conformation after binding a vanillin molecule. The closed conformation is able to bind a Trg protein. This part can be used to engineer a sensor genetic device if used with the part BBa_J58104 (which implements a synthetic two-component signal transduction pathway based on a Trg-EnvZ fusion protein). This device would use phosphorylated OmpR as output.
This receptor protein has been designed computationally using a ribose binding protein as a scaffold and finding the necessary mutations to change its ligand affinity towards a vanillin molecule making E. Coli tasting flavors.
By Valencia iGEM 2006
A. Aparici (2), MC. Aroca (2), J. Carrera (1), C. Edo (1,2), G. Fuertes (2), D. Jimenez (2), C. Mata (2), JV. Medrano (2), A. Montagud (2), C. Navarrete (2), E. Navarro (1), G. Rodrigo (1), M. Baguena (1), P. Tortosa (3), P. Fernandez-de-Cordoba (1), A. Ferrando (2), J. Salgado (2), J. Urchueguia (1), A. Jaramillo (3).
1 Universidad Politecnica de Valencia, Spain
2 Universitat de Valencia, Spain
3 Ecole Polytechnique, France
Usage and Biology
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]