Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1080006"
Leah.Simmons (Talk | contribs) (→Operon Usage) |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1080006 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1080006 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | <br><b> Chloroplast precursor </b> - | + | <br><b> Chloroplast precursor </b> - Plastocyanin contains <b>copper</b> and is a chloroplast precursor protein. It is taken up after post translation and placed on its functional site where it is involved in electron transfer between cytochrome f of the cytochrome b6f complex from photosystem II and P700+ from photosystem I. |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | ===Operon Usage=== | ||
| + | [[File:pSB1C3_Operon 2.png]] | ||
| + | <br>This gene has been used in an operon with other genes responsible for catalysing the biosynthesis pathway from Mg-protoporphyrin IX to Protochlorophyllide. [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K1080005 CTH1], [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1080006 Plastocyanin], and [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K1080010 YCF54] are involved in the oxidative cyclase pathway. [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1080004 ChlM] methylates Mg-protoporphyrin IX, facilitating the highly-regulated catalysis of Mg-chelatase. [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K1080005 CTH1] catalyses the conversion of Mg-protoporphyrin IX monomethyl into divinyl protochlorophyllide, interacting with [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K1080010 YCF54] and [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1080006 Plastocyanin]. | ||
| + | <br>The insertion of magnesium is the key component of the chlorophyll biosynthesis pathway. | ||
| + | <br>The plasmid is under the control of the [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K864400 lac promoter]. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Structure=== | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[File:plastocyanin.jpg]] | ||
| + | Figure 1. Structure of Plastocyanin with emphasis on the copper binding site and the Tyr-83 side chain. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Shown above is a structure of plastocyanin with emphasis on the tetrahedral structured copper binding site which is located at the "north" end of the molecule. The Tyr-83 side chain is also shown on the "east" end of the molecule also known as the "remote" site of electron transfer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <b><h4>Biobrick Design:</h4></b> | ||
| + | Source Genbank accession: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/AAA32834.1 AAA32834.1] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
| Line 10: | Line 35: | ||
<span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | <span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1080006 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1080006 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <center><font size=4><u>Characterisation of Plastocyanin</u></font size></center> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Our tac+plastocyanin composite biobrick theoretically expresses a copper containing protein. Colonies containing this biobrick should turn blue in the presence of inducer (IPTG) and copper. To test this, we plated this culture out on a regular LB plate, and a copper + IPTG LB plate. We also plated out a control plate with both Plasto and CHLI1 expressing colonies. <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The first image below show plastocyanin expressing colonies growing blue on LB+copper+IPTG plates seen on the right, and white/yellow on regular LB plates shown on the left: <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><img src=https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/4/49/MQ_copper_no_copper_comparison_cropped.JPG><br><br></center> | ||
| + | The second image shows a LB+copper+IPTG plate with plastocyanin colonies growing on one half, and non-expressing colonies (ChlI1) on the other half:<br><br> | ||
| + | <center><img src=https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/5/50/MQ_copper_control2_cropped.JPG></center><br><br> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <b> Ribbon diagram of protein structure</b> | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk/structure/getimage?id=2plt | ||
| + | |||
| + | <b>Amino acid sequence</b> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <FONT FACE="courier">MATVKLGADS GALEFVPKTL TIKSGETVNF VNNAGFPHNI VFDEDAIPSG VNADAISRDD<br> YLNAPGETYS VKLTAAGEYG YYCEPHQGAG MVGKIIVQ </font> | ||
| + | |||
| + | References and documentation are available. | ||
| + | Please note the modified algorithm for extinction coefficient. | ||
| + | |||
| + | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ||
| + | Number of amino acids: 98 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Molecular weight: 10339.5 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Theoretical pI: 4.57 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <b>Amino acid composition: | ||
| + | </b> | ||
| + | Ala(A) 11 ( 11.2% )<br> | ||
| + | Arg(R) 01 ( 1.0% )<br> | ||
| + | Asn(N) 06 ( 6.1% )<br> | ||
| + | Asp(D) 06 ( 6.1% )<br> | ||
| + | Cys(C) 01 ( 1.0% )<br> | ||
| + | Gln(Q) 02 ( 2.0% )<br> | ||
| + | Glu(E) 06 ( 6.1% )<br> | ||
| + | Gly(G) 11 ( 11.2% )<br> | ||
| + | His(H) 02 ( 2.0% )<br> | ||
| + | Ile(I) 06 ( 6.1% )<br> | ||
| + | Leu(L) 05 ( 5.1% )<br> | ||
| + | Lys(K) 05 ( 5.1% )<br> | ||
| + | Met(M) 02 ( 2.0% )<br> | ||
| + | Phe(F) 04 ( 4.1% )<br> | ||
| + | Pro(P) 05 ( 5.1% )<br> | ||
| + | Ser(S) 05 ( 5.1% )<br> | ||
| + | Thr(T) 06 ( 6.1% )<br> | ||
| + | Trp(W) 00 ( 0.0% )<br> | ||
| + | Tyr(Y) 05 ( 5.1% )<br> | ||
| + | Val(V) 09 ( 9.2% )<br> | ||
| + | Pyl(O) 00 ( 0.0% )<br> | ||
| + | Sec(U) 00 ( 0.0% )<br></FONT> | ||
| + | |||
| + | (B) 0 0.0% | ||
| + | (Z) 0 0.0% | ||
| + | (X) 0 0.0% | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Total number of negatively charged residues (Asp + Glu): 12 | ||
| + | Total number of positively charged residues (Arg + Lys): 6 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Atomic composition: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Carbon C 460 | ||
| + | Hydrogen H 708 | ||
| + | Nitrogen N 118 | ||
| + | Oxygen O 147 | ||
| + | Sulfur S 3 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Formula: C460H708N118O147S3 | ||
| + | Total number of atoms: 1436 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Extinction coefficients: | ||
| + | |||
| + | This protein does not contain any Trp residues. Experience shows that | ||
| + | this could result in more than 10% error in the computed extinction coefficient. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Extinction coefficients are in units of M-1 cm-1, at 280 nm measured in water. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ext. coefficient 7450 | ||
| + | Abs 0.1% (=1 g/l) 0.721, assuming all pairs of Cys residues form cystines | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Ext. coefficient 7450 | ||
| + | Abs 0.1% (=1 g/l) 0.721, assuming all Cys residues are reduced | ||
| + | |||
| + | Estimated half-life: | ||
| + | |||
| + | The N-terminal of the sequence considered is M (Met). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The estimated half-life is: | ||
| + | 30 hours (mammalian reticulocytes, in vitro). | ||
| + | >20 hours (yeast, in vivo). | ||
| + | >10 hours (Escherichia coli, in vivo). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Instability index: | ||
| + | |||
| + | The instability index (II) is computed to be 18.58 | ||
| + | This classifies the protein as stable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Aliphatic index: 81.63 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY): -0.065 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Source=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | From genome of <i>Chlamydomonas reinhardtii</i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | Redinbo, M.R., et al. (1994). "Plastocyanin: structural and functional analysis". Journal of bioenergetics and biomembranes. Vol. 26, No.1 | ||
<!-- Uncomment this to enable Functional Parameter display | <!-- Uncomment this to enable Functional Parameter display | ||
Latest revision as of 17:47, 16 October 2014
Plastocyanin
Chloroplast precursor - Plastocyanin contains copper and is a chloroplast precursor protein. It is taken up after post translation and placed on its functional site where it is involved in electron transfer between cytochrome f of the cytochrome b6f complex from photosystem II and P700+ from photosystem I.
Operon Usage
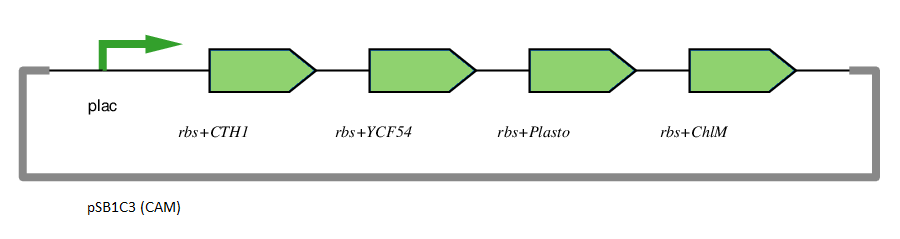
This gene has been used in an operon with other genes responsible for catalysing the biosynthesis pathway from Mg-protoporphyrin IX to Protochlorophyllide. CTH1, Plastocyanin, and YCF54 are involved in the oxidative cyclase pathway. ChlM methylates Mg-protoporphyrin IX, facilitating the highly-regulated catalysis of Mg-chelatase. CTH1 catalyses the conversion of Mg-protoporphyrin IX monomethyl into divinyl protochlorophyllide, interacting with YCF54 and Plastocyanin.
The insertion of magnesium is the key component of the chlorophyll biosynthesis pathway.
The plasmid is under the control of the lac promoter.
Structure
Figure 1. Structure of Plastocyanin with emphasis on the copper binding site and the Tyr-83 side chain.
Shown above is a structure of plastocyanin with emphasis on the tetrahedral structured copper binding site which is located at the "north" end of the molecule. The Tyr-83 side chain is also shown on the "east" end of the molecule also known as the "remote" site of electron transfer.
Biobrick Design:
Source Genbank accession: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/AAA32834.1 AAA32834.1]
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 100
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 223
Our tac+plastocyanin composite biobrick theoretically expresses a copper containing protein. Colonies containing this biobrick should turn blue in the presence of inducer (IPTG) and copper. To test this, we plated this culture out on a regular LB plate, and a copper + IPTG LB plate. We also plated out a control plate with both Plasto and CHLI1 expressing colonies.
The first image below show plastocyanin expressing colonies growing blue on LB+copper+IPTG plates seen on the right, and white/yellow on regular LB plates shown on the left:


Ribbon diagram of protein structure
http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk/structure/getimage?id=2plt
Amino acid sequence
MATVKLGADS GALEFVPKTL TIKSGETVNF VNNAGFPHNI VFDEDAIPSG VNADAISRDD
YLNAPGETYS VKLTAAGEYG YYCEPHQGAG MVGKIIVQ
References and documentation are available. Please note the modified algorithm for extinction coefficient.
Number of amino acids: 98
Molecular weight: 10339.5
Theoretical pI: 4.57
Amino acid composition:
Ala(A) 11 ( 11.2% )
Arg(R) 01 ( 1.0% )
Asn(N) 06 ( 6.1% )
Asp(D) 06 ( 6.1% )
Cys(C) 01 ( 1.0% )
Gln(Q) 02 ( 2.0% )
Glu(E) 06 ( 6.1% )
Gly(G) 11 ( 11.2% )
His(H) 02 ( 2.0% )
Ile(I) 06 ( 6.1% )
Leu(L) 05 ( 5.1% )
Lys(K) 05 ( 5.1% )
Met(M) 02 ( 2.0% )
Phe(F) 04 ( 4.1% )
Pro(P) 05 ( 5.1% )
Ser(S) 05 ( 5.1% )
Thr(T) 06 ( 6.1% )
Trp(W) 00 ( 0.0% )
Tyr(Y) 05 ( 5.1% )
Val(V) 09 ( 9.2% )
Pyl(O) 00 ( 0.0% )
Sec(U) 00 ( 0.0% )
</FONT>
(B) 0 0.0% (Z) 0 0.0% (X) 0 0.0%
Total number of negatively charged residues (Asp + Glu): 12
Total number of positively charged residues (Arg + Lys): 6
Atomic composition:
Carbon C 460 Hydrogen H 708 Nitrogen N 118 Oxygen O 147 Sulfur S 3
Formula: C460H708N118O147S3 Total number of atoms: 1436
Extinction coefficients:
This protein does not contain any Trp residues. Experience shows that this could result in more than 10% error in the computed extinction coefficient.
Extinction coefficients are in units of M-1 cm-1, at 280 nm measured in water.
Ext. coefficient 7450 Abs 0.1% (=1 g/l) 0.721, assuming all pairs of Cys residues form cystines
Ext. coefficient 7450
Abs 0.1% (=1 g/l) 0.721, assuming all Cys residues are reduced
Estimated half-life:
The N-terminal of the sequence considered is M (Met).
The estimated half-life is:
30 hours (mammalian reticulocytes, in vitro).
>20 hours (yeast, in vivo).
>10 hours (Escherichia coli, in vivo).
Instability index:
The instability index (II) is computed to be 18.58 This classifies the protein as stable.
Aliphatic index: 81.63
Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY): -0.065
Source
From genome of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
References
Redinbo, M.R., et al. (1994). "Plastocyanin: structural and functional analysis". Journal of bioenergetics and biomembranes. Vol. 26, No.1
