Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1150050"
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1150050 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1150050 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | Behind a strong CMV promoter a HA-tag, a NLS and | + | |
| + | Behind a strong CMV promoter a [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1150016 HA-tag], a [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1150010 NLS] and [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1150000 dCas9] in a shortened version followed by another NLS and a [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1150012 BGH terminator] were assembled via the iGEM cloning method. | ||
The truncation of the huge dCas9 gene was performed by PCR over the backbone (=dCas9 in pSB1C3). The part between the primer pair is not amplified. One of the primers has an overlap compatible to the first bases of the other one, so that after this PCR a one fragment Gibson assembly could be performed. | The truncation of the huge dCas9 gene was performed by PCR over the backbone (=dCas9 in pSB1C3). The part between the primer pair is not amplified. One of the primers has an overlap compatible to the first bases of the other one, so that after this PCR a one fragment Gibson assembly could be performed. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| − | This part can be used in the uniCAS Toolkit of team Freiburg as a shorter version of | + | This part can be used in the uniCAS Toolkit of team Freiburg as a shorter version of dCas9. |
| − | Truncation 4: | + | |
| + | Truncation 4: 1926 bp in the middle of dCas9 are missing. | ||
| + | |||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
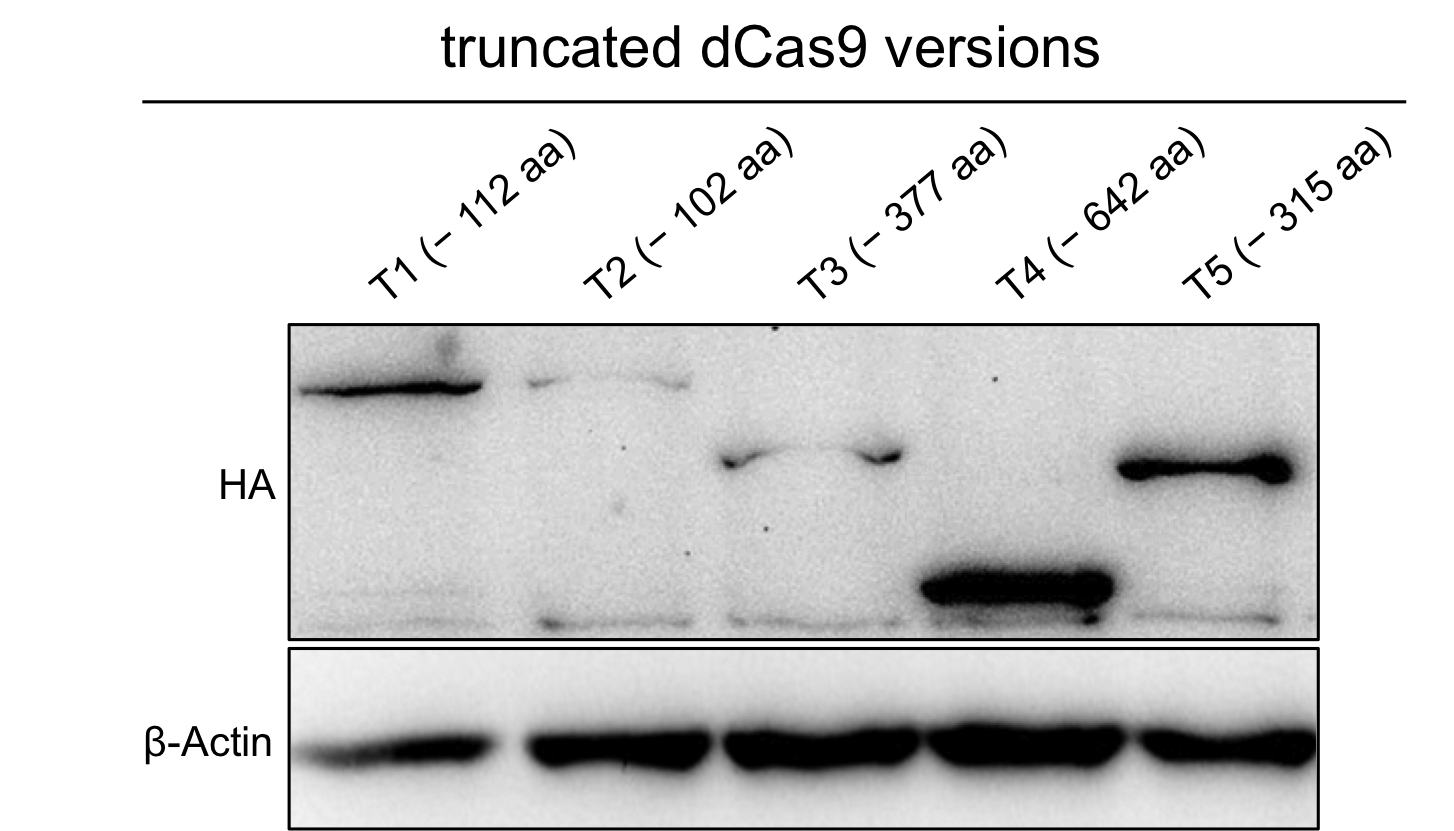
To verify the expression of the truncated dCas9 version we performed westernblot with anti-HA antibody. | To verify the expression of the truncated dCas9 version we performed westernblot with anti-HA antibody. | ||
[[File:Blots-truncation-registry1_Team_Freiburg.PNG|700px|]] | [[File:Blots-truncation-registry1_Team_Freiburg.PNG|700px|]] | ||
| + | |||
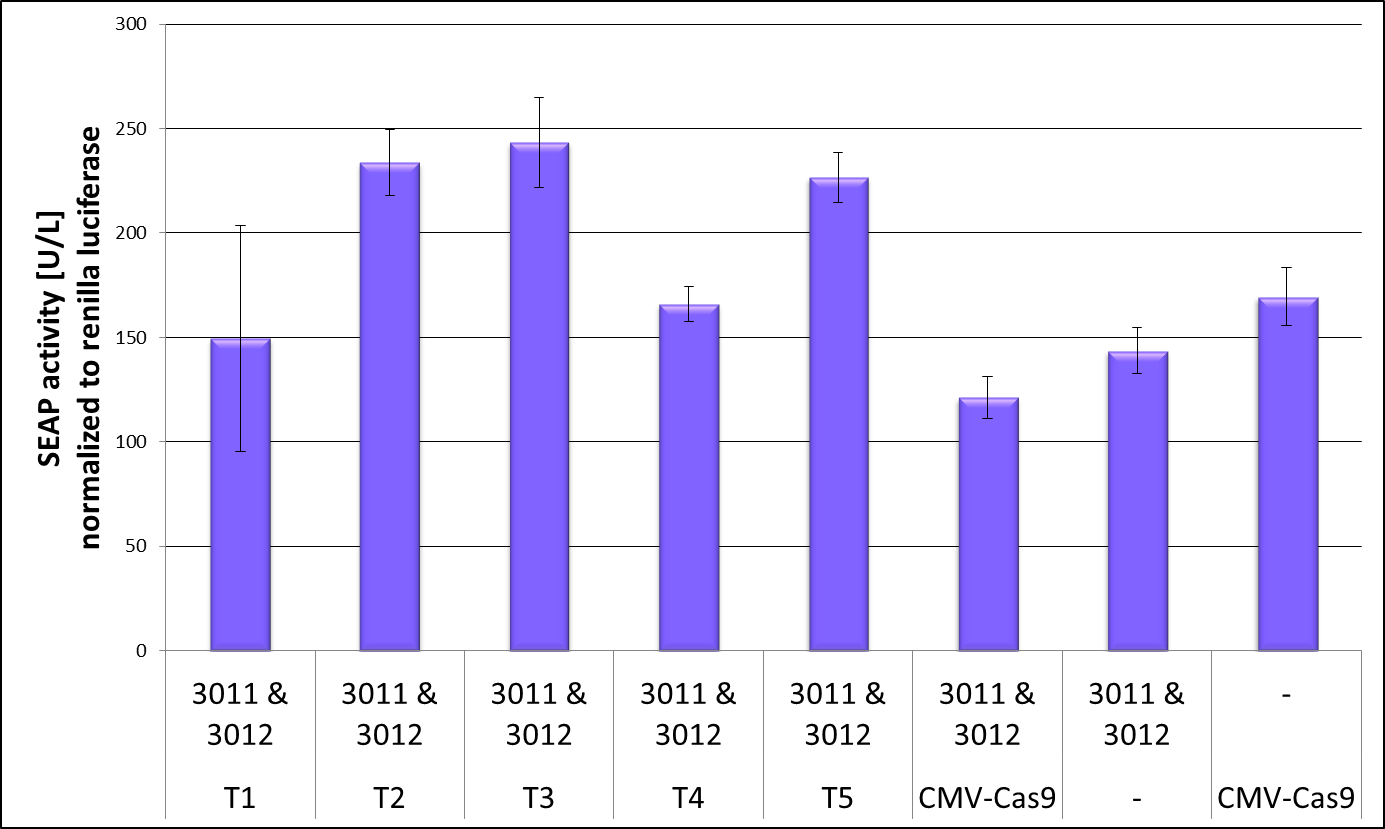
| + | CRISPR interference is the process that the catalytically dead Cas9 targeted to a gene can repress its transcription. [1] We used this effect to test if our truncated dCas9 versions are still able to bind to DNA and therefore can cause the CRISPRi effect which we measured by repression of our reporter gene SEAP. To get reliable data we co-transfected the luciferase Renilla to be able to normalize the SEAP values on the cell number. Figure 2 shows the result of the CRISPRi repression experiment. The full-length dCas9 served as a positive control and showed repression of the SEAP levels. But also the negative controls, one without crRNA and one without dCas9 showed smaller SEAP levels than truncation 2,3 and 5. As the positive and negative controls in this experiment show similar values not much conclusion could be drawn out of it. Nevertheless truncation 4 sees to be a very promising candidate for further investigation as it leads to SEAP levels as low as the positive control. Before the Renilla normalization this effect was even more prominent and therefore all following experiments to validate the DNA binding capacity of a truncated dCas9 version concentrate on truncation 4, this BioBrick, our uniCas. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:TruncationCRISPi-for-registry1.png|700px|]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:29, 29 October 2013
Truncated CMV dCas9 Device #4
Behind a strong CMV promoter a HA-tag, a NLS and dCas9 in a shortened version followed by another NLS and a BGH terminator were assembled via the iGEM cloning method. The truncation of the huge dCas9 gene was performed by PCR over the backbone (=dCas9 in pSB1C3). The part between the primer pair is not amplified. One of the primers has an overlap compatible to the first bases of the other one, so that after this PCR a one fragment Gibson assembly could be performed.
Usage and Biology
This part can be used in the uniCAS Toolkit of team Freiburg as a shorter version of dCas9.
Truncation 4: 1926 bp in the middle of dCas9 are missing.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 576
Illegal BglII site found at 900 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Functional Parameters
To verify the expression of the truncated dCas9 version we performed westernblot with anti-HA antibody.
CRISPR interference is the process that the catalytically dead Cas9 targeted to a gene can repress its transcription. [1] We used this effect to test if our truncated dCas9 versions are still able to bind to DNA and therefore can cause the CRISPRi effect which we measured by repression of our reporter gene SEAP. To get reliable data we co-transfected the luciferase Renilla to be able to normalize the SEAP values on the cell number. Figure 2 shows the result of the CRISPRi repression experiment. The full-length dCas9 served as a positive control and showed repression of the SEAP levels. But also the negative controls, one without crRNA and one without dCas9 showed smaller SEAP levels than truncation 2,3 and 5. As the positive and negative controls in this experiment show similar values not much conclusion could be drawn out of it. Nevertheless truncation 4 sees to be a very promising candidate for further investigation as it leads to SEAP levels as low as the positive control. Before the Renilla normalization this effect was even more prominent and therefore all following experiments to validate the DNA binding capacity of a truncated dCas9 version concentrate on truncation 4, this BioBrick, our uniCas.