Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K801080:Experience"
(→Ion exchange chromatography) |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==== Ion exchange chromatography ==== | ==== Ion exchange chromatography ==== | ||
[[Image:TUM12_ThaumatinIEC.png|500px|thump|right|Experimental Results]] | [[Image:TUM12_ThaumatinIEC.png|500px|thump|right|Experimental Results]] | ||
| − | Preprothaumatin becomes posttranslationally modified by cleaving a part of the N- and the C-terminal polypeptide. Therefore it was not possible to add a tag for affinity chromatography. For this reason it was necessary to purify the protein from the cytoplasm of the | + | Preprothaumatin becomes posttranslationally modified by cleaving a part of the N- and the C-terminal polypeptide. Therefore it was not possible to add a tag for affinity chromatography. For this reason it was necessary to purify the protein from the cytoplasm of the disintegrated yeast cells using ion exchange chromatography to have a proof of principle. |
'''Experimental details:''' | '''Experimental details:''' | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
*Chromatography with a Äkta purifier equipped with a Ressource S 6ml (S: Methyl sulfonate (strong cation exchanger)) | *Chromatography with a Äkta purifier equipped with a Ressource S 6ml (S: Methyl sulfonate (strong cation exchanger)) | ||
*Sample was applied using a super-loop | *Sample was applied using a super-loop | ||
| − | *Wash with two | + | *Wash with two column volumes 20mM MES Buffer pH 6.0 |
*Elution with a gradient of 0 - 500 mM NaCl over 5 column volumes | *Elution with a gradient of 0 - 500 mM NaCl over 5 column volumes | ||
*Fractions of 1 ml were collected during the elution<br> | *Fractions of 1 ml were collected during the elution<br> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
'''Experimental results:''' | '''Experimental results:''' | ||
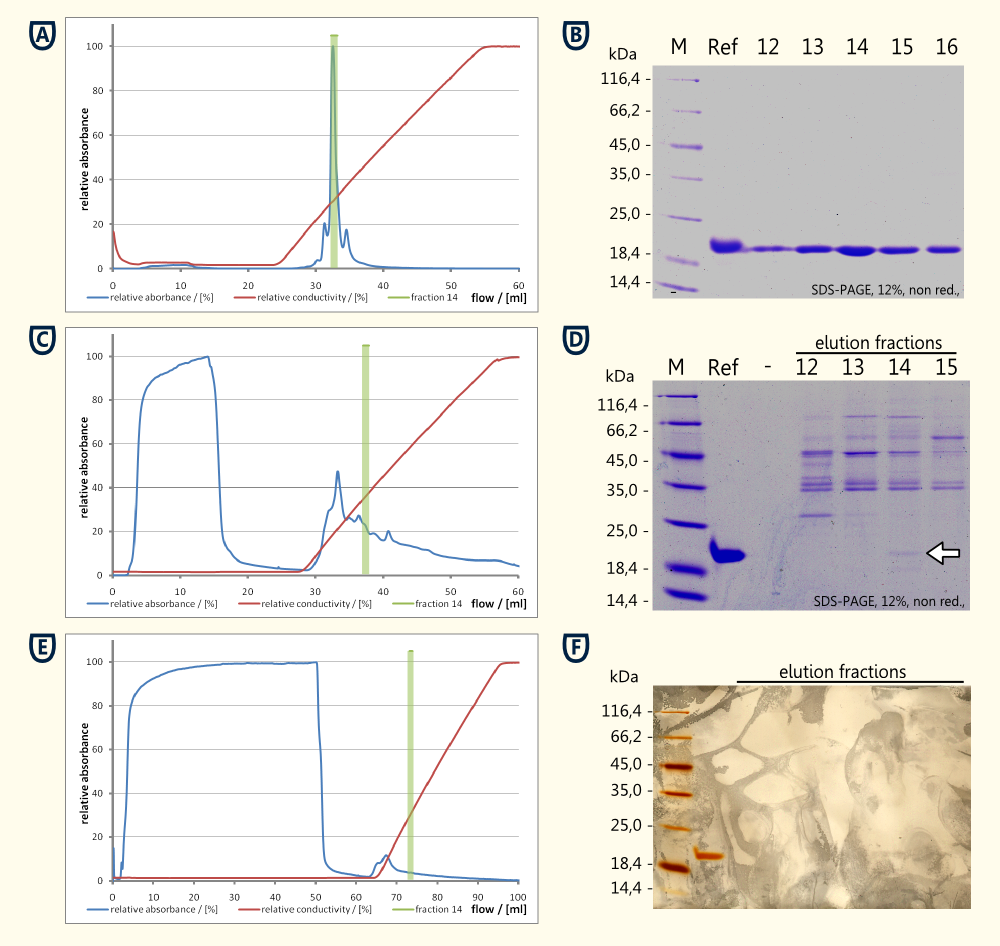
*Reference Thaumatin (see figure A and B) | *Reference Thaumatin (see figure A and B) | ||
| − | ** | + | **nearly no protein in the flow through during sample application (see figure A) |
**a major peak eluting at ~14 mS*cm-1 which corresponds to fraction Nr. 14 see figure A) | **a major peak eluting at ~14 mS*cm-1 which corresponds to fraction Nr. 14 see figure A) | ||
** The corresponding SDS-PAGE showed a clear band around fraction Nr. 14 corresponding matching the expected 22 kDa | ** The corresponding SDS-PAGE showed a clear band around fraction Nr. 14 corresponding matching the expected 22 kDa | ||
*Cell lysate | *Cell lysate | ||
**high concentration of protein in the flow through (see figure C and D) | **high concentration of protein in the flow through (see figure C and D) | ||
| − | **no clear peak | + | **no clear peak around fraction 14 could be detected |
| − | **The SDS-PAGE performed from the reference and the fractions 12 to 15 showed a weak band at the height of the reference. This band having the same size as the reference (see running | + | **The SDS-PAGE performed from the reference and the fractions 12 to 15 showed a weak band at the height of the reference. This band having the same size as the reference (see running properties on SDS-PAGE in figure D) and the same isoelectric point (both eluted in fraction 14) is very likely to be thaumatin which was produced by the yeast cells. |
*Supernatant of yeast culture (see figure E and F) | *Supernatant of yeast culture (see figure E and F) | ||
**Export of the protein in high concentrations was unlikely to happen, therefore 48 ml of supernatant were loaded on the column | **Export of the protein in high concentrations was unlikely to happen, therefore 48 ml of supernatant were loaded on the column | ||
| − | **Ratio between | + | **Ratio between flowthrough and eluted protein was less favorable compared to the cell lysate. |
| − | **Total protein quantities were to low to be detected by | + | **Total protein quantities were to low to be detected by Comassie stain, therefore a silver stain was performed (see figure F) |
**Beside the reference no additional proteinbands could be detected on the silver stained SDS-PAGE<br> | **Beside the reference no additional proteinbands could be detected on the silver stained SDS-PAGE<br> | ||
'''Conclusion from this experiment:'''<br> | '''Conclusion from this experiment:'''<br> | ||
| − | A '''proof of principle for the expression of | + | A '''proof of principle for the expression of thaumatin was achieved using ion exchange chromotography and comparison of bands obtained on an SDS-PAGE relative to a standard of thaumatin'''. <br> |
===Applications of BBa_K801080=== | ===Applications of BBa_K801080=== | ||
Revision as of 18:09, 26 September 2012
Expression of Thaumatin
Ion exchange chromatography
Preprothaumatin becomes posttranslationally modified by cleaving a part of the N- and the C-terminal polypeptide. Therefore it was not possible to add a tag for affinity chromatography. For this reason it was necessary to purify the protein from the cytoplasm of the disintegrated yeast cells using ion exchange chromatography to have a proof of principle.
Experimental details:
- Samples: cell lysate, supernatant from culture, reference for thaumatin (MedHerbs)
- Dialysis against 20mM MES Buffer pH 6.0 (twice) using a 12-16 kDa dialysis membrane
- Chromatography with a Äkta purifier equipped with a Ressource S 6ml (S: Methyl sulfonate (strong cation exchanger))
- Sample was applied using a super-loop
- Wash with two column volumes 20mM MES Buffer pH 6.0
- Elution with a gradient of 0 - 500 mM NaCl over 5 column volumes
- Fractions of 1 ml were collected during the elution
Experimental results:
- Reference Thaumatin (see figure A and B)
- nearly no protein in the flow through during sample application (see figure A)
- a major peak eluting at ~14 mS*cm-1 which corresponds to fraction Nr. 14 see figure A)
- The corresponding SDS-PAGE showed a clear band around fraction Nr. 14 corresponding matching the expected 22 kDa
- Cell lysate
- high concentration of protein in the flow through (see figure C and D)
- no clear peak around fraction 14 could be detected
- The SDS-PAGE performed from the reference and the fractions 12 to 15 showed a weak band at the height of the reference. This band having the same size as the reference (see running properties on SDS-PAGE in figure D) and the same isoelectric point (both eluted in fraction 14) is very likely to be thaumatin which was produced by the yeast cells.
- Supernatant of yeast culture (see figure E and F)
- Export of the protein in high concentrations was unlikely to happen, therefore 48 ml of supernatant were loaded on the column
- Ratio between flowthrough and eluted protein was less favorable compared to the cell lysate.
- Total protein quantities were to low to be detected by Comassie stain, therefore a silver stain was performed (see figure F)
- Beside the reference no additional proteinbands could be detected on the silver stained SDS-PAGE
Conclusion from this experiment:
A proof of principle for the expression of thaumatin was achieved using ion exchange chromotography and comparison of bands obtained on an SDS-PAGE relative to a standard of thaumatin.
Applications of BBa_K801080
User Reviews
UNIQf56edff035ce4316-partinfo-00000000-QINU UNIQf56edff035ce4316-partinfo-00000001-QINU