Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K808003"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K808003 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K808003 short</partinfo> | ||
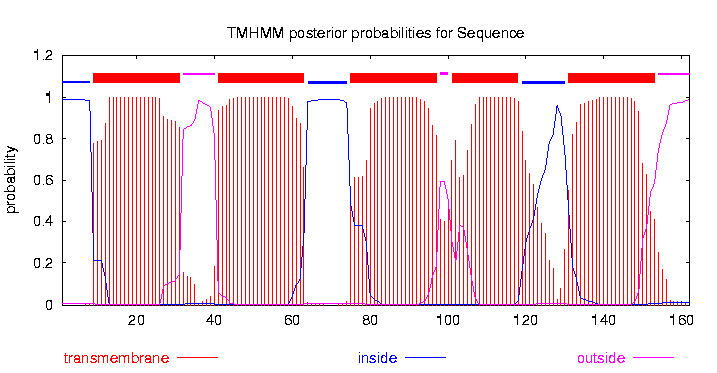
| − | + | The small subunit B1 of the tripartite tricarboxylate transporter family (tctB_162, 17 kDa) was isolated from ''Comamonas testosteroni KF-1.'' The tripartite tricarboxylate transporter system consists of three different proteins: a periplasmatic solute binding receptor, a membrane protein with 12 putative transmembrane alpha-helical spanners (in this case tctB_162), and a small poorly conserved membrane proteine with four putative transmembrane alpha-helical spanners<sup>[1]</sup>.The strain was purchased from Leibniz Institute DMSZ-German Collection of Microorganism and Cell Cultures (DMSZ no. 14576). The original sequence contains a Pst1 recognition site. To eliminate this recognition site a directed-site mutagenic PCR was performed. (For more datails: link zu dem PCR protokoll und dem Labjournal, wo isolations PCR beschrieben wird) To characterized the structure of the tctB_162 bioinformatic tools like '''P '''rotein '''H '''omology/anolog '''Y ''' '''R '''ecognition '''E '''ngine V 2.0 (PHYRE2), I-TASSER servers, protein '''B '''asic '''L '''ocal '''A '''ligment '''S '''earch '''T '''ool (BLAST) and TMHMM was used. The TMHMM predicted a transmembrane protein with 5 alpha-helical spanners (Fig. 1). The N-teminus is with a probability of over 99 % in cytoplasmatic. The NCBI Protein BLAST results shows that the tctB_162 subunit B1 belongs to the tctB superfamily. | |
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:File-tctb162_tmhmm.png|900px|thumb|center|Figure 1. '''TMHMM prediction of the tctB_162 subunit B1''' It shows 5 alpha-helical spanners.]] | ||
| + | |||
<!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
| Line 11: | Line 13: | ||
<span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | <span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K808003 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K808003 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | [1] Sasoh, M., E. Masai, et al. (2006). "Characterization of the terephthalate degradation genes of Comamonas sp. strain E6." Appl Environ Microbiol 72(3): 1825-1832. | ||
Revision as of 17:17, 23 September 2012
tctB_162: small subunit B1 of the tripartite tricarboxylate transporter family
The small subunit B1 of the tripartite tricarboxylate transporter family (tctB_162, 17 kDa) was isolated from Comamonas testosteroni KF-1. The tripartite tricarboxylate transporter system consists of three different proteins: a periplasmatic solute binding receptor, a membrane protein with 12 putative transmembrane alpha-helical spanners (in this case tctB_162), and a small poorly conserved membrane proteine with four putative transmembrane alpha-helical spanners[1].The strain was purchased from Leibniz Institute DMSZ-German Collection of Microorganism and Cell Cultures (DMSZ no. 14576). The original sequence contains a Pst1 recognition site. To eliminate this recognition site a directed-site mutagenic PCR was performed. (For more datails: link zu dem PCR protokoll und dem Labjournal, wo isolations PCR beschrieben wird) To characterized the structure of the tctB_162 bioinformatic tools like P rotein H omology/anolog Y R ecognition E ngine V 2.0 (PHYRE2), I-TASSER servers, protein B asic L ocal A ligment S earch T ool (BLAST) and TMHMM was used. The TMHMM predicted a transmembrane protein with 5 alpha-helical spanners (Fig. 1). The N-teminus is with a probability of over 99 % in cytoplasmatic. The NCBI Protein BLAST results shows that the tctB_162 subunit B1 belongs to the tctB superfamily.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 291
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI site found at 55
References
[1] Sasoh, M., E. Masai, et al. (2006). "Characterization of the terephthalate degradation genes of Comamonas sp. strain E6." Appl Environ Microbiol 72(3): 1825-1832.