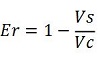Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K731722"
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
<hr> | <hr> | ||
'''MEASUREMENTS''' | '''MEASUREMENTS''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Our experiments exploited an ''E. coli'' lysogen strain carrying T7 RNA polymerase and lacIq. Additionally, the cells, i.e. ''E. coli'' BL21(DE3) pLysS, also contained a plasmid encoding T7 lysozyme and chloramphenicol resistance. T7 lysozyme is a natural inhibitor of T7 RNA polymerase activity, thus reducing background expression of the target genes. The T7 RNA polymerase is behind a lacUV5 promoter. | ||
The activity of this part was analyzed both with T7 and ''E. coli'' RNA polymerases ''in vivo'' and with T7 RNA polymerase ''in vitro''. | The activity of this part was analyzed both with T7 and ''E. coli'' RNA polymerases ''in vivo'' and with T7 RNA polymerase ''in vitro''. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 42: | ||
-''Vs'' is the A206K Venus peak’s intensity of the construct with the terminator of interest inserted in the prefix-suffix linker | -''Vs'' is the A206K Venus peak’s intensity of the construct with the terminator of interest inserted in the prefix-suffix linker | ||
| − | -''Vc'' is the A206K Venus peak’s intensity of the control construct | + | -''Vc'' is the A206K Venus peak’s intensity of the control construct without intervening terminator |
-''Cs'' is the mCherry peak’s intensity of the construct with the terminator inserted | -''Cs'' is the mCherry peak’s intensity of the construct with the terminator inserted | ||
| Line 48: | Line 50: | ||
| − | '''In vivo measurements:''' | + | '''''In vivo'' measurements:''' |
<div style="text-align:center">[[Image:Ecoliterminatorinvivo.jpg]]</div> | <div style="text-align:center">[[Image:Ecoliterminatorinvivo.jpg]]</div> | ||
| Line 58: | Line 60: | ||
Briefly, BL21(DE3)pLysS were grown in 10 mL of LB until an OD of 0.6 was reached and induced with 0.5 mM IPTG. After 3 hours of induction, 4 separate aliquots of 1 mL were taken and sonicated 3 times for 10 seconds at intervals of 30 seconds. After sonication the samples were diluted 1:2 with PBS 1X directly into a cuvette and incubated overnight at 4°C. Fluorescence measurements were taken with a Cary Eclipse Varian fluorimeter with a window ranging from 450 nm to 700 nm, a slit of 5nm, a voltage of 570V for the characterization with T7 polymerase and of 520V for the measurements with ''E. coli'' RNA polymerase. We used the following excitation and emission wavelengths. | Briefly, BL21(DE3)pLysS were grown in 10 mL of LB until an OD of 0.6 was reached and induced with 0.5 mM IPTG. After 3 hours of induction, 4 separate aliquots of 1 mL were taken and sonicated 3 times for 10 seconds at intervals of 30 seconds. After sonication the samples were diluted 1:2 with PBS 1X directly into a cuvette and incubated overnight at 4°C. Fluorescence measurements were taken with a Cary Eclipse Varian fluorimeter with a window ranging from 450 nm to 700 nm, a slit of 5nm, a voltage of 570V for the characterization with T7 polymerase and of 520V for the measurements with ''E. coli'' RNA polymerase. We used the following excitation and emission wavelengths. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="text-align:center"> | ||
| + | {|border = "1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" align="centre" | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |Excitation (nm) | ||
| + | |Emission(nm) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |mCherry | ||
| + | |587 | ||
| + | |615 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Venus | ||
| + | |485 | ||
| + | |528 | ||
| + | |}</div> | ||
</em> </p> | </em> </p> | ||
| Line 69: | Line 86: | ||
<div style="text-align:center">[[Image:Ecoliterminatortabinvitro.jpg]]</div> | <div style="text-align:center">[[Image:Ecoliterminatortabinvitro.jpg]]</div> | ||
<p style="width:600px; margin-left:150px; margin-bottom:60px; | <p style="width:600px; margin-left:150px; margin-bottom:60px; | ||
| − | text-align:justify "><em><strong>FIGURE 2.</strong> '''E.coli terminator's effect on in vitro protein synthesis with the T7 RNA polymerases'''<br/>Cell free measurements were done with the PurExpress kit from New England Biolabs, using 250 ng of DNA previously purified by ethanol precipitation, following the protocol suggested by the manufacturer. Measurements were done with a PTI fluorimeter using the | + | text-align:justify "><em><strong>FIGURE 2.</strong> '''E.coli terminator's effect on in vitro protein synthesis with the T7 RNA polymerases'''<br/>Cell free measurements were done with the PurExpress kit from New England Biolabs, using 250 ng of DNA previously purified by ethanol precipitation, following the protocol suggested by the manufacturer. Measurements were done with a PTI fluorimeter using the same excitation and emission wavelengths used for the ''in vivo'' characterization. |
</em> </p> | </em> </p> | ||
More information can be found in the iGEM Trento 2012 wiki page. | More information can be found in the iGEM Trento 2012 wiki page. | ||
Revision as of 08:11, 21 September 2012
|
T1 terminator from E. coli rrnB
Since many different teams had problems using BBa_B0010, this is the same part newly submitted, confirmed by sequencing and by experience...ready to use! The characterization of this part was done by the Trento iGEM team 2012 using the new platforms for terminator characterization that they have built and submitted to the Registry as BBa_K731700 and BBa_K731710. |
Examples of Secondary Structures
MEASUREMENTS
Our experiments exploited an E. coli lysogen strain carrying T7 RNA polymerase and lacIq. Additionally, the cells, i.e. E. coli BL21(DE3) pLysS, also contained a plasmid encoding T7 lysozyme and chloramphenicol resistance. T7 lysozyme is a natural inhibitor of T7 RNA polymerase activity, thus reducing background expression of the target genes. The T7 RNA polymerase is behind a lacUV5 promoter.
The activity of this part was analyzed both with T7 and E. coli RNA polymerases in vivo and with T7 RNA polymerase in vitro.
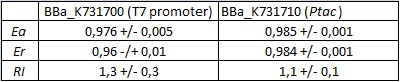
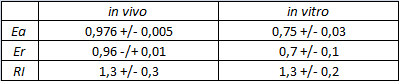
The parameters used to analyze the data are:
apparent termination efficiency, 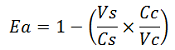
relative increase in the upstream gene expression, 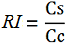
(the last parameter was added as some terminators were found to increase the expression of the upstream gene)
where
-Vs is the A206K Venus peak’s intensity of the construct with the terminator of interest inserted in the prefix-suffix linker
-Vc is the A206K Venus peak’s intensity of the control construct without intervening terminator
-Cs is the mCherry peak’s intensity of the construct with the terminator inserted
-Cc is the mCherry peak’s intensity of the control construct
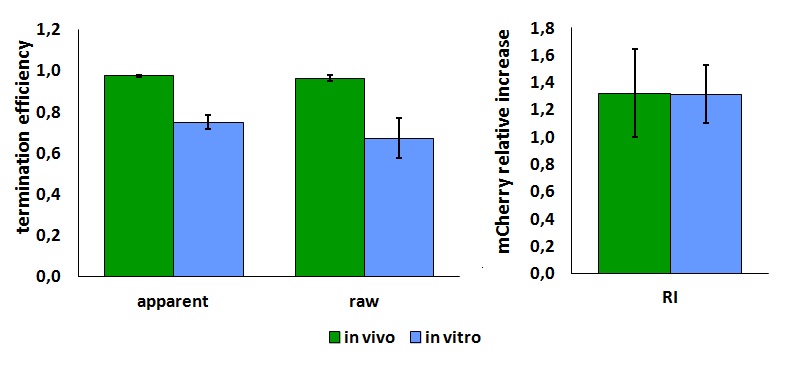
In vivo measurements:
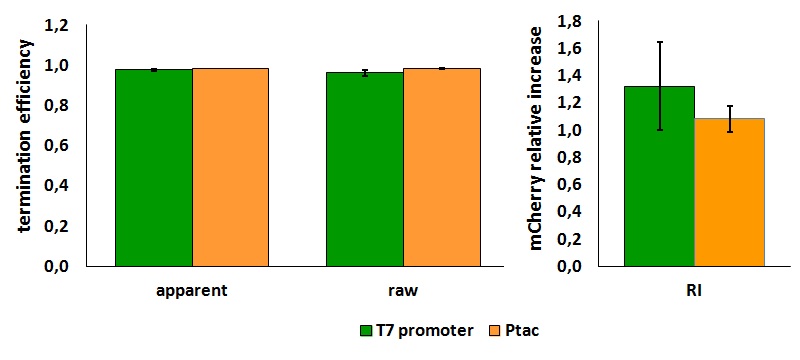
FIGURE 1. E.coli terminator's effect on protein expression with two different RNA polymerases
The data shown in figure 1 were acquired in two different days. For each day 4 different replicates were measured at different times.
Briefly, BL21(DE3)pLysS were grown in 10 mL of LB until an OD of 0.6 was reached and induced with 0.5 mM IPTG. After 3 hours of induction, 4 separate aliquots of 1 mL were taken and sonicated 3 times for 10 seconds at intervals of 30 seconds. After sonication the samples were diluted 1:2 with PBS 1X directly into a cuvette and incubated overnight at 4°C. Fluorescence measurements were taken with a Cary Eclipse Varian fluorimeter with a window ranging from 450 nm to 700 nm, a slit of 5nm, a voltage of 570V for the characterization with T7 polymerase and of 520V for the measurements with E. coli RNA polymerase. We used the following excitation and emission wavelengths.
Excitation (nm)
Emission(nm)
mCherry
587
615
Venus
485
528
In vitro measurements:
FIGURE 2. E.coli terminator's effect on in vitro protein synthesis with the T7 RNA polymerases
Cell free measurements were done with the PurExpress kit from New England Biolabs, using 250 ng of DNA previously purified by ethanol precipitation, following the protocol suggested by the manufacturer. Measurements were done with a PTI fluorimeter using the same excitation and emission wavelengths used for the in vivo characterization.
More information can be found in the iGEM Trento 2012 wiki page.