Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa I716462:Experience"
Liszabruder (Talk | contribs) (→Analysis of Genomic DNA) |
Liszabruder (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
====Introduction==== | ====Introduction==== | ||
| − | + | Part I716462 was previously characterized by the UC Berkeley iGEM team in 2007. The purpose of this part was to prevent unwanted cell proliferation by engineering a genetic self-destruct mechanism into bacteria that upon induction would express a genetic material-degrading toxin, the endonuclease BamHI that would kill cells yet preserve their physical integrity. <i>Bam</i>HI has a restriction cut site of G'GATCC, generating sticky ends (1). The restriction endonuclease was placed under the control of the arabinose- inducible promoter, pBAD. In 2007, the UC Berkeley iGEM team was able to show that cells lost their ability to reproduce but did not lyse upon induction with arabinose (2). The University of Lethbridge 2011 iGEM team wished to further characterize this part to degrade the genomic DNA of E. coli in order to have a functional chassis for our tailings pond clean-up kit without the risk of DNA contamination. In this way, tight control and regulation over our engineered bacterial cells is possible. | |
| − | Part I716462 was previously characterized by the UC Berkeley iGEM team in 2007. The purpose of this part was to prevent unwanted cell proliferation by engineering a genetic self-destruct mechanism into bacteria that upon induction would express a genetic material-degrading toxin, the endonuclease BamHI that would kill cells yet preserve their physical integrity. | + | <br><br> |
| − | + | Registry Entry - BBa_I716462 | |
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | Length – 1918 bp | ||
====Characterization==== | ====Characterization==== | ||
=====Cell Survival===== | =====Cell Survival===== | ||
| Line 21: | Line 23: | ||
The <i>Bam</i>HI construct was overexpressed in <i>E. coli</i> DH5α cells. Cultures were induced with arabinose at an OD<sub>600</sub> of 0.6 and grown overnight. Samples of the induced culture and an uninduced culture were plated on LB agar plates to monitor growth of colony forming units. | The <i>Bam</i>HI construct was overexpressed in <i>E. coli</i> DH5α cells. Cultures were induced with arabinose at an OD<sub>600</sub> of 0.6 and grown overnight. Samples of the induced culture and an uninduced culture were plated on LB agar plates to monitor growth of colony forming units. | ||
======Results====== | ======Results====== | ||
| − | [[image:uoflBamHIgrowthcurve.png]] | + | [[image:uoflBamHIgrowthcurve.png|center|400px]] |
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | <b>Figure 1.</b> | + | <b>Figure 1.</b> Growth curves of <i>E. coli</i> DH5α cells induced (blue) and uninduced (red) for expression of <i>Bam</i>HI. Cultures were induced at an OD<sub>600</sub> of 0.60. |
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | [[image:uoflBamHICFU.png]] | + | [[image:uoflBamHICFU.png|center|400px]] |
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | <b>Figure 2. </b><i>E.coli</i>DH5α cells containing the <i>Bam</i>HI construct from overnight cultures. The samples were plated on LB agar plates and the number of colony forming units (CFU) was counted. Left: culture induced for | + | <b>Figure 2. </b><i>E. coli</i> DH5α cells containing the <i>Bam</i>HI construct from overnight cultures. The samples were plated on LB agar plates and the number of colony forming units (CFU) was counted. Left: culture induced for <i>Bam</i>HI expression with arabinose, right: uninduced culture. |
=====Analysis of Genomic DNA===== | =====Analysis of Genomic DNA===== | ||
======Materials and Methods====== | ======Materials and Methods====== | ||
| − | <i>E. coli</i> DH5α cells were grown and induced to overexpress one of three samples: <i>Bam</i>HI construct induced with arabinose ( | + | <i>E. coli</i> DH5α cells were grown and induced to overexpress one of three samples: <i>Bam</i>HI construct induced with arabinose (10µM) at an OD<sub>600</sub> of 0.6, <i>Bam</i>HI construct uninduced, non-<i>Bam</i>HI construct induced with arabinose (10µM) at OD<sub>600</sub> of 0.6. Cells were grown in LB media with 100 ng/mL ampicillin. |
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | Qiagen Blood and Tissue Kit was used to isolate the genomic DNA of gram-negative bacteria. A 0.8% agarose gel was ran at 150 V for 90 minutes to separate the genomic DNA of <i>E. coli</i> DH5α cells collected at different time points (pre-induced and 30 min, 1 hr, 2 hr, and 3 hr post induction) for all three samples. | + | Qiagen Blood and Tissue Kit was used to isolate the genomic DNA of gram-negative bacteria. A 0.8% agarose gel was ran at 150 V for 90 minutes to separate the genomic DNA of <i>E. coli</i> DH5α cells collected at different time points (pre-induced and 30 min, 1 hr, 2 hr, and 3 hr post induction) for all three samples. One absorbance unit of cells were collected and analyzed by SDS-PAGE to monitor cellular protein levels. |
======Results====== | ======Results====== | ||
| − | [[image:uoflBamHIgenomicDNA.png]] | + | [[image:uoflBamHIgenomicDNA.png|center|400px]] |
<br> | <br> | ||
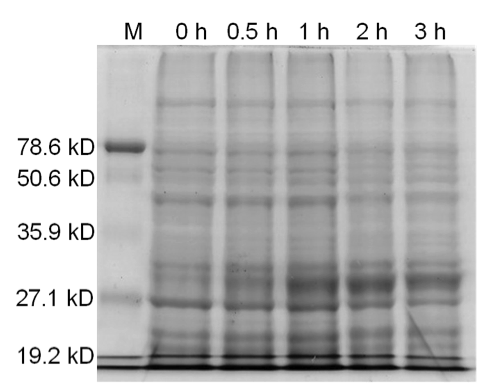
| − | <b>Figure 3.</b> | + | <b>Figure 3.</b> Induced <i>Bam</i>HI. 12% SDS-PAGE of cell lysate from <i>E. coli</i> DH5α cells containing BBa_I716462 induced for overexpression of <i>Bam</i>HI. Left to right: protein marker, 0 h, 0.5 h, 1 h, 2 h, and 3 h after induction with lactose. |
| − | + | [[image:uoflBamHIfigure4.png|center|400px]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | + | <b>Figure 4.</b> Induced <i>Bam</i>HI. 12% SDS-PAGE of cell lysate from uninduced <i>E. coli</i> DH5α cells containing BBa_I716462. Left to right: protein marker, 0 h, 0.5 h, 1 h, 2 h, and 3 h after induction with lactose. | |
| − | + | <br><br> | |
| + | [[image:uoflBamHIfigure5.png|center|400px]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <b>Figure 5.</b> Uninduced <i>Bam</i>HI. 12% SDS-PAGE of cell lysate from <i>E. coli</i> DH5α cells. Left to right: protein marker, 0 h, 0.5 h, 1 h, 2 h, and 3 h after induction with lactose. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | ====Conclusion==== | ||
| + | Upon induction with arabinose, <i>E. coli</i> DH5α cells containing the <i>Bam</i>HI construct did not reproduce as the overexpression of the <i>Bam</i>HI endonuclease digested the genomic DNA of the host cell. This is why in Figure 2 there are only 4 colonies seen as opposed to the control which shows a lawn of growth. In Figure 1, the optical density of the <i>Bam</i>HI expressing cells reaches a plateau; however, the same sample which has not been induced kept increasing, which indicates that the expression of <i>Bam</i>HI is affecting normal growth of the cells. | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | Samples analyzed by SDS-PAGE after induction of <i>Bam</i>HI expression show that protein concentration is not significantly affected (Figures 3-5). | ||
====References==== | ====References==== | ||
| − | |||
(1) Viadiu H, Aggarwal AK (2000). Structure of BamHI bound to nonspecific DNA: a model for DNA sliding. Mol. Cell 5 (5): 889-895. | (1) Viadiu H, Aggarwal AK (2000). Structure of BamHI bound to nonspecific DNA: a model for DNA sliding. Mol. Cell 5 (5): 889-895. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | (2) iGEM 2007. (2011, May 10). BerkiGEM2007Present5. Retrieved from http:// | + | (2) iGEM 2007. (2011, May 10). BerkiGEM2007Present5. Retrieved from http://2007.igem.org/BerkiGEM2007Present5. |
Latest revision as of 23:39, 28 September 2011
This experience page is provided so that any user may enter their experience using this part.
Please enter
how you used this part and how it worked out.
Applications of BBa_I716462
Datasheet for Part BBa_I716462 in E. coli strain DH5alpha.

User Reviews
Characterization by Lethbridge iGEM Team 2011
Introduction
Part I716462 was previously characterized by the UC Berkeley iGEM team in 2007. The purpose of this part was to prevent unwanted cell proliferation by engineering a genetic self-destruct mechanism into bacteria that upon induction would express a genetic material-degrading toxin, the endonuclease BamHI that would kill cells yet preserve their physical integrity. BamHI has a restriction cut site of G'GATCC, generating sticky ends (1). The restriction endonuclease was placed under the control of the arabinose- inducible promoter, pBAD. In 2007, the UC Berkeley iGEM team was able to show that cells lost their ability to reproduce but did not lyse upon induction with arabinose (2). The University of Lethbridge 2011 iGEM team wished to further characterize this part to degrade the genomic DNA of E. coli in order to have a functional chassis for our tailings pond clean-up kit without the risk of DNA contamination. In this way, tight control and regulation over our engineered bacterial cells is possible.
Registry Entry - BBa_I716462
Length – 1918 bp
Characterization
Cell Survival
Materials and Methods
The BamHI construct was overexpressed in E. coli DH5α cells. Cultures were induced with arabinose at an OD600 of 0.6 and grown overnight. Samples of the induced culture and an uninduced culture were plated on LB agar plates to monitor growth of colony forming units.
Results
Figure 1. Growth curves of E. coli DH5α cells induced (blue) and uninduced (red) for expression of BamHI. Cultures were induced at an OD600 of 0.60.
Figure 2. E. coli DH5α cells containing the BamHI construct from overnight cultures. The samples were plated on LB agar plates and the number of colony forming units (CFU) was counted. Left: culture induced for BamHI expression with arabinose, right: uninduced culture.
Analysis of Genomic DNA
Materials and Methods
E. coli DH5α cells were grown and induced to overexpress one of three samples: BamHI construct induced with arabinose (10µM) at an OD600 of 0.6, BamHI construct uninduced, non-BamHI construct induced with arabinose (10µM) at OD600 of 0.6. Cells were grown in LB media with 100 ng/mL ampicillin.
Qiagen Blood and Tissue Kit was used to isolate the genomic DNA of gram-negative bacteria. A 0.8% agarose gel was ran at 150 V for 90 minutes to separate the genomic DNA of E. coli DH5α cells collected at different time points (pre-induced and 30 min, 1 hr, 2 hr, and 3 hr post induction) for all three samples. One absorbance unit of cells were collected and analyzed by SDS-PAGE to monitor cellular protein levels.
Results
Figure 3. Induced BamHI. 12% SDS-PAGE of cell lysate from E. coli DH5α cells containing BBa_I716462 induced for overexpression of BamHI. Left to right: protein marker, 0 h, 0.5 h, 1 h, 2 h, and 3 h after induction with lactose.
Figure 4. Induced BamHI. 12% SDS-PAGE of cell lysate from uninduced E. coli DH5α cells containing BBa_I716462. Left to right: protein marker, 0 h, 0.5 h, 1 h, 2 h, and 3 h after induction with lactose.
Figure 5. Uninduced BamHI. 12% SDS-PAGE of cell lysate from E. coli DH5α cells. Left to right: protein marker, 0 h, 0.5 h, 1 h, 2 h, and 3 h after induction with lactose.
Conclusion
Upon induction with arabinose, E. coli DH5α cells containing the BamHI construct did not reproduce as the overexpression of the BamHI endonuclease digested the genomic DNA of the host cell. This is why in Figure 2 there are only 4 colonies seen as opposed to the control which shows a lawn of growth. In Figure 1, the optical density of the BamHI expressing cells reaches a plateau; however, the same sample which has not been induced kept increasing, which indicates that the expression of BamHI is affecting normal growth of the cells.
Samples analyzed by SDS-PAGE after induction of BamHI expression show that protein concentration is not significantly affected (Figures 3-5).
References
(1) Viadiu H, Aggarwal AK (2000). Structure of BamHI bound to nonspecific DNA: a model for DNA sliding. Mol. Cell 5 (5): 889-895.
(2) iGEM 2007. (2011, May 10). BerkiGEM2007Present5. Retrieved from http://2007.igem.org/BerkiGEM2007Present5.
UNIQa8babbbbbaa789aa-partinfo-00000000-QINU
UNIQa8babbbbbaa789aa-partinfo-00000001-QINU