Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K510012"
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
| − | pUC18R6KT-miniTn7BB-Gm is a vehicle vector for the minitransposon miniTn7BB-Gm. This transposon is a part of the [http://2011.igem.org/Team:UPO-Sevilla/Foundational_Advances/MiniTn7/Overview miniTn7 BioBrick toolkit] , a set of plasmids harboring Tn7 derivatives that can be used for '''integration''' | + | pUC18R6KT-miniTn7BB-Gm is a vehicle vector for the minitransposon miniTn7BB-Gm. This transposon is a part of the [http://2011.igem.org/Team:UPO-Sevilla/Foundational_Advances/MiniTn7/Overview miniTn7 BioBrick toolkit] , a set of plasmids harboring Tn7 derivatives that can be used for '''integration of BioBricks''' in single copy at a conserved target (the attTn7 site), in multiple '''bacterial genomes'''. |
| − | + | Our [http://2011.igem.org/Team:UPO-Sevilla/Foundational_Advances/MiniTn7/Bioinformatics/attTn7_Insertion_Site Bioinformatic analysis] reveal that the insertion site of the miniTn7 is highly conserved along the philogeny. This means that the miniTn7 BioBrick tool kit is possibly useful non only in bacteria, but in other Archaea or Eukaryotic species. If the target site for the insertion of the miniTn7 is not present in your working organism, we also provide a portable attTn7 ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K510022 BBa K510022]). | |
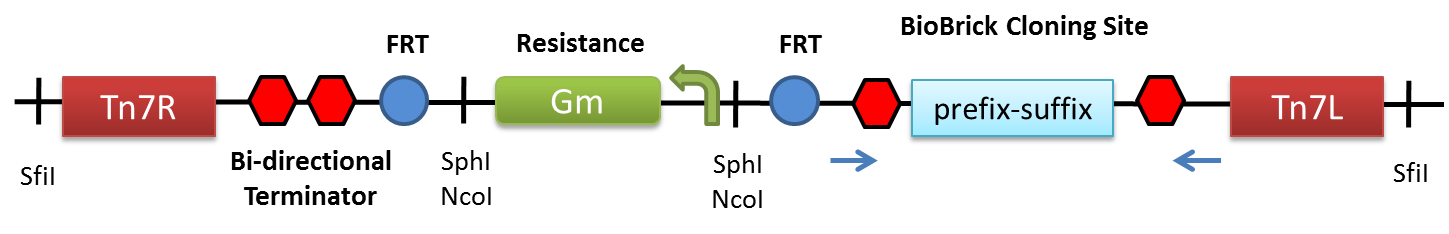
| − | + | The main features of '''miniTn7BB-Gm''' are: (i) wild-type '''Tn7R and Tn7L ends''', enabling transposition in vivo when the Tn7 transposase is expressed in trans, (ii) '''prefix and suffix''' with unique EcoRI, XbaI, SpeI and PstI restriction sites, fully compatible with Assembly Standard 10, (iii) annealing sequences for '''standard primers''' to facilitate amplification and sequencing of cloned BioBricks, (iv) '''transcriptional terminators''' flanking the multi-cloning site to efficiently insulate cloned BioBricks from vector transcription, (v) a selectable gentamycin (Gm) '''resistance cassette''' flanked by duplicated SphI and NcoI sites to facilitate marker replacement, (vi) '''flipase recognition elements''' (FRTs) flanking the gentamycin resistance cassette, to allow clean excision of the marker in strains bearing transposon insertions, and (vii) SfiI sites flanking the complete transposon to facilitate cloning into the appropriate plasmid vectors. A schematic of miniTn7BB-Gm showcasing the aforementioned features is shown in the figure below. | |
| + | |||
| + | '''pUC18R6KT''' is a pUC18-derived ampicillin resistant vector, which harbors the low- to medium-copy number '''R6K replication origin''', which is dependent on the presence of the replication protein π, and is only replicative in a small subset of E. coli strains engineered to express π (typically from a specialized λ prophage named λ-pir). Genetic manipulation of pUC18R6KT-derived plasmids is more cumbersome than pUC18Sfi because of its lower copy number and the requirement of specific E. coli strains, but their major advantage over pUC18Sfi-based plasmids is that they can be used for '''transposon delivery in E. coli and other enterobacteria'''. In addition, the presence of mobilization functions enables '''conjugative transfer''' of pUC18R6KT and its derivatives to a wide range of recipient bacteria. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As a BioBrick cloning vector, pUC18Sfi-miniTn7BB-Gm is fully compatible with''' Assembly Standard 10'''. | ||
[[Image:Mini-Tn7-Gm1.png|700px|center]] | [[Image:Mini-Tn7-Gm1.png|700px|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | More information about this plasmid from the UPO-Sevilla 2011 team in the '''Experience section'''. | ||
<!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
Latest revision as of 22:37, 24 September 2011
pUC18R6KT-miniTn7BB-Gm
pUC18R6KT-miniTn7BB-Gm is a vehicle vector for the minitransposon miniTn7BB-Gm. This transposon is a part of the [http://2011.igem.org/Team:UPO-Sevilla/Foundational_Advances/MiniTn7/Overview miniTn7 BioBrick toolkit] , a set of plasmids harboring Tn7 derivatives that can be used for integration of BioBricks in single copy at a conserved target (the attTn7 site), in multiple bacterial genomes.
Our [http://2011.igem.org/Team:UPO-Sevilla/Foundational_Advances/MiniTn7/Bioinformatics/attTn7_Insertion_Site Bioinformatic analysis] reveal that the insertion site of the miniTn7 is highly conserved along the philogeny. This means that the miniTn7 BioBrick tool kit is possibly useful non only in bacteria, but in other Archaea or Eukaryotic species. If the target site for the insertion of the miniTn7 is not present in your working organism, we also provide a portable attTn7 (BBa K510022).
The main features of miniTn7BB-Gm are: (i) wild-type Tn7R and Tn7L ends, enabling transposition in vivo when the Tn7 transposase is expressed in trans, (ii) prefix and suffix with unique EcoRI, XbaI, SpeI and PstI restriction sites, fully compatible with Assembly Standard 10, (iii) annealing sequences for standard primers to facilitate amplification and sequencing of cloned BioBricks, (iv) transcriptional terminators flanking the multi-cloning site to efficiently insulate cloned BioBricks from vector transcription, (v) a selectable gentamycin (Gm) resistance cassette flanked by duplicated SphI and NcoI sites to facilitate marker replacement, (vi) flipase recognition elements (FRTs) flanking the gentamycin resistance cassette, to allow clean excision of the marker in strains bearing transposon insertions, and (vii) SfiI sites flanking the complete transposon to facilitate cloning into the appropriate plasmid vectors. A schematic of miniTn7BB-Gm showcasing the aforementioned features is shown in the figure below.
pUC18R6KT is a pUC18-derived ampicillin resistant vector, which harbors the low- to medium-copy number R6K replication origin, which is dependent on the presence of the replication protein π, and is only replicative in a small subset of E. coli strains engineered to express π (typically from a specialized λ prophage named λ-pir). Genetic manipulation of pUC18R6KT-derived plasmids is more cumbersome than pUC18Sfi because of its lower copy number and the requirement of specific E. coli strains, but their major advantage over pUC18Sfi-based plasmids is that they can be used for transposon delivery in E. coli and other enterobacteria. In addition, the presence of mobilization functions enables conjugative transfer of pUC18R6KT and its derivatives to a wide range of recipient bacteria.
As a BioBrick cloning vector, pUC18Sfi-miniTn7BB-Gm is fully compatible with Assembly Standard 10.
More information about this plasmid from the UPO-Sevilla 2011 team in the Experience section.
Sequence and Features
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal prefix found in sequence at 4528
Illegal suffix found in sequence at 1 - 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal EcoRI site found at 4528
Illegal SpeI site found at 2
Illegal PstI site found at 16
Illegal NotI site found at 9
Illegal NotI site found at 4534 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal EcoRI site found at 4528
Illegal BglII site found at 3212
Illegal BglII site found at 3483
Illegal BglII site found at 3769 - 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal prefix found in sequence at 4528
Illegal suffix found in sequence at 2 - 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal prefix found in sequence at 4528
Illegal XbaI site found at 4543
Illegal SpeI site found at 2
Illegal PstI site found at 16 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 1854
Illegal SapI site found at 518