Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K525403"
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K525403 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K525403 short</partinfo> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Bielefeld-Germany2011-S-Layer-Geometrien.jpg|300px|thumb|right]] | ||
S-Layer SbpA from ''Lysinbacillus sphaericus'' | S-Layer SbpA from ''Lysinbacillus sphaericus'' | ||
Latest revision as of 03:17, 22 September 2011
S-Layer SbpA from Lysinibacillus sphaericus with T7/lac
S-Layer SbpA from Lysinbacillus sphaericus
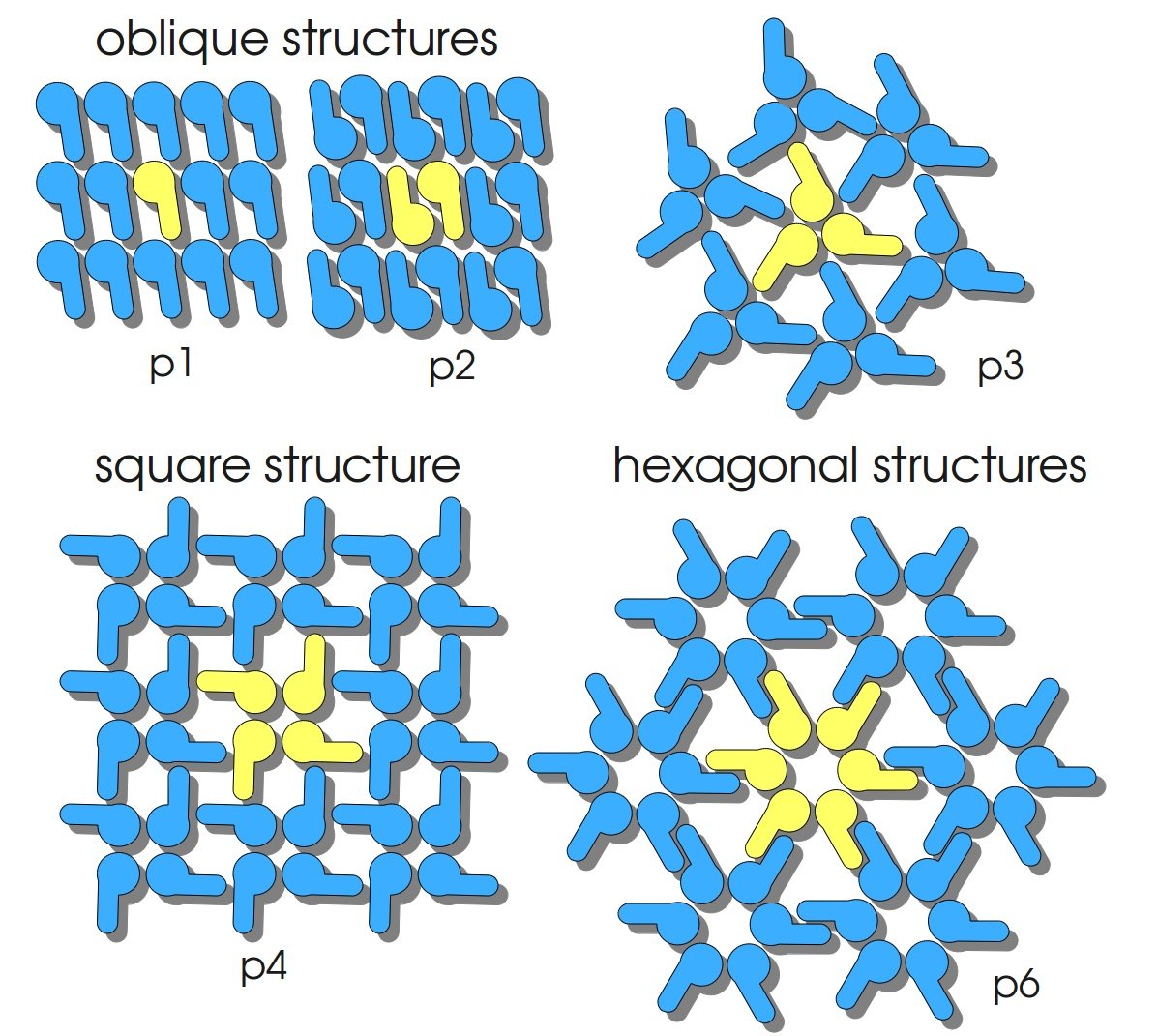
S-layers (crystalline bacterial surface layer) are crystal-like layers consisting of multiple protein monomers and can be found in various (archae-)bacteria. They constitute the outermost part of the cell wall. Especially their ability for self-assembly into distinct geometries is of scientific interest. At phase boundaries, in solutions and on a variety of surfaces they form different lattice structures. The geometry and arrangement is determined by the C-terminal self assembly-domain, which is specific for each S-layer protein. The most common lattice geometries are oblique, square and hexagonal. By modifying the characteristics of the S-layer through combination with functional groups and protein domains as well as their defined position and orientation to eachother (determined by the S-layer geometry) it is possible to realize various practical applications ([http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00573.x/full Sleytr et al., 2007]).
Usage and Biology
S-layer proteins can be used as scaffold for nanobiotechnological applications and devices by e.g. fusing the S-layer's self-assembly domain to other functional protein domains. It is possible to coat surfaces and liposomes with S-layers. A big advantage of S-layers: after expressing in E. coli and purification, the nanobiotechnological system is cell-free. This enhances the biological security of a device.
This S-layer gene is downsteam of a T7 / lac fusion promoter and in the Freiburg BioBrick Assembly standard so functional protein domains can easily be fused to its N-terminus and expressed and purified afterwards. SbpA was characterized with BBa_K525405.
Important parameters
| Experiment | Characteristic | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Expression (E. coli) | Localisation | Inclusion body |
| Compatibility | E. coli KRX and BL21(DE3) | |
| Induction of expression | expression of T7 polymerase + IPTG or lactose | |
| Purification | Molecular weight | 110.0 kDa |
| Theoretical pI | 4.75 | |
| Immobilization behaviour | Immobilization time | 4 h |
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 104
Illegal BglII site found at 221
Illegal XhoI site found at 1996 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 76
Illegal AgeI site found at 3193 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 493
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 622