Help:Terminators/Glossary
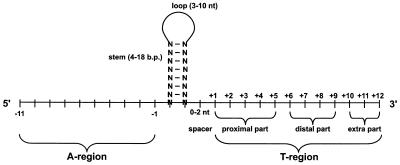
Stem loop
A self-complementary or palindromic sequence of DNA usually 4-18 base pairs in length and rich in G-C base pairs that forms a "hairpin" structure. The hairpin causes the E. coli RNA polymerase to pause transcription.
Poly(T) tract
A stretch of T nucleotides on the sense DNA strand just downstream of the stem loop. Transcription of the corresponding A nucleotides results in an RNA:DNA duplex that is quite weak, because A-U base pairs only have 2 hydrogen bonds versus 3 for G-C base pairs.
Loop
3-10 nucleotides in the middle of the self-complementary or palindromic sequence that do not base pair but enable the terminator to fold back on itself into the hairpin structure.
Terminator efficiency
In the Registry, termination efficiency is usually defined as the number of terminated transcripts divided by the total number of transcripts (terminated transcripts + read-through transcripts). However, some papers instead define termination efficiency as number of read-through transcripts divided by the total number of transcripts (terminated transcripts + read-through transcripts) McDowell, so be careful when interpreting termination efficiencies from papers.
References
<biblio>
- Lesnik pmid=11522828
- McDowell pmid=7526463
</biblio>