< Back to Cell-free chassis help
Different compartmentalization strategies have been explored to prolong the expression lifespan of the cell-free chassis.
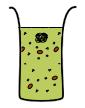 |
Batch mode cell-free chassis
Transcription-translation reaction is carried out in bulk solution. Expression is usually limited by nutrient (nucleotides and amino acids) and energy supplies.
|
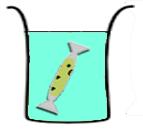 |
Continuous-exchange
Transcription-translation reaction is separated from the feeding solution by a dialysis membrane. Expression is sustained by diffusion of nutrients from the feeding soltuion to the reaction, and wastes generated by the reaction is diluted in the feeding solution.
|
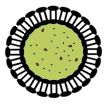 |
Vesicle-encapsulated cell-free chassis
The reaction is separated from the feeding solution by a phospholipid bilayer. Expression is maintained for a longer time period than batch-mode CFS because of exchange of materials between the reaction and the feeding solution across the membrane. More reliable exchange of materials is established by inserting a non-specific pore protein with a suitable channel size into the phospholipid bilayer.
|